Table of Contents
White OG is a prominent cannabis strain celebrated for its potency, distinct terpene profile, and wide-ranging effects. Developed through the crossbreeding of two iconic strains, The White and OG Kush, White OG embodies the best traits of its parentage, delivering a unique combination of flavors, aromas, and effects. This article explores the genetic lineage, chemical composition, cultivation characteristics, and both medical and recreational uses of White OG.
Genetic Lineage and Origins
White OG is the result of combining The White, known for its frosty, trichome-laden buds, with OG Kush, a strain synonymous with robust flavors and powerful effects. This indica-dominant hybrid (approximately 70% indica, 30% sativa) inherits the relaxing and sedative properties of its indica parentage while retaining subtle cerebral stimulation from its sativa lineage.

Parent Strains:
- The White: Famous for its almost pure white appearance due to heavy trichome production. It is known for a neutral aroma and balanced effects.
- OG Kush: Revered for its earthy, woody, and pine-like flavors, OG Kush is a cornerstone of modern cannabis genetics with strong euphoric and relaxing properties.
Terpene Profile
The terpene profile of White OG contributes significantly to its distinct aroma, flavor, and effects. The dominant terpenes include:
- Myrcene: This terpene imparts a musky, earthy aroma and is known for its sedative and anti-inflammatory effects. Myrcene levels in White OG are typically high, contributing to its relaxing effects.
- Limonene: Adding a citrusy zing, limonene uplifts mood and reduces stress.
- Caryophyllene: A spicy, peppery terpene that interacts with CB2 receptors, offering anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties.
- Pinene: Present in smaller quantities, pinene contributes a fresh, pine-like aroma and can promote alertness.
The interplay of these terpenes creates a pungent, earthy scent with undertones of citrus and spice, making White OG an aromatic and flavorful strain.
Cannabinoid Profile
White OG’s potency is one of its standout features. It typically contains high levels of THC, ranging from 20% to 25%, with negligible levels of CBD (<1%). This cannabinoid profile makes White OG particularly effective for its psychoactive effects while offering limited non-psychoactive benefits.
Key Cannabinoids:
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): The primary psychoactive compound responsible for White OG’s euphoric and sedative effects.
- CBD (Cannabidiol): Present in trace amounts, CBD’s anti-inflammatory and anxiolytic properties are minor contributors to the strain’s overall effect.
- CBG (Cannabigerol): Found in smaller concentrations, CBG may enhance the strain’s potential for reducing inflammation and pain.
Effects and Experience
White OG’s effects are predominantly relaxing and sedative, with a touch of cerebral euphoria. Its indica dominance makes it a popular choice for evening or nighttime use.
- Initial Onset: Users often report a wave of euphoria shortly after consumption, accompanied by a sense of mental clarity and happiness. This phase is influenced by the sativa genetics and limonene content.
- Peak Effects: As the effects intensify, the indica traits take center stage. A profound sense of relaxation spreads throughout the body, alleviating tension and stress.
- Duration: The effects of White OG can last for 2-3 hours, depending on dosage and individual tolerance levels. The sedative qualities often culminate in a deep, restful sleep.
Recreational Uses:
- Relaxation: Perfect for relaxing after a demanding day.
- Social Settings: In moderate doses, it can enhance social interactions by reducing inhibitions and promoting a mellow mood.
- Creativity: While predominantly relaxing, White OG’s cerebral effects may inspire creative thinking during the initial euphoric phase.
Medical Applications
White OG’s combination of cannabinoids and terpenes makes it a versatile option for managing various medical conditions. Below is a detailed analysis of its therapeutic potential:
1. Pain Management
The high THC content and presence of caryophyllene and myrcene provide potent analgesic effects, making White OG effective for chronic pain conditions such as:
- Arthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Migraines
2. Stress and Anxiety Relief
The calming effects of myrcene and limonene, combined with THC-induced euphoria, help alleviate symptoms of:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Stress-induced insomnia
3. Sleep Disorders
White OG’s sedative properties are particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from:
- Insomnia
- Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS)
- Sleep apnea (as a complementary aid)
4. Appetite Stimulation
THC’s well-documented ability to stimulate appetite is enhanced in White OG, making it a valuable option for individuals with:
- Cancer-related cachexia
- Eating disorders such as anorexia
5. Inflammation
The presence of caryophyllene and myrcene contributes to anti-inflammatory effects, providing relief for:
- Autoimmune disorders
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Crohn’s Disease
Methods of Ingestion
White OG can be consumed through various methods, each influencing the onset, duration, and intensity of effects. Here are the primary methods:

1. Smoking
- Method: Rolled into joints, smoked in pipes or bongs.
- Onset: Immediate to 5 minutes.
- Duration: 1.5–3 hours.
- Advantages:
- Rapid delivery of THC and terpenes to the bloodstream.
- Full flavor profile due to combustion releasing terpenes.
- Drawbacks:
- Inhalation of combusted plant material can irritate the respiratory system.
- Potential loss of cannabinoids and terpenes due to high combustion temperatures.
2. Vaping
- Method: Vaporizing dried flower or concentrates using a vaporizer.
- Onset: Immediate to 5 minutes.
- Duration: 2–3 hours.
- Advantages:
- Efficient delivery of cannabinoids with fewer harmful byproducts compared to smoking.
- Lower temperatures preserve terpenes and deliver a more nuanced flavor.
- More discreet and less odor-producing.
- Drawbacks:
- Requires a vaporizer, which can be an upfront investment.
3. Edibles
- Method: Infused into food or beverages (e.g., gummies, chocolates, or teas).
- Onset: 30 minutes to 2 hours (dependent on digestion and metabolism).
- Duration: 4–8 hours.
- Advantages:
- Long-lasting effects suitable for extended symptom relief.
- Avoids respiratory irritation.
- Drawbacks:
- If dosed carelessly, delayed onset can result in overconsumption.
- Effects are less predictable due to individual metabolic differences.
4. Sublingual (Tinctures)
- Method: Drops placed under the tongue for absorption through oral mucosa.
- Onset: 15–30 minutes.
- Duration: 2–6 hours.
- Advantages:
- Bypasses digestion, allowing for faster onset compared to edibles.
- Discreet and easy to dose precisely.
- Drawbacks:
- Effects are less immediate compared to smoking or vaping.
5. Topical Application
- Method: Applied to the skin as balms, creams, or transdermal patches.
- Onset: 15–60 minutes.
- Duration: 2–12 hours (patches may last longer).
- Advantages:
- Localized relief without psychoactive effects (unless using transdermal patches).
- Effective for inflammation, pain, and skin conditions.
- Drawbacks:
- Limited to localized effects; does not provide systemic relief.
6. Dabbing
- Method: Flash-vaporizing cannabis concentrates using a dab rig.
- Onset: Immediate.
- Duration: 2–4 hours.
- Advantages:
- Extremely potent and fast-acting.
- Ideal for seasoned users looking for strong effects.
- Drawbacks:
- High THC concentrations may overwhelm novice users.
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
Onset and Duration of Effects
The onset and duration of effects vary by ingestion method due to differences in absorption pathways:
| Method | Onset | Peak Effects | Total Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking | 0–5 minutes | 15–30 minutes | 1.5–3 hours |
| Vaping | 0–5 minutes | 15–30 minutes | 2–3 hours |
| Edibles | 30–120 minutes | 1–3 hours | 4–8 hours |
| Sublingual | 15–30 minutes | 30–60 minutes | 2–6 hours |
| Topical | 15–60 minutes | Varies | 2–12 hours |
| Dabbing | Immediate | 5–15 minutes | 2–4 hours |
Effects
Psychoactive Effects
White OG, with its high THC content (20–25%), delivers a range of psychoactive effects based on dose and individual tolerance:
- Euphoria: An initial uplifting effect due to THC’s interaction with CB1 receptors in the brain.
- Relaxation: Indica-dominant genetics produce a sense of physical and mental calm.
- Sedation: Higher doses promote deep relaxation, often leading to drowsiness or couch lock.
- Cerebral Effects: Subtle mental clarity or creative bursts during the initial phase, particularly in smaller doses.
Medical Effects
- Pain Relief: THC and caryophyllene reduce pain perception by interacting with the endocannabinoid system and CB2 receptors.
- Stress Reduction: Limonene contributes to mood elevation and stress relief.
- Sleep Aid: Myrcene sedative properties, combined with THC, make White OG ideal for insomnia.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Caryophyllene targets inflammation, offering localized and systemic relief.
Adverse Effects
- Dry Mouth (Cottonmouth): THC reduces saliva production by binding to submandibular gland receptors.
- Dry Eyes: Common with high-THC strains, manageable with artificial tears.
- Dizziness: Possible due to blood pressure changes; mitigated by hydration and sitting down.
- Paranoia/Anxiety: Rare in lower doses but may occur in sensitive users or with overconsumption.
- Couch Lock: Overindulgence leads to extreme lethargy due to White OG indica dominance.
Scientific Explanation of Effects
- THC and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS):
- THC mimics anandamide, binding to CB1 receptors in the brain to produce psychoactive effects like euphoria and relaxation.
- The interaction also stimulates dopamine release, enhancing mood.
- Terpenes and the Entourage Effect:
- Myrcene: Enhances THC permeability through the blood-brain barrier, intensifying effects.
- Caryophyllene: Targets CB2 receptors, providing anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Limonene: Modulates serotonin receptors, contributing to stress relief and mood elevation.
- Bioavailability Differences:
- Smoking/vaping delivers THC directly to the bloodstream via the lungs, resulting in rapid onset.
- Edibles are metabolized in the liver, converting THC to 11-hydroxy-THC, a more potent and long-lasting form.
Cultivation Techniques for White OG

1. Germination and Seedling Stage
- Optimal Medium: Use a well-draining, nutrient-rich substrate such as coco coir, peat moss, or a commercial seed starter mix.
- Moisture Levels: Keep the medium consistently moist but not waterlogged to prevent root rot.
- Temperature Range: Maintain a steady temperature of 70–75°F (21–24°C).
- Lighting: Use a low-intensity LED or fluorescent grow light (18–20 hours of light daily).
- pH Levels: Ideal pH range is 6.0–6.5 for soil and 5.5–6.0 for hydroponic systems.
2. Vegetative Stage
- Lighting: Provide 18–24 hours of light using full-spectrum LEDs or metal halide lights. White OG thrives under high-intensity light conditions.
- Nutrients: Apply a balanced nitrogen-rich fertilizer to promote vigorous vegetative growth. Use nutrients with a ratio close to 3:1:2 (Nitrogen: Phosphorus: Potassium).
- Humidity Levels: Maintain a relative humidity (RH) of 50–70% during the vegetative phase.
- Training Methods:
- Topping: Cut the main stem to encourage bushier growth and multiple cola formations.
- Low-Stress Training (LST): To increase airflow and light penetration, gently bend and tie branches.
- Screen of Green (SCROG): Use a mesh screen to create an even canopy and maximize yield in indoor setups.
- Watering: Ensure deep watering cycles with proper drainage, allowing the medium to dry slightly between waterings.
3. Flowering Stage
- Photoperiod: Adjust to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness to induce flowering.
- Nutrients: Switch to a phosphorus- and potassium-rich fertilizer during this stage (e.g., 1:3:4 NPK ratio) to aid in the formation of trichomes and bud development.
- Humidity and Temperature:
- Lower RH to 40–50% to reduce the risk of mold and mildew.
- Maintain temperatures between 68–78°F (20–26°C) during the day and slightly cooler at night.
- pH Adjustments: Fine-tune the pH to the 6.0–6.2 range for soil and 5.8–6.0 for hydroponics to improve nutrient uptake.
- Defoliation: Remove excess fan leaves to improve light penetration and airflow to the lower buds.
- CO2 Enrichment: Supplement CO2 levels to approximately 1000–1200 ppm in sealed indoor environments to enhance growth and yield.
4. Harvesting
- Trichome Observation: Use a magnifying glass or microscope to check trichome color:
- Milky Trichomes: Peak potency.
- Amber Trichomes: Sedative effects become more pronounced.
- Flush Period: Cease feeding nutrients 1–2 weeks before harvest and water with pH-balanced water to remove residual salts and improve flavor.
- Harvest Timing: Typically 8–10 weeks into the flowering stage for White OG.
Advanced Cultivation Techniques
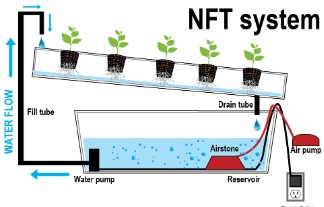
1. Hydroponics for Maximum Yield
- System Options: Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), or drip systems.
- Advantages: Faster growth, higher yields, and better control over nutrients.
- Nutrient Solution: Maintain electrical conductivity (EC) levels between 1.5–2.0 mS/cm for optimal growth.
- Oxygenation: Use air pumps and stones to oxygenate the nutrient solution, preventing root diseases.
2. Organic Cultivation
- Soil Medium: Enrich with organic amendments like worm castings, bat guano, and composted manure.
- Living Soil: Promote microbial activity using mycorrhizal fungi and beneficial bacteria for natural nutrient cycling.
- Pest Management: Employ organic methods such as neem oil, diatomaceous earth, or predatory insects like ladybugs.
3. Climate Control for Indoor Cultivation
- VPD (Vapor Pressure Deficit): Maintain a VPD range of 0.8–1.2 kPa during vegetative and flowering stages to optimize transpiration and nutrient uptake.
- Airflow: Install oscillating fans to prevent hot spots and ensure even air distribution.
4. Soil vs. Soilless vs. Hydroponics
- Soil: Provides a forgiving medium for beginners with slower nutrient release.
- Soilless: Coco coir or rockwool offers faster nutrient delivery and more control.
- Hydroponics: Ideal for experienced growers seeking high yields and faster growth rates.
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Pest Management
- Spider Mites: Introduce predatory mites (e.g., Phytoseiulus persimilis) or use insecticidal soap
- Fungus Gnats: Utilize yellow sticky traps and avoid overwatering to prevent larvae growth.
2. Nutrient Deficiencies
- Nitrogen Deficiency: Yellowing of lower leaves; increase nitrogen during vegetative growth.
- Calcium/Magnesium Deficiency: Correct with Cal-Mag supplements.
3. Mold and Mildew
- Prevention: Maintain low humidity during flowering and ensure proper ventilation.
- Treatment: Apply organic fungicides like potassium bicarbonate or neem oil.
Scientific Studies and Research
While strain-specific research on White OG is limited, studies on its parent strains and dominant compounds provide valuable insights:
- Analgesic Effects:
- Research indicates that THC and caryophyllene interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors, reducing pain perception (Russo et al., 2008).
- Anti-Anxiety Properties:
- Limonene’s uplifting effects have been studied for their potential to reduce stress and anxiety (Komori et al., 1995).
- Sedative Potential:
- Myrcene’s role in promoting sedation and sleep has been supported by studies exploring its synergy with THC (Surendran et al., 2014).
- Appetite Stimulation:
- THC’s ability to enhance appetite has been documented in clinical settings, particularly in patients undergoing chemotherapy (Whiting et al., 2015).
Potential Side Effects
While White OG offers numerous benefits, users should be aware of potential side effects, particularly at higher doses:
- Dry Mouth and Eyes: Common side effects of THC-rich strains.
- Dizziness: More likely in individuals with low tolerance.
- Paranoia and Anxiety: Rare but possible in sensitive users or when consumed in large quantities.
- Couch Lock: Due to its potent sedative effects, overconsumption can lead to excessive lethargy.
Conclusion
White OG is a versatile and potent cannabis strain that appeals to both recreational and medical users. Its rich terpene profile, high THC content, and balanced effects make it a standout choice for relaxation, pain relief, and stress management. Whether you are seeking a strain to unwind after a long day or to address specific medical concerns, White OG’s robust profile delivers consistent and reliable results.
For cultivators, its rewarding yields and resin-heavy buds are an added bonus, though attention to detail is required to maximize its potential. With its deep lineage rooted in cannabis royalty, White OG continues to cement its place as a favorite among enthusiasts and patients alike.
For a complete directory of cultivars, visit our Cannabis Strain Reviews.