
What is Medical CBD Cannabis?
Introduction
Medical CBD cannabis refers to cannabis strains that are specifically cultivated and processed for their high cannabidiol (CBD) content and minimal tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) levels. Unlike recreational cannabis, which is often bred for its psychoactive effects, medical CBD cannabis is designed to maximize therapeutic benefits without causing a “high.” This distinction is crucial for patients who seek symptom relief without the cognitive impairment or other side effects associated with THC.
Understanding medical CBD cannabis requires an exploration of its components, growing conditions, medical applications, and regulatory environment. This comprehensive guide delves into what constitutes medical CBD cannabis, its benefits, and how it is grown to meet medical standards.
1. Components of Medical CBD Cannabis
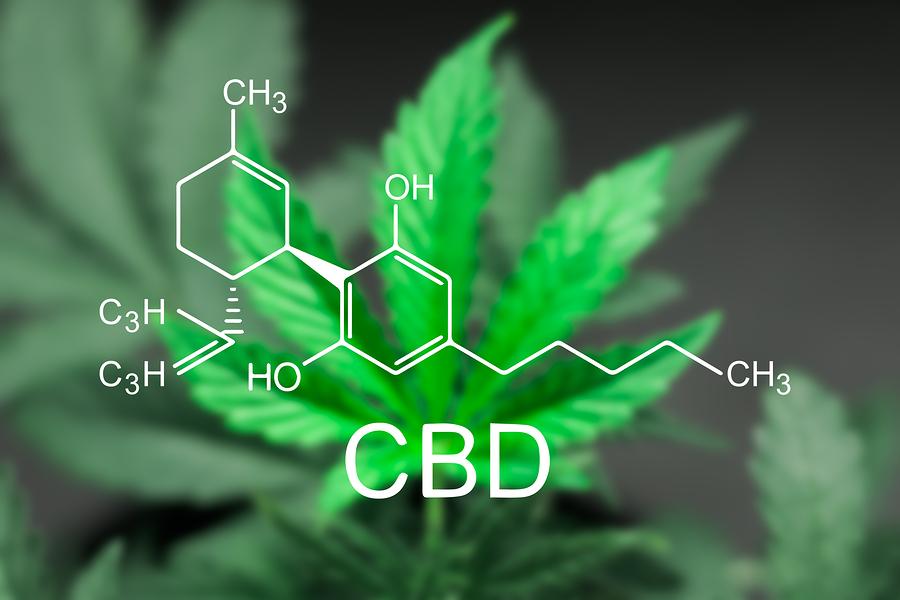
Medical CBD cannabis is primarily characterized by its high levels of CBD, a non-psychoactive compound that offers numerous health benefits. CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) of the body, which is important in controlling pain, mood, hunger, and immunological response, among other physiological processes.
Key Cannabinoids in Medical CBD Cannabis:
- Cannabidiol (CBD): The primary therapeutic compound in medical CBD cannabis. It is known for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-anxiety, anti-seizure, and neuroprotective properties. Since CBD doesn’t get you high like THC does, it’s safe for patients of all ages, even young ones and the elderly.
- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): The psychoactive compound in cannabis. In medical CBD cannabis, THC levels are kept low (usually below 0.3%) to minimize any psychoactive effects while still allowing for the entourage effect, a synergistic interaction between various cannabinoids that enhances therapeutic benefits.
- Minor Cannabinoids: These include cannabigerol (CBG), cannabichromene (CBC), and cannabinol (CBN), which may also have therapeutic benefits. While they are present in smaller amounts, they contribute to the overall efficacy of medical CBD cannabis through the entourage effect.
- Terpenes and Flavonoids: These compounds contribute to the aroma, flavor, and therapeutic properties of the cannabis plant. Terpenes such as myrcene, limonene, and linalool may enhance CBD’s effects by providing additional anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and analgesic properties.
2. Growing Medical CBD Cannabis
The cultivation of medical CBD cannabis is a highly regulated process designed to ensure the highest quality, safety, and efficacy of the final product. Growing conditions, strain selection, and farming techniques are all tailored to produce cannabis plants with optimal CBD content and minimal THC.
Strain Selection: Choosing the right strain is fundamental to cultivating medical CBD cannabis. Popular strains like Charlotte’s Web, ACDC, and Harlequin have been specifically bred to contain high levels of CBD and low levels of THC.
- Charlotte’s Web: A renowned strain with less than 0.3% THC and about 17% CBD, known for its effectiveness in treating seizures and anxiety.
- ACDC: A strain with a CBD
ratio of 20:1, making it ideal for managing chronic pain, anxiety, and inflammation without psychoactive effects. - Harlequin: With a CBD
ratio of 5:2, this strain offers a balanced profile, providing pain relief and anti-anxiety benefits.
Cultivation Conditions:
Growing medical CBD cannabis requires stringent control over environmental factors to ensure high-quality yields.
- Climate Control: Cannabis plants thrive in temperatures between 70-85°F (21-29°C) during the day and slightly cooler at night. Humidity levels must be carefully monitored, as high humidity can promote mold growth, while low humidity can cause plants to dry out.
- Lighting: For indoor grows, full-spectrum LED lights are preferred as they provide the right balance of wavelengths for photosynthesis. The light cycle is crucial, with an 18-hour light period during the vegetative stage and a 12-hour light period during the flowering stage to optimize CBD production.
- Soil and Nutrients: High-quality soil with a pH of 6.0 to 7.0 is essential. Organic nutrients rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are used to promote healthy growth and enhance CBD production.
- Watering: Overwatering or underwatering can stress the plants and negatively affect CBD content. Consistent watering schedules, using filtered water, are recommended to avoid chlorine and other contaminants that may harm the plants.
Cultivation Methods:
- Organic Farming: Medical CBD cannabis is often grown organically, without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, to ensure purity and prevent any harmful substances from entering the final product. Organic farming practices also promote soil health and sustainability.
- Hydroponics and Aeroponics: Higher CBD yields and faster growth are possible with these soilless growing techniques because they provide exact control over water and nutrients. In aeroponics, plants are suspended in the air and nutrient-sprayed directly into their roots, whereas hydroponics grows plants in nutrient-rich water.
- Pest and Disease Management: Integrated pest management (IPM) is employed to control pests and diseases. This involves using natural predators, organic pesticides, and other non-toxic methods to maintain plant health without compromising quality.
3. Medical Applications of CBD Cannabis

Medical CBD cannabis has gained widespread acceptance in the medical community for its diverse therapeutic applications. Its non-psychoactive nature makes it an ideal option for patients seeking relief from various conditions without the high associated with THC.
Pain Management:
Because of its well-known analgesic qualities, CBD is widely used to treat chronic pain disorders like neuropathic pain, arthritis, and fibromyalgia. It modulates pain perception and lowers inflammation by interacting with the ECS.
Anxiety and Depression:
Significant anxiolytic and depressive effects of CBD have been demonstrated. It affects the brain’s serotonin receptors, which are essential for controlling mood. Because it doesn’t have the negative effects of traditional antidepressants and anxiolytics, it presents a promising alternative for treating anxiety disorders, PTSD, and depression.
Neurological Disorders:
CBD’s neuroprotective properties make it valuable in treating neurological disorders. Most famously, it is used to treat epilepsy, especially when other treatments haven’t worked. The FDA-approved drug Epidiolex, which is derived from CBD, has proven effective in reducing seizures in patients with Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Inflammatory Conditions:
CBD has potent anti-inflammatory effects, making it beneficial for conditions like multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and autoimmune diseases. By modulating immune responses, CBD helps reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
Cancer Symptom Relief:
CBD is increasingly used to manage symptoms associated with cancer and its treatments, such as pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Although it cannot treat cancer, it can greatly enhance the quality of life for those who are receiving radiation or chemotherapy.
Cardiovascular Health:
Preliminary studies suggest that CBD may have cardioprotective effects, such as reducing blood pressure and preventing heart damage caused by inflammation or oxidative stress. It can be used as a medicinal agent to treat cardiovascular diseases because of these qualities.
Skin Conditions:
CBD is being explored for its benefits in treating various skin conditions, including acne, psoriasis, and eczema. It can help lessen inflammation and improve skin health because to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory qualities.
4. Regulatory Considerations for Medical CBD Cannabis
The cultivation, processing, and use of medical CBD cannabis are subject to strict regulatory frameworks that vary by country and region. These regulations are designed to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of CBD products, as well as to control their distribution and use.
Cultivation Regulations:
Medical CBD cannabis cultivation is regulated to ensure that plants meet specific standards for CBD and THC content. In the United States, for example, the 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp cultivation (cannabis with less than 0.3% THC), but growers must be licensed and comply with state and federal guidelines. Similar regulations exist in Canada, Europe, and other regions where medical cannabis is legal.
Processing and Testing Standards:
To ensure patient safety, medical CBD cannabis products undergo rigorous testing for cannabinoid content, pesticides, heavy metals, mold, and other contaminants. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are often required to ensure consistency and quality in the production process.
Prescription and Distribution:
In many countries, medical CBD cannabis is only available through a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. The prescription must specify the product’s CBD content, dosage, and method of administration. Distribution is often controlled through pharmacies, dispensaries, or licensed healthcare providers.
Patient Eligibility and Monitoring:
Eligibility for medical CBD cannabis varies by jurisdiction, with some regions requiring patients to have a specific qualifying condition. Additionally, patients might be observed in order to evaluate the efficacy of the medication as well as any possible side effects.
5. Research and Future Directions

While the medical use of CBD cannabis is supported by a growing body of research, there is still much to learn about its full range of applications and long-term effects. Ongoing clinical trials and studies are exploring new therapeutic uses, optimal dosages, and potential interactions with other medications.
Emerging Research Areas:
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: The potential of CBD to treat neurological illnesses like Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s disease is still being investigated. Its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties make it a promising candidate for these conditions.
- Mental Health Disorders: Studies are investigating the use of CBD for treating conditions like schizophrenia, OCD, and bipolar disorder. Its antipsychotic and anxiolytic properties may offer new avenues for managing these complex disorders.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Given CBD’s immunomodulatory effects, research is also exploring its potential in treating autoimmune diseases like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
- Addiction and Substance Abuse: According to preliminary study, CBD may be able to lessen withdrawal symptoms and cravings in those who are struggling with opiate, cigarette, or alcohol dependency, among other substance use disorders.
Technological Advances in Cultivation:
Technological advancements in cannabis cultivation, such as genetic engineering, precision agriculture, and automated growing systems, are likely to improve the quality and consistency of medical CBD cannabis. These innovations can help optimize cannabinoid profiles, increase yields, and reduce costs, making medical CBD cannabis more accessible to patients worldwide.
6. Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising potential of medical CBD cannabis, there are several challenges and considerations to address:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The regulatory landscape for medical CBD cannabis remains complex and fragmented, with different rules in different jurisdictions. Harmonizing these regulations is necessary to facilitate research, development, and patient access.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality and potency of medical CBD cannabis products is essential for patient safety and efficacy. This requires standardized testing methods, GMP compliance, and transparent labeling practices.
- Public Perception: There is still some stigma associated with cannabis use, even for medical purposes. For medicinal CBD cannabis to be more widely accepted, it is essential to educate the general public and medical experts about its advantages and safety.
- Cost and Accessibility: The cost of medical CBD cannabis can be prohibitive for some patients, especially in regions where it is not covered by insurance. Policies to improve affordability and access are needed to ensure that all patients can benefit from this therapeutic option.
Restrictions on Using Cannabis in the Medical Field as a Last Resort
1. Last-Resort Use Guidelines:
- Established Treatment Hierarchy: Medical cannabis is typically reserved as a last-resort option after conventional treatments (like pharmaceuticals, physical therapy, etc.) have failed or caused adverse effects. Physicians must document the exhaustion of standard therapies before prescribing cannabis.
- Qualifying Conditions: Restrictions often limit medical cannabis use to specific conditions such as epilepsy, chronic pain, cancer-related symptoms, multiple sclerosis, and PTSD. Each jurisdiction has a different list of acceptable criteria.
- Prescription Control: Only licensed healthcare providers can prescribe medical cannabis, often requiring special certification or registration to do so.
2. Monitoring THC Levels in Medications:
- THC Limits: Regulations generally require medical cannabis products to contain low THC levels (often less than 0.3%) to minimize psychoactive effects, especially in products intended for vulnerable populations like children or the elderly.
- Standardized Testing: Products must undergo rigorous third-party testing for THC and CBD concentrations. This ensures consistency in dosing and prevents unintended psychoactive effects.
- Labeling Requirements: Medical cannabis products must clearly label THC and CBD content, allowing for precise patient dosing and minimizing the risk of psychoactive exposure.
- Regular Patient Monitoring: Healthcare providers are required to monitor patients for any signs of psychoactive effects, side effects, or dependency, adjusting dosages as needed to ensure safety.
Conclusion
Medical CBD cannabis has emerged as a transformative option in the field of medicine, offering a broad range of therapeutic benefits without the psychoactive effects associated with THC. As the understanding of cannabinoids deepens, medical CBD cannabis is being recognized for its ability to manage a variety of conditions, from chronic pain and anxiety to neurological disorders and cancer-related symptoms. Unlike recreational cannabis, which is bred for its psychoactive properties, medical CBD cannabis is cultivated with a focus on maximizing its health benefits, ensuring safety, and providing consistent therapeutic effects.
The Role of Cannabinoids in Medical Use
The primary component of medical CBD cannabis, cannabidiol (CBD), interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system to promote balance and health. CBD is known for its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-anxiety, and neuroprotective properties, making it a versatile treatment option. Unlike THC, CBD does not produce a high, which makes it suitable for a broad patient demographic, including those who are particularly vulnerable, such as children, the elderly, and individuals with mental health disorders.
Medical CBD cannabis also contains minor cannabinoids like cannabigerol (CBG), cannabichromene (CBC), and cannabinol (CBN), as well as terpenes and flavonoids, which contribute to the therapeutic effects through the entourage effect. This synergy among different compounds enhances the medicinal properties of CBD and makes it more effective for treating complex conditions.
Cultivating Medical CBD Cannabis
Growing medical CBD cannabis involves meticulous attention to strain selection, environmental control, and cultivation techniques to ensure a high-quality product. Strains like Charlotte’s Web, ACDC, and Harlequin are specifically bred for their high CBD content and low THC levels, making them ideal for medical use. Cultivation conditions, including controlled climate, lighting, soil quality, and water management, are optimized to promote healthy growth and maximize CBD yield. Techniques such as organic farming, hydroponics, and aeroponics are employed to ensure purity, prevent contamination, and improve the consistency of the final product.
This cultivation process is governed by stringent regulations to maintain quality, safety, and efficacy. Medical CBD cannabis must meet specific standards for cannabinoid content, undergo rigorous testing for contaminants, and adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP). These measures are crucial for ensuring that patients receive safe and effective treatments.
Therapeutic Applications
Medical CBD cannabis is increasingly used to manage a variety of health conditions. Because of its analgesic qualities, it is a useful treatment for chronic pain, including neuropathic and arthritic conditions. For mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, and PTSD, CBD offers anxiolytic and antidepressant effects without the side effects of conventional medications. In neurological disorders, including epilepsy and multiple sclerosis, CBD’s neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties have shown significant promise, as evidenced by the approval of CBD-based medications like Epidiolex.
CBD is also used to alleviate symptoms associated with cancer treatments, such as nausea and pain, and it is being studied for its potential to support cardiovascular health, skin conditions, and addiction recovery. As research continues to expand, new therapeutic applications for CBD are likely to emerge, offering hope for patients with a wide range of medical conditions.
Regulatory Considerations
There is a complicated regulatory framework surrounding the use of medical CBD cannabis that is intended to protect patient safety and product quality. Countries and regions have different regulations, but in general, processing and production must adhere to strict guidelines for THC and CBD concentration. Potency, consistency, and contaminant testing are required for products, which are normally only available with a prescription. This regulatory oversight helps maintain high standards for medical CBD cannabis, but it also creates challenges related to access, cost, and public perception.
Restrictions on using cannabis as a last resort in medical settings ensure that it is only prescribed after other treatments have been tried and found ineffective or unsuitable. This approach balances the potential benefits of medical cannabis with the need to prioritize established medical practices. Additionally, the monitoring of THC levels in medical cannabis products ensures that patients receive the therapeutic benefits of CBD without the risk of psychoactive effects, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Future Directions and Challenges
The future of medical CBD cannabis looks promising, with ongoing research exploring new therapeutic uses, optimizing cultivation methods, and refining our understanding of its effects. However, challenges remain, including regulatory hurdles, quality control, public perception, and access to affordable treatment. Harmonizing global regulations, educating healthcare providers and the public, and developing standardized testing and labeling practices will be critical to overcoming these challenges and expanding the availability of medical CBD cannabis.
Technological advancements in cultivation, such as precision agriculture and genetic engineering, offer the potential to improve the quality, consistency, and accessibility of medical CBD cannabis. These innovations will help address some of the current challenges, such as high production costs and variable product quality, and may lead to new formulations and delivery methods that enhance the therapeutic efficacy of CBD.