Table of Contents
What is hhc
Introduction to HHC: Understanding Hexahydrocannabinol

This document provides a comprehensive introduction to Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), a hydrogenated derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal psychoactive component of the cannabis plant. The discussion includes an examination of HHC’s chemical structure, its synthesis, potential effects, and the legal framework governing its use, emphasizing its emerging role in both medicinal and recreational contexts.
Introduction
Hexahydrocannabinol, commonly referred to as HHC, has garnered significant attention for its distinctive chemical properties and potential uses. Initially synthesized in the 1940s by chemist Roger Adams, HHC is created through the hydrogenation of THC. This method involves modifying THC’s molecular structure by adding hydrogen atoms, resulting in a compound that potentially possesses enhanced stability and potency. This summary is designed to illuminate the key features of HHC, examining its properties, effects, and the regulatory context in which it is used.
Chemical Structure and Synthesis
The synthesis of HHC involves the hydrogenation of THC, where hydrogen atoms are added to THC’s molecular framework. This alteration breaks the double bonds within the THC molecule, resulting in a saturated form that enhances the molecule’s stability and possibly its pharmacological potency. The hydrogenation process not only changes the compound’s molecular structure but could also affect how it interacts with the human endocannabinoid system.
Pharmacological Effects
While research on HHC is still emerging, initial studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that it exhibits psychoactive effects akin to those of THC, though they may vary in intensity. HHC is believed to interact with the body’s cannabinoid receptors, potentially inducing sensations of euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception. However, detailed and systematic research is necessary to fully understand the range and mechanism of effects HHC has on the body.
Legal Status
The legal landscape for HHC is complex and varies widely depending on the jurisdiction. In places like the United States, HHC currently occupies a legal gray area, as it is not specifically listed as a controlled substance federally. However, the evolving nature of cannabis legislation means that the status of HHC could change as new laws are enacted. Those interested in using or distributing HHC must stay well-informed about the applicable laws in their area, which may affect the legality of HHC’s distribution and use.
Conclusion
HHC stands out as a promising cannabinoid with potential applications that extend across therapeutic and recreational domains. Its unique properties, derived from the hydrogenation of THC, warrant further scientific exploration to better understand its benefits, safety, and pharmacological efficacy. As research progresses and regulatory frameworks evolve, it will be critical for the scientific and regulatory communities to provide updated insights and guidelines regarding HHC’s use and regulation.
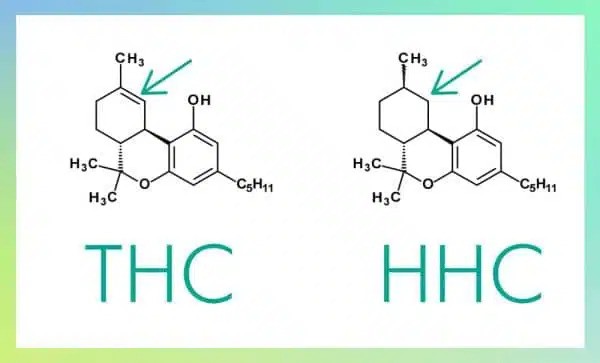
The Chemical Structure of HHC: How It Differs from THC
This document provides an in-depth analysis of the chemical structure of Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) and its differentiation from Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive component of cannabis. By focusing on molecular modifications and their implications, this analysis sheds light on how structural changes influence the pharmacological properties and stability of HHC compared to THC.
Introduction
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a derivative of THC, obtained through a process known as hydrogenation. This chemical alteration modifies THC’s original structure, thereby altering its chemical and biological characteristics. This paper describes the specific structural transformations that occur during this process and explores their potential impacts on the pharmacological profile and stability of HHC.
Chemical Structure Analysis
- Original Molecular Structure of THC: THC features a complex structure with a phenolic ring and a pyran ring, highlighted by the presence of carbon-carbon double bonds within a cyclic hydrocarbon system. These double bonds are crucial as they influence THC’s pharmacological interactions, particularly its binding affinity for cannabinoid receptors.
- Hydrogenation Process: Transforming THC into HHC involves the addition of hydrogen atoms to the THC structure, a process that primarily affects the double bonds. Hydrogenation saturates these bonds, transforming THC into a hydrogen-rich compound that differs significantly in chemical stability.
- Resultant Molecular Structure of HHC: In HHC, the introduction of hydrogen atoms leads to the elimination of double bonds, resulting in a fully saturated hydrocarbon ring. This saturation not only enhances the molecule’s stability against oxidation and thermal decomposition but also may alter its interaction with cannabinoid receptors due to the structural changes.
Pharmacological Consequences
The structural distinctions between THC and HHC likely result in differing pharmacological effects. While both molecules interact with the endocannabinoid system, the saturated nature of HHC could modify its effectiveness, potency, or the duration of its effects. Initial findings indicate that HHC might share psychoactive properties with THC but with variations in their effects’ strength and duration, highlighting the need for extensive research to clarify these differences.
Conclusion
The distinctive chemical structure of HHC, marked by its hydrogenated form compared to THC, opens new avenues for cannabinoid research. Delving into how these structural changes affect HHC’s pharmacological actions and stability is crucial for advancing scientific knowledge and potential therapeutic applications. Further investigations are essential to fully understand the diverse physiological impacts of HHC and to assess its viability in medical and recreational contexts. This deeper comprehension will enhance the cannabinoid field, potentially leading to innovative health solutions.
Legal Status of HHC: Regulations and Considerations
The legal treatment of hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), a synthesized cannabinoid derivative typically produced from hemp-derived cannabidiol (CBD), constitutes a complex and evolving area of law. This document aims to clarify the existing regulations governing HHC, emphasizing the essential legal aspects and considerations for those engaged in this emerging industry.
- Overview of Regulations: HHC is related to delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive component found in cannabis. However, unlike THC which is clearly regulated under the 1970 Controlled Substances Act (CSA), HHC occupies a gray area in federal law. This uncertainty arises largely due to its synthesis from legally grown hemp, which was federally legalized by the 2018 Agricultural Improvement Act (Farm Bill).
- Variations Across States: The regulatory landscape for HHC is inconsistent across different states. While some states have classified HHC as a controlled substance, effectively limiting its production and sale, others have yet to specifically address the cannabinoid, creating a regulatory gap that complicates enforcement and business operations.
- Considerations for Industry Participants: Companies involved in the production or distribution of HHC must carefully navigate a complicated mix of federal and state laws. It is critical for these entities to engage in comprehensive legal due diligence, develop strong compliance measures, stay updated on regulatory changes, secure necessary permits, and comply with applicable legal requirements.
- Anticipated Changes in Regulations: Industry participants should anticipate possible shifts in HHC’s regulatory status. As legislative and public interest in cannabinoid products continues to grow, future legal or regulatory adjustments could profoundly impact how HHC is governed.
- Risk Management Strategies: Given the legal uncertainties surrounding HHC, prioritizing risk management is crucial. Companies should implement protective measures, including lobbying for favorable laws, joining industry groups, and obtaining expert legal counsel to enhance their operational stability.
In summary, the legal environment for HHC is marked by substantial regulatory variation and complexity. Companies in this field should remain alert, adapt to new laws, and implement proactive legal and compliance strategies to navigate these challenges effectively.
Effects of HHC: Comparing Psychoactive Properties with Other Cannabinoids
This detailed analysis aims to explore the psychoactive properties of hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), examining how it compares to other prominent cannabinoids such as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). The objective is to offer a comprehensive comparison based on current scientific knowledge, providing insights into HHC’s psychoactive potential and its implications within the cannabinoid research field.
- Chemical Characteristics and Psychoactive Dynamics: HHC is a hydrogenated form of THC, sharing a similar molecular structure but differing in the saturation of its chemical bonds, which impacts its stability and potency. This modification impacts the way HHC engages with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is responsible for regulating a variety of physiological and cognitive functions. While the binding affinity of HHC to CB1 receptors—central to producing psychoactive effects—is less defined than THC’s, further research is necessary to clarify these interactions fully.
- Effects Comparison: Early studies and user reports indicate that HHC may produce psychoactive effects that are generally milder compared to THC. Descriptions of HHC’s effects include mild euphoria and relaxation, akin to THC but with potentially fewer side effects like anxiety or paranoia. In contrast, CBD, which is mostly non-psychoactive, is sought after for its anti-anxiety and anti-inflammatory benefits. Thus, HHC occupies a unique position in the psychoactive spectrum of cannabinoids.
- Potential Therapeutic Benefits: Emerging research into HHC’s therapeutic potential suggests uses in pain relief, appetite stimulation, and as an anti-emetic, similar to other cannabinoids but with a unique pharmacological profile due to its interaction with various cannabinoid and non-cannabinoid receptors.
- Regulatory and Safety Issues: The legal landscape for HHC remains complex and variable, significantly impacting research and the development of therapeutic applications. Regulatory fluctuations influence the availability of controlled studies necessary for a deep scientific understanding and safe medical use. Additionally, the synthesis of HHC from CBD may lead to inconsistencies in product purity and quality, raising further concerns regarding its clinical utility and regulatory status.
In summary, while HHC shares psychoactive traits with THC, its unique effects and potential reduced side effects position it distinctively among cannabinoids. Nonetheless, rigorous scientific exploration is crucial to substantiate these attributes and to integrate HHC safely into medical practices, considering the ongoing changes in its legal classification and the need for stringent scientific evaluation.
How Is HHC Made? A Look at the Production Process
The creation of hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) involves intricate chemical processes that require an advanced understanding of cannabinoid chemistry. This document aims to detail the steps involved in the production of HHC, outlining the key chemical processes and techniques utilized in transforming cannabidiol (CBD) from hemp into HHC.
- Extraction of CBD: The production of HHC begins with the extraction of CBD from hemp plants. Frequently used extraction techniques encompass CO2 extraction, ethanol extraction, and hydrocarbon extraction. These techniques efficiently separate cannabinoids from the plant material, yielding a high-purity CBD extract.
- Conversion to HHC: Central to the production process is the transformation of CBD into HHC, predominantly via hydrogenation. This technique involves exposing CBD to high pressure alongside a catalyst, typically palladium on carbon, and hydrogen gas.
- The hydrogenation process saturates the CBD’s molecular double bonds with hydrogen atoms, transforming it into HHC. This step requires precise management of several variables, including temperature, pressure, and the rate of hydrogen flow, to ensure the reaction yields a high-quality product.
- Purification and Quality Assurance: After hydrogenation, the resulting HHC is further refined to eliminate any residual impurities, reactants, or byproducts. Techniques such as chromatography, distillation, and crystallization are utilized to purify the HHC to a pharmaceutical-grade standard.
Every batch of HHC is subject to thorough testing, which includes high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), and mass spectrometry (MS), to confirm its purity, strength, and chemical makeup. - Regulatory Compliance and Safety Protocols: Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and safety measures is crucial throughout the HHC production process.
- This entails compliance with the standards set by regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and other international health authorities. Producers must maintain high standards in facility operations and process controls to ensure the safety and quality of the HHC produced.

In summary, the synthesis of HHC from CBD is a complex, multi-step chemical process that demands precision, expertise, and strict regulatory compliance. Each phase of production, from CBD extraction to the final quality control of HHC, must be meticulously executed to ensure the final product is effective, safe, and consistent. As research in cannabinoid synthesis advances, these processes continue to be refined, contributing to the broader understanding and application of cannabinoids like HHC in various fields.
Potential Health Benefits and Risks of HHC
This analytical document aims to dissect the health implications associated with hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), a synthesized cannabinoid that has piqued the interest of both the medical field and scientific researchers. As a derivative of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), HHC is produced through a hydrogenation process that alters its chemical structure, potentially affecting its pharmacological effects. Below, we detail the prospective health benefits and risks linked with HHC usage.
- Potential Health Benefits:
- Pain Relief: Emerging data indicates that HHC may have analgesic properties, suggesting it could be effective in managing chronic pain, offering an alternative for those seeking pain relief without the psychoactive intensity of traditional THC.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties:
- Appetite Enhancement: HHC could help boost appetite in users experiencing appetite suppression due to medical conditions, a benefit commonly associated with THC.
- Nausea Reduction: There is potential for HHC to serve as an antiemetic, useful in reducing nausea and vomiting, especially in chemotherapy patients. Like other cannabinoids, HHC is believed to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which could be advantageous in managing inflammatory conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Risks and Concerns:
- Psychoactive Potential: While generally considered less potent than THC, HHC still exhibits psychoactive effects, which may alter perception, mood, and cognitive functions. These effects necessitate caution, especially among sensitive individuals or those involved in activities that demand mental alertness.
- Regulatory Ambiguities: The legal landscape surrounding HHC is not clearly defined in many areas, which complicates its usage and scientific study. This lack of regulation can impact the quality and safety of HHC products, posing health risks due to insufficient oversight.
- Research Deficiency: There is a notable lack of extensive clinical research on HHC, leaving its long-term health impacts largely unknown. This gap in knowledge hinders the ability to fully evaluate its safety profile.
- Contamination Risk: The synthesis process of HHC can lead to contamination with impurities and byproducts if not strictly controlled, highlighting the necessity for rigorous production standards and comprehensive product testing.
- Call for Further Investigation and Regulatory Oversight:
- Research Enhancement: To fully understand the effects and potential therapeutic applications of HHC, detailed scientific investigations, including controlled clinical trials, are imperative. These studies should aim to clarify its effectiveness and safety.
- Regulatory Development: It is critical to establish clear regulations for the manufacturing, distribution, and consumption of HHC to ensure safety, quality, and consistency of products. Such regulations would safeguard consumers and facilitate ongoing research.
In summary, while HHC offers promising health benefits that could be valuable in various medical applications, the associated risks and uncertainties cannot be overlooked. Advancing research and establishing stringent regulatory standards are crucial steps to safely and effectively tap into the therapeutic capabilities of HHC.
HHC Products: Various Forms and Their Uses
This document aims to provide an in-depth review of the diverse array of hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) products currently on the market, examining their various forms and practical applications. HHC, a synthetic derivative of cannabidiol (CBD) achieved through hydrogenation, possesses psychoactive properties akin to but distinct from those of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The range of HHC products mirrors the expanding interest and innovation within the field of cannabinoid-based solutions, accommodating a broad spectrum of uses from recreational activities to prospective medicinal benefits.
- Types of HHC Products:
- Vape Cartridges and E-liquids: These are intended for use in vaporizers and e-cigarettes, providing a method of inhalation that many consider a safer alternative to smoking traditional cannabis products. HHC vapes are favored for their portability and for delivering rapid effects.
- Edibles: HHC-infused edibles, including gummies, chocolates, and baked items, offer a discreet consumption method. The effects of edibles are long-lasting, though they require more time to take effect compared to inhalation.
- Oils and Tinctures:
- This makes them popular among both recreational and medical users.
- Capsules and Pills: These products provide a highly controlled dose of HHC, preferred by those who require consistent and specific cannabinoid intake, often for health-related reasons. These liquid varieties are administered sublingually or added to food and beverages, enabling accurate dosing and a relatively rapid onset of effects.
- Uses of HHC Products:
- Recreational Purposes: HHC is predominantly used recreationally for its capacity to enhance mood and induce euphoria. Many users choose HHC for its reportedly milder effects and lower likelihood of causing anxiety compared to THC.
- Potential Medical Benefits: Early studies hint at HHC’s possible health benefits, such as pain relief, reduction of inflammation, appetite enhancement, and anti-nausea effects, all of which are subjects of ongoing research.
- Lifestyle and Wellness: HHC is also integrated into some users’ wellness routines, where it is used to help reduce stress, promote relaxation, and improve general well-being, similar to the role of CBD in wellness regimes.
- Regulatory and Safety Aspects:
- The diverse product forms and varying strengths of HHC necessitate accurate labeling and adherence to local cannabinoid product regulations. The legal status of HHC varies by area, influencing both its availability and lawful consumption.
- Consumers are encouraged to confirm the purity and source of HHC products due to the nascent nature of the market, which can expose them to varying levels of product quality and standards.
In summation, the assortment of HHC products reflects the burgeoning interest and developmental pace of cannabinoid research and application. As knowledge and regulatory structures evolve, the role of HHC in both recreational and therapeutic domains is expected to become clearer, underscoring the importance of ongoing research and judicious policy development to fully realize the potential of this emerging cannabinoid.

The Future of HHC in the Cannabis Industry
As the cannabis industry continues its rapid growth, hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is emerging as a significant cannabinoid with the potential to reshape market dynamics and consumer behaviors. This document provides an analysis of the future role of HHC within the industry, assessing its market potential, innovative applications, and the regulatory hurdles that could influence its trajectory.
- Market Dynamics and Consumer Adoption:
- Product Diversification: The incorporation of HHC into various cannabis products such as vapes, edibles, and topicals is expanding. This diversification caters to a growing consumer base eager for alternatives to traditional THC offerings, positioning HHC as a distinctive choice in a crowded market.
- Consumer Education and Acceptance: The success of HHC hinges on effective consumer education regarding its distinct characteristics and potential advantages. Strategic marketing that emphasizes these unique qualities can enhance consumer understanding and drive broader market acceptance.
- Therapeutic Potential and Medical Applications:
- Research and Validation of Health Benefits: Early studies hint at possible benefits of HHC, including pain relief, anti-inflammatory effects, and nausea reduction.
- Engagement with Medical Communities: Building relationships with healthcare providers and exploring the medicinal qualities of HHC may facilitate its inclusion in medical treatments, thus broadening its acceptance and use in healthcare settings. Additional research is required to corroborate these claims, which could facilitate the creation of specialized medical products containing HHC.
- Regulatory Environment and Compliance Issues:
- Legal Frameworks and Classification: The complex and varied legal status of HHC across different regions poses a significant challenge. Clear regulatory guidelines are necessary to ensure HHC’s safe integration into the market and to foster stability within the industry.
- Quality Assurance and Standards: Establishing standards for the safe production, accurate labeling, and distribution of HHC products is critical. These measures will protect consumers from low-quality or counterfeit products and help establish a trustworthy market presence for HHC.
- Industry Relationships and Market Strategy:
- Collaborations with Industry Leaders: Partnerships with established players in the cannabis industry could help propel HHC into mainstream markets, utilizing existing research, development, and distribution networks.
- Responsiveness to Consumer Trends: The ability to adapt to ongoing shifts in consumer preferences, such as the demand for wellness-focused and personalized cannabis experiences, will be crucial for maintaining HHC’s relevance and success in the industry.
In conclusion, the future of HHC in the cannabis industry is poised for growth, dependent on robust research, adept market strategies, and effective navigation of the regulatory landscape. Addressing these areas will be vital for leveraging HHC’s potential and ensuring its successful and sustainable presence in the market, thereby influencing the future contours of the cannabis industry.