Cannabis Flavonoids: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
Cannabis, a plant known for its psychoactive and medicinal properties, contains a myriad of chemical compounds, each contributing to its unique characteristics and effects. While cannabinoids like THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) often dominate discussions about cannabis, there is a lesser-known but equally important group of compounds known as flavonoids. These naturally occurring substances play a significant role in the plant’s biochemistry and therapeutic potential. This article delves into what cannabis flavonoids are, their properties, and their importance in both the plant kingdom and medicinal applications.
1. Understanding Flavonoids
1.1 Definition and Classification
Nearly all fruits and vegetables include a wide range of phytonutrients, or plant compounds, called flavonoids. They belong to a larger class of compounds known as polyphenols and are responsible for many of the vivid colors in the plant kingdom. There are over 6,000 types of flavonoids, categorized into various subclasses, including flavonols, flavones, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, anthocyanins, and isoflavones.
1.2 Structure and Biosynthesis
Flavonoids share a common basic structure comprising 15 carbon atoms, arranged in a C6-C3-C6 configuration. This structure consists of two phenyl rings (A and B rings) and a heterocyclic ring (C ring). The specific arrangement and the presence of various functional groups lead to the diversity of flavonoids. In plants, flavonoid biosynthesis involves a complex pathway starting from the amino acid phenylalanine, proceeding through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
2. Cannabis Flavonoids
2.1 Types of Flavonoids in Cannabis
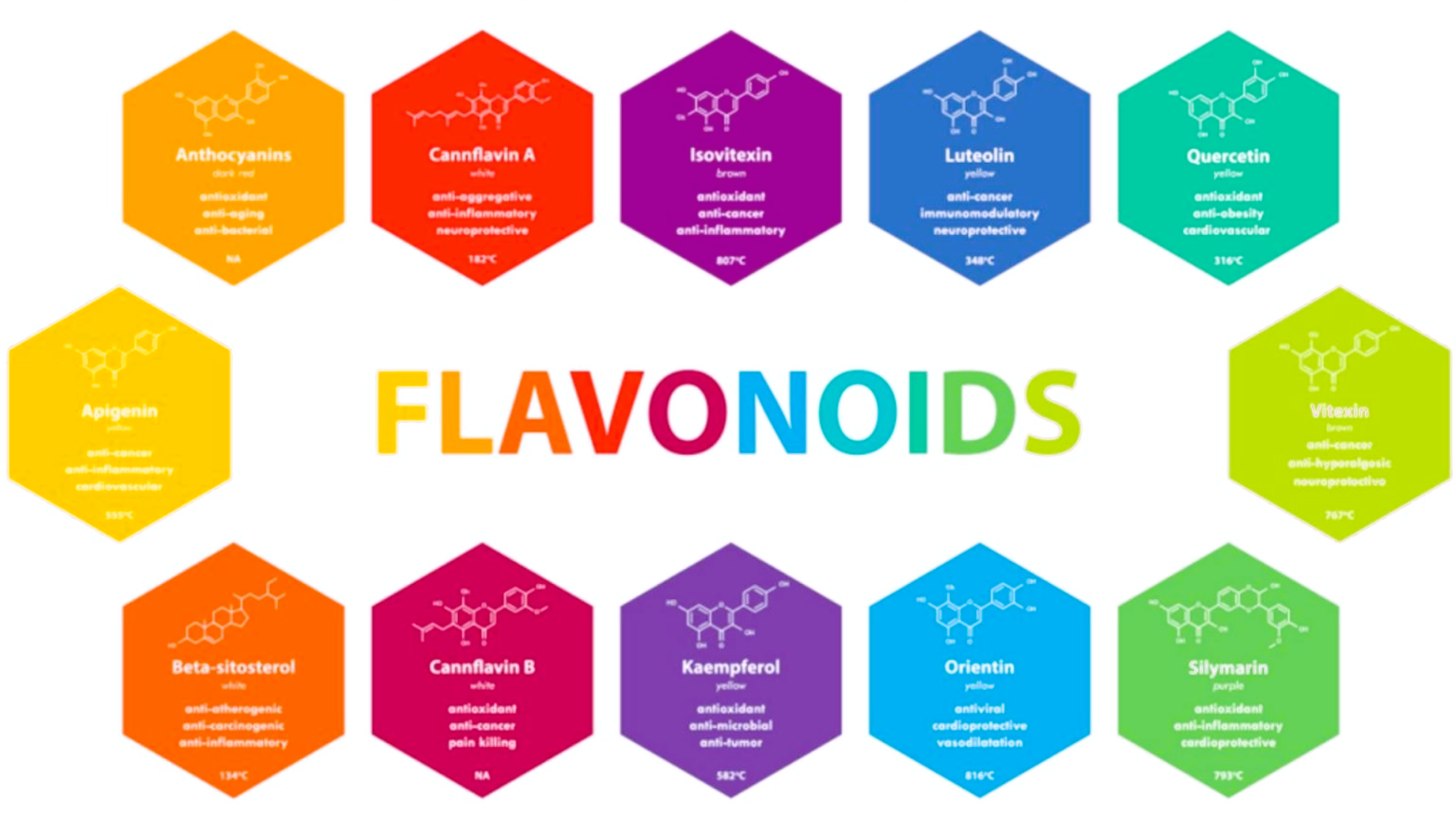
Cannabis plants contain around 20 different flavonoids. Some of the notable ones include:
- Cannflavins A, B, and C: These flavonoids are specific to cannabis and have anti-inflammatory qualities.
- Apigenin: Known for its anxiolytic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Quercetin: A potent antioxidant with anti-viral and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Kaempferol: Exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, and may have anti-cancer properties.
2.2 Flavonoid Concentration and Distribution
Flavonoids are found in various parts of the cannabis plant, including the leaves, stems, and flowers. Their concentration can vary significantly depending on the strain, growing conditions, and processing methods. Unlike cannabinoids, which are concentrated in the resin glands (trichomes) of the flowers, flavonoids are more evenly distributed throughout the plant.
3. The Role of Flavonoids in Cannabis Plants
3.1 Plant Physiology and Protection
Flavonoids play several crucial roles in the life of cannabis plants:
- UV Filtration: They protect the plant from harmful ultraviolet rays by absorbing UV light.
- Pigmentation: Flavonoids contribute to the plant’s coloration, which can attract pollinators and deter herbivores.
- Disease Resistance: They possess antimicrobial properties that help defend the plant against pathogens.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Flavonoids can facilitate symbiotic relationships with beneficial microorganisms in the soil.
3.2 Interaction with Other Compounds
Flavonoids can interact synergistically with other compounds in the cannabis plant, such as cannabinoids and terpenes. This interaction can enhance the overall effects of cannabis, a phenomenon known as the “entourage effect.
4. Medicinal Importance of Cannabis Flavonoids
4.1 Anti-inflammatory Properties
While inflammation is a normal reaction to damage or infection, prolonged inflammation has been linked to a number of illnesses, such as autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular illnesses, and arthritis. Cannabis flavonoids exhibit potent anti-inflammatory properties that could be harnessed to treat these conditions.
- Cannflavins A and B: Unique to cannabis, cannflavins A and B have shown to inhibit the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE-2), a compound involved in the inflammatory process, with a potency greater than aspirin. By blocking the inflammatory pathways, these flavonoids can potentially alleviate symptoms of chronic inflammatory diseases without the side effects associated with long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Apigenin: Found in many plants, including cannabis, apigenin has been documented to possess anti-inflammatory properties. It can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes such as COX-2, thereby reducing inflammation and associated pain.
4.2 Antioxidant Properties
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance in the body’s free radicals and antioxidants, has been linked to aging and a variety of chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Cannabis flavonoids, like other flavonoids, are powerful antioxidants that can neutralize free radicals and protect the body from oxidative damage.
- Quercetin: A well-known flavonoid, quercetin exhibits strong antioxidant properties. It scavenges free radicals, reduces oxidative stress, and enhances the body’s antioxidant defenses. These properties make it beneficial in preventing and managing conditions linked to oxidative stress.
- Kaempferol: Another potent antioxidant found in cannabis, kaempferol helps protect cells from oxidative damage. Its ability to reduce oxidative stress can lower the risk of chronic diseases and support overall health.
4.3 Neuroprotective Effects
A hallmark of neurodegenerative illnesses including Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and multiple sclerosis is the progressive loss of neuronal structure and function. Some cannabis flavonoids have shown potential in protecting neurons and promoting brain health.
- Apigenin: This flavonoid has been found to promote neurogenesis, the growth of new neurons, and protect against neuroinflammation. By modulating signaling pathways involved in neuron survival and plasticity, apigenin could be beneficial in treating neurodegenerative disorders.
- Cannflavins: Preliminary studies suggest that cannflavins may also possess neuroprotective properties, helping to shield neurons from damage and potentially slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
4.4 Anti-cancer Potential
Cancer is a complex disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth. Emerging research suggests that cannabis flavonoids might have anti-cancer properties, either by directly inhibiting cancer cell growth or by enhancing the efficacy of conventional treatments.
- Kaempferol: Studies have shown that kaempferol can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, inhibit cancer cell proliferation, and prevent the spread of tumors. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties further support its potential as an anti-cancer agent.
- Quercetin: This flavonoid has been extensively studied for its anti-cancer effects. It can modulate multiple signaling pathways involved in cancer cell survival, proliferation, and metastasis. Quercetin’s ability to enhance the effects of chemotherapy and reduce its side effects makes it a promising adjunct in cancer therapy.
4.5 Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Effects
Mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression affect millions of people worldwide. Certain flavonoids in cannabis may offer natural alternatives for managing these conditions.
- Apigenin: Apigenin is known for its anxiolytic qualities and can bind to benzodiazepine receptors in the brain, encouraging relaxation and lowering anxiety. Its capacity to alter neurotransmitter activity, such as GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), is critical for treating anxiety and mood disorders.
- Luteolin: Another flavonoid with potential antidepressant effects, luteolin has been found to influence serotonin and dopamine pathways in the brain. These neurotransmitters play key roles in regulating mood and emotional responses.
5. Flavonoids in Cannabis Research and Development
5.1 Challenges in Flavonoid Research
Despite their potential, researching flavonoids poses several challenges:
- Complex Extraction and Isolation: Flavonoids are often present in low concentrations, making their extraction and isolation from the plant material complex and time-consuming.
- Stability Issues: Flavonoids can degrade during processing and storage, affecting their efficacy.
- Limited Clinical Trials: There is a scarcity of clinical trials specifically focusing on cannabis flavonoids, partly due to regulatory restrictions on cannabis research.
5.2 Advances in Flavonoid Research
Recent advances in technology and methodologies are helping overcome some of these challenges:
- Improved Extraction Techniques: Techniques such as supercritical CO2 extraction and advanced chromatography are enhancing the efficiency and purity of flavonoid extraction.
- Synthetic Biology: Researchers are exploring the use of synthetic biology to produce flavonoids in microbial hosts, potentially enabling large-scale production.
- Enhanced Analytical Methods: Advanced analytical techniques like mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy are providing deeper insights into the structure and function of flavonoids.
6. Flavonoids and the Entourage Effect
6.1 Synergistic Interactions
The concept of the entourage effect suggests that the various compounds in cannabis work together synergistically to enhance the plant’s therapeutic effects. Flavonoids are believed to contribute significantly to this effect, interacting with cannabinoids and terpenes to modulate their activity.
- Cannabinoid Modulation: Flavonoids can influence the metabolism and bioavailability of cannabinoids, potentially enhancing their therapeutic effects.
- Terpene Interaction: Flavonoids and terpenes may work together to produce a wider range of therapeutic outcomes, from anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects to mood enhancement.
6.2 Clinical Implications
Understanding the entourage effect and the role of flavonoids could lead to more effective cannabis-based therapies. By carefully selecting strains and extraction methods that preserve and concentrate specific flavonoids, it may be possible to tailor treatments for individual patients’ needs.
7. Future Directions
7.1 Personalized Medicine
The future of cannabis flavonoid research lies in personalized medicine. By identifying the specific flavonoid profiles that work best for different conditions, it may be possible to develop customized treatments that maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing side effects.
7.2 Expanded Research
Continued research into the pharmacology and therapeutic potential of cannabis flavonoids is essential. This includes more extensive clinical trials, studies on the mechanisms of action, and investigations into the long-term effects of flavonoid use.
7.3 Regulatory Considerations
As research progresses, regulatory frameworks will need to adapt to facilitate the development and approval of flavonoid-based therapies. This includes establishing standardized testing protocols and ensuring quality control in the production of flavonoid-rich cannabis products.
Conclusion: In-Depth Analysis of Cannabis Flavonoids
The study of cannabis flavonoids presents a rich and intricate field of inquiry, one that holds immense potential for both botanical science and medicinal applications. As we delve deeper into the complexity of these compounds, several key points emerge, each underscoring the significance of flavonoids in cannabis and their broader implications.
1. Multifaceted Role in Plant Physiology
Cannabis flavonoids are integral to the plant’s survival and functionality. They serve multiple roles, from providing pigmentation that attracts pollinators to offering UV protection and disease resistance. These compounds are vital in mediating the plant’s interactions with its environment, thereby ensuring its growth and reproduction. Their presence in various parts of the plant and their distribution patterns also indicate a complex system of plant defense and adaptation.
2. Therapeutic Potential
The medicinal properties of cannabis flavonoids are increasingly coming to light through ongoing research. Their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective, and anti-cancer activities make them promising candidates for a variety of therapeutic applications. For instance, cannflavins A and B have demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects, surpassing some traditional medications in efficacy. This emphasizes how flavonoids may aid in the creation of novel, more potent anti-inflammatory medications.
Furthermore, the antioxidant properties of flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol could play a crucial role in combating oxidative stress-related diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases and certain types of cancer. The neuroprotective effects of apigenin and other flavonoids open avenues for potential treatments for neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
3. The Entourage Effect and Synergy
The concept of the entourage effect emphasizes the importance of the synergistic interactions between flavonoids, cannabinoids, and terpenes. This synergy can enhance the overall therapeutic efficacy of cannabis. Understanding these interactions can lead to more targeted and effective treatments, harnessing the full potential of the plant’s chemical profile. The entourage effect underscores the necessity of whole-plant medicine, where the combined effect of all the plant’s compounds is greater than the sum of its parts.
4. Research Challenges and Advances
Despite their potential, flavonoids pose several research challenges. These include difficulties in extraction and isolation, stability issues, and a lack of extensive clinical trials. However, advances in technology are helping to overcome these hurdles. Improved extraction techniques, synthetic biology approaches, and enhanced analytical methods are paving the way for more comprehensive and detailed studies of flavonoids.
Recent breakthroughs in synthetic biology, for instance, allow for the production of flavonoids in microbial hosts, which could lead to more consistent and scalable production methods. This is crucial for conducting large-scale clinical trials and for the eventual commercialization of flavonoid-based therapeutics.
5. Personalized Medicine and Future Directions
The future of cannabis flavonoid research lies in personalized medicine. By understanding individual responses to different flavonoid profiles, researchers can develop tailored treatments that maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing side effects. This approach could revolutionize the way we treat conditions like chronic pain, inflammation, and neurological disorders.
Moreover, continued research is essential to fully elucidate the mechanisms of action of flavonoids and their long-term effects. Expanding clinical trials to include diverse populations and conditions will provide a more comprehensive understanding of their potential applications. Regulatory frameworks will also need to evolve to support the development of flavonoid-based therapies, ensuring that they meet rigorous standards of safety and efficacy.
6. Regulatory and Quality Control Considerations
As the field progresses, there is a growing need for standardized testing protocols and stringent quality control measures in the production of flavonoid-rich cannabis products. This ensures that consumers and patients receive products that are both safe and effective. Regulatory bodies will play a crucial role in facilitating research and development while maintaining high standards for product quality and safety.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Cannabis flavonoids represent a frontier in both plant science and medicinal research. Their multifaceted roles in plant physiology and their broad therapeutic potential underscore their importance. As research continues to advance, flavonoids could play a pivotal role in the development of new, more effective treatments for a range of health conditions. Embracing the complexity of these compounds and understanding their interactions within the plant matrix will unlock new possibilities in both natural and medical sciences. The path forward is one of continued exploration and innovation, with the promise of significant breakthroughs on the horizon.
By fostering a deeper understanding of flavonoids, we can unlock their full potential and harness their benefits for both plant health and human medicine, ultimately paving the way for a future where the therapeutic use of cannabis is optimized and personalized to meet the needs of individual patients. This holistic approach will not only improve treatment outcomes but also enhance our overall understanding of the intricate biochemistry of cannabis.