
Treat Your Glaucoma with Medical Cannabis: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
A major global cause of irreversible blindness, glaucoma affects millions of people, especially those over 60. It is typified by optic nerve injury, which is frequently linked to increased intraocular pressure (IOP). While traditional treatments focus on reducing IOP to prevent further optic nerve damage, recent research has highlighted the potential role of medical cannabis in managing glaucoma symptoms. This guide will delve into the medical use of cannabis for glaucoma, emphasizing scientific insights, patient outcomes, and potential therapeutic advantages, while avoiding any discussion of recreational use or consumption methods.
Understanding Glaucoma
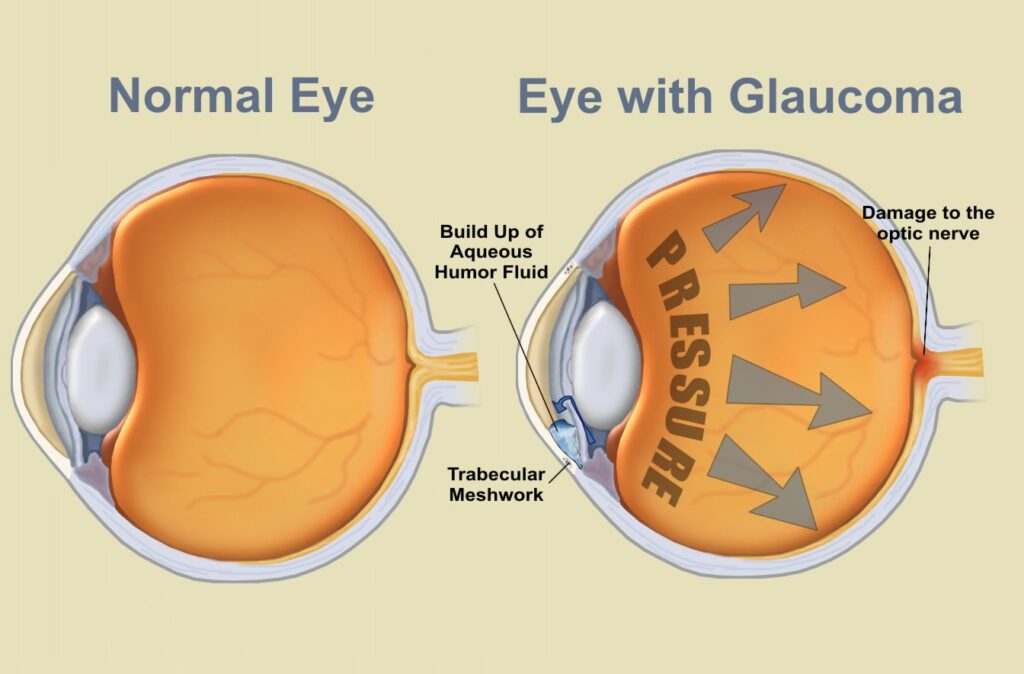
Glaucoma is a collection of eye disorders that can cause damage to the optic nerve rather than a single illness. The most common variety, open-angle glaucoma, develops slowly over time and frequently has no visible symptoms in its early stages. Patients may eventually develop peripheral vision loss as the condition worsens, which, if ignored, can result in total blindness.
Although it can also happen with normal eye pressure, elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is the main cause of glaucoma. The increased pressure damages the optic nerve, impairing the brain’s ability to process visual information. Current treatments, such as eye drops, oral medications, laser therapy, or surgery, aim to lower IOP. But not everyone responds well to these medicines, and some people may have unfavorable side effects.
The Role of Cannabis in Glaucoma Treatment
The exploration of medical cannabis as a treatment for glaucoma began in the 1970s when studies suggested that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), a compound found in cannabis, could lower intraocular pressure. These early findings ignited interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabis for glaucoma patients.
Medical cannabis contains over 100 cannabinoids, with THC and cannabidiol (CBD) being the most studied. These compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cell-signaling system that plays a role in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain sensation, and, importantly, eye pressure. CB1 and CB2 receptors, which are present in the eyes as well as other parts of the body, are the receptors in the extracellular matrix (ECS) that cannabinoid binds to.
THC and Intraocular Pressure Reduction
THC is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, but its medicinal properties have been the subject of intense study, particularly in glaucoma research. Studies have shown that THC can reduce intraocular pressure by up to 25-30% in some patients, making it comparable to some traditional glaucoma medications. It works by relaxing the muscles in the eye, allowing for better fluid drainage, which in turn lowers IOP.
Although THC is effective at reducing IOP, its effects are typically short-lived, lasting only three to four hours. This short duration poses a challenge for long-term management, as glaucoma patients need consistent IOP control to prevent optic nerve damage. However, ongoing research is exploring how THC can be integrated into treatment regimens to provide more sustained relief.
CBD and Neuroprotection
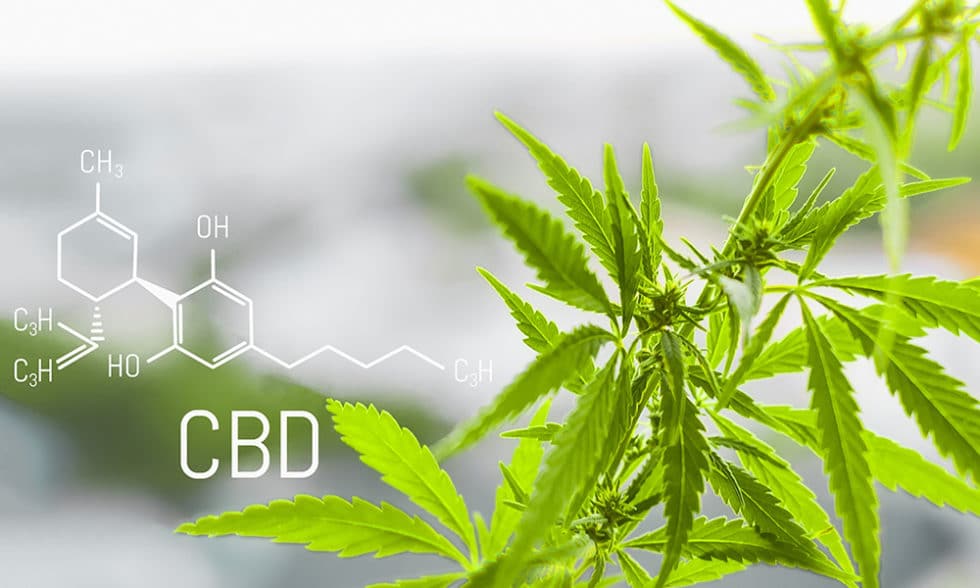

While THC’s ability to lower IOP has garnered attention, CBD, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, offers another therapeutic angle. The neuroprotective qualities of CBD have been investigated; these findings are especially pertinent to glaucoma patients. In glaucoma, damage to the optic nerve is a significant concern. CBD’s potential to protect nerve cells from oxidative stress and inflammation could help slow the progression of the disease, preserving vision for longer periods.
Moreover, CBD’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties could mitigate some of the secondary damage associated with glaucoma. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress play a role in worsening optic nerve damage, so CBD’s ability to modulate these factors could be a game-changer for patients.
Cannabinoid Receptor Activity in the Eye
The discovery of cannabinoid receptors in the eye has provided crucial insights into how cannabis affects eye health. CB1 receptors, in particular, are found in the ciliary body, retina, and corneal epithelium—key areas involved in the regulation of intraocular pressure and visual function. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they can influence the production and outflow of aqueous humor, the fluid responsible for maintaining eye pressure.
This receptor activity suggests that cannabinoids, particularly THC, could offer a targeted approach to managing IOP. Furthermore, CB2 receptors control inflammation and immunological responses, despite being less common in the eye. This dual action on both IOP and inflammation could provide a comprehensive therapeutic strategy for glaucoma patients.
Scientific Research and Studies
The body of research supporting the use of medical cannabis for glaucoma is growing. The effects of THC and CBD on rats’ ocular pressure were examined in a more recent study that was published in the Journal of Glaucoma. The researchers found that while THC significantly reduced IOP, CBD alone did not have the same effect. However, when combined with THC, CBD seemed to enhance the overall neuroprotective effects, indicating a possible synergistic relationship between the two cannabinoids.
Other studies have focused on the role of topical cannabinoids in treating glaucoma. Researchers have developed eye drops containing THC and other cannabinoids to target eye pressure directly. Preliminary results have been promising, showing that these formulations can reduce IOP without the psychoactive effects associated with systemic cannabis use.
While more clinical trials are needed, the current body of research suggests that medical cannabis could serve as a viable option for glaucoma patients, particularly those who do not respond well to conventional treatments.
Potential Benefits of Medical Cannabis for Glaucoma Patients
1. Reduction of Intraocular Pressure
The most significant benefit of medical cannabis for glaucoma patients is its ability to lower intraocular pressure. This is important since the main risk factor for injury to the optic nerve and loss of vision is excessive IOP. Cannabis presents a viable alternative for those whose IOP has not decreased enough with conventional therapy.
2. Neuroprotective Effects
In addition to lowering IOP, cannabis, particularly CBD, may offer neuroprotective benefits that help preserve optic nerve health. This could slow the progression of glaucoma and protect against further vision loss. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, cannabinoids may help shield the delicate structures of the eye from damage.
3. Alternative for Non-Responders to Conventional Treatment
Some glaucoma patients do not respond well to traditional treatments, such as beta-blockers or prostaglandin analogs. For these patients, medical cannabis may provide a new avenue for managing their condition. The dual action of cannabinoids—reducing IOP and protecting the optic nerve—makes it a potentially valuable addition to glaucoma treatment protocols.
4. Fewer Side Effects Compared to Some Medications
Traditional glaucoma medications can cause side effects such as dry eyes, blurred vision, and even systemic effects like shortness of breath or heart palpitations. Medical cannabis, particularly in controlled dosages, may offer a more tolerable side effect profile for some patients. However, the psychoactive effects of THC must be carefully managed, particularly in elderly patients.
5. Customization and Personalization
One of the strengths of medical cannabis is its versatility. Different strains and formulations can be tailored to the individual needs of patients, providing a more personalized approach to treatment. For example, patients who are sensitive to THC can use high-CBD formulations to avoid psychoactive effects while still benefiting from the neuroprotective properties of cannabis.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, the use of medical cannabis for glaucoma is not without challenges. These include legal, clinical, and practical issues that must be addressed to optimize its use in patient care.
1. Legal Restrictions
The legal status of medical cannabis varies widely by country and even by state or region. While some areas have embraced cannabis as a legitimate medical treatment, others continue to impose strict regulations. Patients and healthcare providers must navigate these legal hurdles to ensure that cannabis can be safely and legally incorporated into glaucoma treatment.
2. Short Duration of Action
As mentioned earlier, THC’s effects on intraocular pressure are relatively short-lived. This means that patients may need to take it multiple times per day to maintain consistent IOP reduction. This poses a challenge for those seeking long-term control of their condition, particularly if traditional treatment options are not effective.
3. Limited Clinical Trials
While preclinical studies and anecdotal evidence are promising, large-scale clinical trials investigating the use of medical cannabis for glaucoma are still lacking. To find the best strains, doses, and formulations for glaucoma sufferers, more study is required. The absence of comprehensive clinical guidelines means that physicians must rely on limited evidence when recommending cannabis for glaucoma.
4. Potential Side Effects
While medical cannabis is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, particularly in high doses or in sensitive populations. These may include dry mouth, dizziness, or, in the case of THC, psychoactive effects. It is crucial for glaucoma patients, particularly elderly individuals, to work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor for any adverse effects.
5. Interactions with Other Medications
Patients who are already taking medications for glaucoma or other conditions should be aware of potential interactions with cannabis. For example, cannabis can enhance the effects of certain drugs, such as sedatives or blood pressure medications. Conversely, it may reduce the effectiveness of other treatments. A thorough review of all medications and careful coordination with healthcare providers is essential.
Future Directions in Research and Treatment
With the growing popularity of medical cannabis, there is hope for novel glaucoma therapies. Advances in cannabinoid research may lead to the development of novel treatments that combine the IOP-lowering effects of THC with the neuroprotective properties of CBD. Additionally, ongoing research into topical cannabinoid formulations could provide more targeted treatments that reduce IOP without the need for systemic cannabis use.
Researchers are also exploring the potential of synthetic cannabinoids, which may offer more predictable and consistent effects compared to plant-based cannabis. These compounds could be engineered to target specific receptors in the eye, providing a more precise approach to glaucoma management.
Restrictions on Using Medical Cannabis as a Last Resort for Treatment
Medical cannabis is often considered a last resort treatment for patients who do not respond to conventional therapies. Several restrictions exist around its use, primarily due to concerns over safety, efficacy, and regulatory guidelines:
- Regulatory Approval: In many countries, medical cannabis is only permitted after exhausting all other treatment options. Physicians must provide documentation proving that conventional treatments were ineffective before prescribing cannabis.
- Strict Prescription Guidelines: Physicians are often required to follow stringent protocols, including prescribing only certain strains or formulations of cannabis that have been approved for medical use.
- Special Patient Populations: Medical cannabis may be restricted for vulnerable populations, such as children, elderly patients, or those with psychiatric conditions, due to the risk of psychoactive side effects.
- Monitoring Programs: In many jurisdictions, medical cannabis prescriptions are closely monitored by health authorities to ensure compliance with legal and medical standards.
Monitoring THC Levels in Medications to Prevent Psychoactive Effects
To prevent the psychoactive effects associated with THC, especially in patients who are sensitive to these effects, several measures are implemented:
- Low-THC or CBD-Dominant Formulations: Medications with minimal THC content or those rich in CBD are often preferred, as CBD does not cause psychoactive effects. These formulations offer therapeutic benefits without impairing cognitive function.
- Regular THC Testing: Medical cannabis products undergo stringent testing to ensure THC levels remain within prescribed limits. Regulatory bodies often mandate specific thresholds for THC content to minimize psychoactivity.
- Personalized Dosing: Physicians may tailor THC doses based on a patient’s tolerance level and medical condition, minimizing the risk of psychoactive effects while maximizing therapeutic outcomes.
- Patient Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of patients for signs of THC-induced psychoactivity is essential. Adjustments to dosage or product formulations can be made to ensure safe use.
Conclusion
The use of medical cannabis in the treatment of glaucoma and other medical conditions is a rapidly evolving area of healthcare, offering potential benefits but also raising critical concerns, particularly when it comes to its application as a last resort. The combination of therapeutic effects, such as intraocular pressure reduction and neuroprotection, makes cannabis a valuable option for patients who have not responded well to traditional treatments. However, the implementation of medical cannabis as a treatment option, particularly in sensitive conditions like glaucoma, requires thorough understanding, strict regulations, and careful monitoring.
Glaucoma, a major cause of irreversible blindness, has long been treated through medications and surgical interventions aimed at reducing intraocular pressure (IOP). However, for many patients, these conventional treatments are not enough, and they are left seeking alternatives. This is where medical cannabis comes into play. Research has shown that cannabinoids, particularly THC, have the ability to lower IOP, thus slowing the progression of optic nerve damage and vision loss. Meanwhile, CBD offers neuroprotective benefits by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which can further damage the optic nerve.
The cannabinoids found in cannabis interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), particularly through CB1 and CB2 receptors located in the eyes. This interaction allows cannabis to not only lower eye pressure but also offer anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. These attributes make cannabis an attractive treatment for glaucoma, especially for patients who do not respond well to traditional therapies. Despite its potential, cannabis is not yet a widespread treatment for glaucoma due to several concerns regarding its psychoactive properties, short duration of effect, and regulatory barriers.
One of the primary challenges with medical cannabis, particularly THC, is its short duration of action. In glaucoma, the reduction of IOP lasts only a few hours, meaning that patients would need frequent dosing to maintain therapeutic levels. This poses practical issues, particularly when considering the psychoactive effects of THC, which could interfere with daily activities. Furthermore, more research is required to fully understand the long-term benefits and potential risks of using medical cannabis to treat glaucoma.
In addition to these logistical issues, there are significant restrictions on the use of medical cannabis as a last resort in treatment protocols. Many countries and regions impose strict regulations that require healthcare providers to exhaust all conventional treatments before considering cannabis. The idea behind this restriction is that cannabis should be reserved for cases where other treatments have proven ineffective or intolerable, ensuring that it is used only when absolutely necessary. Physicians must provide thorough documentation and follow prescribed guidelines when recommending cannabis, particularly to vulnerable populations like children, elderly patients, or those with psychiatric conditions. In these groups, the psychoactive effects of THC could be more harmful than beneficial.
To further mitigate the risks associated with THC, healthcare systems emphasize the importance of monitoring THC levels in medical cannabis products. Low-THC or CBD-dominant formulations are often favored, especially for patients who are more susceptible to psychoactive effects. CBD, unlike THC, does not produce a “high,” making it a safer option for long-term use in sensitive populations. Testing and regulation of THC levels in medications are strictly enforced in many regions to ensure that patients receive the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without the psychoactive side effects. These testing protocols are critical in maintaining the safety and effectiveness of medical cannabis as a legitimate treatment option.
Moreover, personalized treatment plans are essential in the medical use of cannabis. Each patient’s response to cannabinoids can vary, and healthcare providers must tailor treatment plans to minimize risks while maximizing benefits. By regularly monitoring patients and adjusting doses or formulations, physicians can help reduce the likelihood of adverse effects, including the psychoactive effects of THC. This level of care and customization underscores the importance of a carefully monitored and patient-centered approach when using medical cannabis.