Table of Contents
Santa Maria, also known by the moniker “Planck,” is a sativa-dominant hybrid with deep roots in Amazonian spirituality and modern cannabis culture. Santa Maria is unique properties make it an appealing strain for both medical and recreational users. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of its genetics, cannabinoid profile, terpenes, effects, and potential applications with a focus on scientific detail.
Genetics and Phytochemical Foundation
Santa Maria originates from Amazonian landrace strains, historically used in spiritual rituals by indigenous tribes. To stabilize its genetics and broaden its application, it was crossbred in the Netherlands with Mexican Haze and Silver Pearl, two strains renowned for their robust cannabinoid and terpene production. The outcome is a strain that has:
- Sativa dominance (approximately 75% sativa, 25% indica)
- Short flowering period, unusual for sativa-dominant plants
- High resilience to environmental stressors like mold and pests
Santa Maria is now cultivated globally under controlled conditions to ensure genetic consistency and chemical composition.
Chemical Composition
Cannabinoids
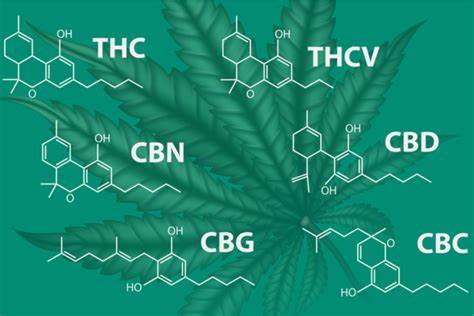
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol):
- Concentrations: 12–14% (moderate potency)
- Mechanism of Action: THC acts as a partial agonist of CB1 receptors in the central nervous system, promoting euphoria and increased energy.
- Effects: Responsible for the strain’s uplifting psychoactivity without overwhelming sedation.
- CBD (Cannabidiol):
- Concentrations: ~1%
- Role: Moderates THC’s psychoactivity, providing subtle anxiolytic and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- CBG (Cannabigerol):
- Trace amounts found in Santa Maria.
- Precursor molecule for THC and CBD biosynthesis.
- CBC (Cannabichromene):
- Present in trace quantities.
- Synergistic with THC for anti-inflammatory effects via interaction with TRPV1 receptors.
Terpenes
Santa Maria’s distinct aroma and therapeutic properties are largely attributed to its terpene profile. Major terpenes include in Santa Maria:
- Limonene:
- Concentration: ~0.3–0.8%
- Properties: Citrus aroma; anxiolytic and antidepressant effects through modulation of serotonin receptors.
- Mechanism: Enhances THC absorption via the entourage effect.
- Humulene:
- Concentration: ~0.2–0.6%
- Properties: Woody and earthy notes; potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Mechanism: Inhibits the production of cytokines and inflammatory mediators.
- Caryophyllene:
- Concentration: ~0.5–1.0%
- Properties: Spicy, peppery aroma; acts as a dietary cannabinoid by binding directly to CB2 receptors.
- Role: Provides analgesic and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Ocimene:
- Concentration: ~0.1–0.3%
- Properties: Sweet, herbal scent; antifungal and antiviral properties.
- Mechanism: May act on peripheral cannabinoid receptors to reduce fatigue.
- Myrcene:
- Concentration: ~0.2–0.7%
- Properties: Sedative and relaxing effects, though less dominant in this sativa-dominant strain.
Pharmacology and Mechanisms of Action
Santa Maria’s effects result from a synergy of cannabinoids and terpenes, often referred to as the entourage effect. Below are its scientifically observed mechanisms:
- Neurological Effects:
- THC’s interaction with CB1 receptors stimulates dopamine release in the mesolimbic pathway, promoting euphoria and enhanced focus.
- Limonene and ocimene modulate serotonin and dopamine pathways, contributing to mood enhancement.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
- Caryophyllene and humulene inhibit the NF-κB pathway, reducing inflammatory responses.
- These effects are beneficial for conditions such as arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
- Energy Boost:
- Sativa-dominant cannabinoids stimulate cerebral blood flow, potentially improving cognitive function and reducing fatigue.
- Appetite Regulation:
- THC’s activation of the hypothalamic CB1 receptors increases the production of ghrelin, the “hunger hormone.”
Medical Applications
Santa Maria has shown promise in treating a variety of conditions, supported by anecdotal and preliminary clinical evidence:

- Mental Health:
- Depression: Limonene and THC collectively elevate mood and promote a sense of well-being.
- Stress: Caryophyllene’s interaction with CB2 receptors alleviates physiological stress responses.
- Anxiety: At lower doses, the strain provides calming effects without over-stimulation.
- Pain Management:
- Useful for chronic pain, migraines, and muscle spasms due to its moderate THC and caryophyllene content.
- Mechanism: Inhibition of nociceptive signaling in the peripheral nervous system.
- Fatigue:
- The energizing properties of its sativa-dominance make it ideal for combating lethargy and promoting focus.
- Appetite Stimulation:
- Especially helpful for patients who are battling eating disorders or receiving chemotherapy.
- Inflammatory Conditions:
- Terpene-driven anti-inflammatory effects may help conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Recreational Uses
Santa Maria is prized for its balanced, clear-headed high, making it a favorite among recreational users who prefer productivity-enhancing strains:

- Creativity and Focus:
- Ideal for artistic endeavors and brainstorming.
- THC’s cerebral effects combined with limonene’s mood-enhancing properties stimulate creative thinking.
- Social Interactions:
- Promotes lightheartedness and sociability.
- Moderate THC levels prevent the overwhelming effects that some high-potency strains can induce.
- Physical Activities:
- Enhances motivation and energy, making it a suitable pre-workout strain.
Potential Side Effects
While Santa Maria is well-tolerated, users may experience some adverse effects:
- Dry Mouth (Cottonmouth):
- THC’s interaction with submandibular glands reduces saliva production.
- Dry Eyes:
- Due to vasodilation caused by THC.
- Paranoia or Anxiety:
- Higher doses may overstimulate CB1 receptors, especially in individuals predisposed to anxiety.
- Dizziness:
- Caused by a temporary drop in blood pressure due to THC’s vasodilatory properties.
Santa Maria, a sativa-dominant hybrid, has distinct cultivation requirements and characteristics that make it aappealing variety for producers of all skill levels. Below is a detailed examination of its cultivation process, optimal conditions, and expected yields.
1. General Cultivation Characteristics
It is well-suited for a variety of cultivation methods due to its hardy genetics and relatively short flowering time for a sativa-dominant strain.
- Plant Type: Sativa-dominant hybrid (approximately 75% sativa, 25% indica).
- Growth Structure:
- Medium height: Typically reaches 100–150 cm (3–5 feet) indoors and up to 2 meters (6–7 feet) outdoors.
- Bushy with lateral branching, ideal for training methods like Screen of Green (ScrOG) or Low-Stress Training (LST).
- Produces dense, resin-rich buds with a high calyx-to-leaf ratio, simplifying post-harvest trimming.
2. Growth Cycle and Flowering Time
Growth Phases

- Germination:
- Time: 2–7 days.
- Optimal Conditions: Humidity at 70–90%, temperature at 22–25°C (71–77°F).
- Vegetative Stage:
- Duration: 4–8 weeks, depending on cultivation goals.
- Lighting: Requires 18–24 hours/day under grow lights indoors.
- Nutrient Needs: High nitrogen levels during this phase to support vigorous foliage growth.
- Growth Rate: Rapid vertical and lateral growth, making pruning or training essential.
- Flowering Stage:
- Duration: 8–9 weeks indoors, harvest-ready by early October outdoors in temperate climates.
- Light Cycle: Requires 12 hours of uninterrupted darkness to induce flowering indoors.
- Nutrient Needs: Requires increased phosphorus and potassium during flowering to support bud formation.
3. Environmental Requirements
Santa Maria thrives in both indoor and outdoor environments, but optimal growth depends on maintaining precise environmental conditions:
Indoor Cultivation
- Lighting: Full-spectrum LED or HID grow lights with at least 600W output.
- Temperature:
- Vegetative phase: 22–26°C (72–79°F).
- Flowering phase: Slightly cooler, 20–24°C (68–75°F), to enhance terpene production.
- Humidity:
- Vegetative phase: 60–70%.
- Flowering phase: Reduced to 40–50% to prevent mold and mildew.
- Ventilation:
- Requires good airflow to prevent mold on its dense buds.
- Inline fans and carbon filters for odor control are recommended.
- Yield: Average yield of 400–450 grams per square meter under optimal conditions.
Outdoor Cultivation
- Climate:
- Prefers warm, temperate climates with ample sunlight (Mediterranean-like conditions).
- Ideal temperatures: 20–30°C (68–86°F).
- Soil:
- Nutrient-rich, well-drained soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5.
- Amend with organic compost or fertilizers rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Watering:
- Requires moderate but consistent watering, avoiding over-saturation to prevent root rot.
- Yield: Higher outdoor yields of 500–600 grams per plant, depending on care and environmental factors.
4. Advanced Cultivation Techniques
Low-Stress Training (LST)
- Involves creating an even canopy by bending and tying down branches.
- Promotes light penetration to lower bud sites, increasing overall yield.
Screen of Green (ScrOG)
- Trains plants horizontally using a screen.
- Maximizes bud production by exposing multiple colas to light.
Defoliation
- Removing excess fan leaves during flowering improves airflow and light penetration.
- Particularly effective for Santa Maria, which tends to develop dense foliage.
Hydroponic Growth
- Santa Maria responds well to hydroponic systems such as Deep Water Culture (DWC) or nutrient film techniques (NFT).
- Santa Maria faster growth and higher yields are achievable, but these systems require meticulous monitoring of nutrient solutions and pH levels.
5. Yield Expectations
Indoor Yield
- Average Yield: 400–450 grams/m².
- Factors Affecting Yield:
- Lighting intensity and spectrum.
- Use of training techniques.
- Nutrient schedule and plant health.
Outdoor Yield
- Average Yield: 500–600 grams per plant.
- Factors Affecting Yield:
- Sunlight exposure and weather conditions.
- Soil quality and watering schedule.
6. Pests and Disease Resistance
Santa Maria is a resilient strain but may still face common cannabis cultivation challenges:
- Pests:
- Vulnerable to spider mites, whiteflies, and aphids.
- Preventative Measures: Regularly inspect plants and use organic insecticides like neem oil.
- Diseases:
- Resistance: Moderate resistance to powdery mildew and botrytis (bud rot).
- Prevention: Make sure there is enough airflow and stay away from high humidity.
7. Post-Harvest Processing
Harvest Timing
- Trichome Maturity:
- Harvest when trichomes are cloudy with a slight amber hue for balanced effects.
- Optimal time of day: Early morning before photosynthesis increases moisture content in the buds.
Drying
- Temperature: 18–22°C (65–72°F).
- Humidity: Maintain 50–60% RH to prevent overdrying.
- Duration: 7–14 days for proper drying.
Curing
- Process:
- Place dried buds in airtight containers (glass jars recommended).
- Open containers daily during the first week for air exchange (“burping”).
- Duration: 2–4 weeks for optimal flavor and potency.
8. Scientific Insights on Yield Maximization
- Light Intensity:
- Increasing light intensity (e.g., using 1000W lights) can boost yields but requires precise temperature management to avoid heat stress.
- CO₂ Enrichment:
- Adding CO₂ to the grow environment (800–1200 ppm) enhances photosynthesis and growth, potentially increasing yields by up to 20–30%.
- Terpene and Cannabinoid Enhancement:
- Reducing night temperatures during the final two weeks of flowering encourages terpene production, enhancing the strain’s aromatic profile.
- Flushing:
- Flush plants with pure water 1–2 weeks before harvest to remove excess nutrients, improving flavor and smoke quality.
9. Phenotypic Variations
Santa Maria exhibits minimal phenotypic variability due to its stabilized genetics, ensuring consistency in growth and chemical composition. However, slight differences in height or bud density may arise based on growing conditions.
Methods of Ingestion of Santa Maria
Santa Maria cannabis strain can be consumed through various methods, each offering unique pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and onset of effects. Below is a detailed analysis of these methods:
1. Smoking
Smoking is the most traditional and widely used method of cannabis consumption.
- Mechanism:
- Combustion heats the plant material to release active cannabinoids and terpenes as smoke.
- THC and other cannabinoids rapidly enter the bloodstream through alveoli in the lungs.
- Onset:
- Effects begin within 2–5 minutes due to the high bioavailability (approximately 30%).
- Peak effects occur within 20–30 minutes, lasting up to 2–3 hours.
- Advantages:
- Immediate feedback for dosing.
- Rapid onset allows users to titrate their dose effectively.
- Disadvantages:
- Combustion produces tar and other carcinogens, potentially irritating respiratory pathways.
- Loss of some cannabinoids and terpenes due to high combustion temperatures (>600°F).
2. Vaping
Cannabis is heated through vaporization to a temperature that releases terpenes and cannabinoids without burning.
- Mechanism:
- Heating to 315–440°F (157–226°C) activates cannabinoids and terpenes while preserving their integrity.
- Inhalation delivers compounds directly into the bloodstream via alveoli.
- Onset:
- Effects manifest within 2–3 minutes, similar to smoking.
- Bioavailability is slightly higher (35–50%), and effects last for 2–4 hours.
- Advantages:
- Decreased exposure to toxic combustion byproducts.
- More efficient use of cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires specific equipment (vape pens or desktop vaporizers).
- Potential for unknown long-term effects with certain vape liquids.
3. Edibles
Cannabis-infused food or drink products allow for oral ingestion.
- Mechanism:
- Cannabinoids are metabolized by the liver, converting delta-9 THC into 11-hydroxy-THC, a more potent and long-lasting psychoactive compound.
- Absorption occurs through the gastrointestinal tract, with delayed onset.
- Onset:
- Effects begin within 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the user’s metabolism, food intake, and individual tolerance.
- Peak effects occur after 2–4 hours and can last up to 6–8 hours.
- Advantages:
- Discreet and easy to use.
- Longer-lasting effects compared to inhalation methods.
- Disadvantages:
- Difficult to titrate dosage due to delayed onset.
- Risk of overconsumption leading to uncomfortable or prolonged psychoactive effects.
4. Sublingual Administration
Tinctures, sprays, or lozenges are applied under the tongue for absorption through sublingual capillaries.
- Mechanism:
- Direct absorption into the bloodstream bypasses the digestive system and first-pass liver metabolism.
- Cannabinoids and terpenes remain intact and rapidly accessible.
- Onset:
- Effects begin within 15–30 minutes, with peak effects at 1–2 hours.
- Duration is shorter than edibles, lasting approximately 3–5 hours.
- Advantages:
- Rapid onset without inhalation.
- Dosing is easier to regulate than with edibles.
- Disadvantages:
- Some users find the taste of tinctures unpleasant.
- Requires precise dosing to avoid overconsumption.
5. Topical Application
Cannabis-infused creams, balms, or transdermal patches allow for localized or systemic absorption through the skin.
- Mechanism:
- Cannabinoids bind to CB2 receptors in the skin and underlying tissues, providing localized relief without psychoactive effects.
- Transdermal patches can deliver cannabinoids into the bloodstream for systemic effects.
- Onset:
- Localized effects occur within 15–30 minutes, lasting up to 6 hours.
- Systemic effects via transdermal patches may take 1–2 hours to onset.
- Advantages:
- Non-psychoactive when used topically.
- Beneficial for skin disorders, inflammation, or localized pain.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited use for recreational effects.
- Slow onset with transdermal applications compared to inhalation.
6. Dabbing
Dabbing involves vaporizing concentrated cannabis extracts using a dab rig or similar device.
- Mechanism:
- High temperatures (500–700°F) instantly vaporize the concentrate, delivering a potent dose of cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Absorption occurs through the lungs.
- Onset:
- Effects are almost immediate (within seconds), peaking at 10–15 minutes and lasting 2–3 hours.
- Advantages:
- High potency allows for quick and intense effects.
- Preserves terpene profiles for a rich sensory experience.
- Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for novice users due to its intensity.
- Demands exact temperature control and sophisticated equipment.
Onset of Effects: A Detailed Timeline
Santa Maria’s effects vary based on the method of ingestion. Below is a general timeline for onset, peak, and duration of effects:
| Method | Onset | Peak Effects | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking | 2–5 minutes | 20–30 minutes | 2–3 hours |
| Vaping | 2–3 minutes | 20–30 minutes | 2–4 hours |
| Edibles | 30–120 minutes | 2–4 hours | 6–8 hours |
| Sublingual | 15–30 minutes | 1–2 hours | 3–5 hours |
| Topical (localized) | 15–30 minutes | Not applicable | 6 hours (localized) |
| Dabbing | Seconds | 10–15 minutes | 2–3 hours |
Effects Based on Ingestion Method
Santa Maria’s effects are largely determined by its cannabinoid and terpene profiles, as well as the consumption method:
- Smoking/Vaping:
- Energetic and uplifting effects dominate.
- Enhanced focus, creativity, and sociability are quickly noticeable.
- Edibles:
- Effects are more sedative and body-centered due to the formation of 11-hydroxy-THC.
- A slower onset but longer-lasting experience suitable for evening use or sustained relief.
- Sublingual:
- Balanced effects with moderate psychoactivity.
- Suitable for users seeking relief without prolonged waiting times.
- Topical:
- Non-psychoactive and localized relief for pain and inflammation.
- Does not affect mood or cognition.
- Dabbing:
- Intense cerebral effects.
- Suitable for experienced users seeking a potent and immediate high.
Factors Influencing Effects and Onset
Several variables affect how Santa Maria’s effects manifest:
- Individual Metabolism:
- Faster metabolism leads to quicker onset and shorter duration (particularly relevant for edibles).
- Tolerance Levels:
- Higher dosages may be necessary for regular cannabis users to get the results they want.
- Terpene Profile:
- Terpenes like limonene and caryophyllene modulate the strain’s uplifting and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Dosing:
- Smaller doses often promote mild euphoria and focus, while larger doses can lead to sedation or heightened psychoactivity.
Conclusion
Santa Maria’s scientifically validated cannabinoid and terpene profile offers a versatile experience for both medical and recreational users. Its moderate THC levels, combined with a balanced terpene composition, provide uplifting and energizing effects suitable for various applications. Additionally, its straightforward cultivation makes it an excellent choice for growers aiming for consistent quality. Future studies may further elucidate its therapeutic potential, especially in mood disorders and inflammatory conditions.
For a complete directory of cultivars, visit our Cannabis Strain Reviews.