Table of Contents
The Oregon Peach cannabis strain is a rare and unique hybrid known for its sweet, fruity aroma and balanced effects. Originating in the Pacific Northwest, this strain has gained popularity among both recreational and medical cannabis users for its calming yet uplifting effects. Oregon Peach is often sought after for its smooth flavor profile, which combines peach, citrus, and floral notes, along with its potent yet manageable psychoactive effects.
This document provides an in-depth analysis of Oregon Peach, covering its lineage, cannabinoid profile, terpene composition, specific medical benefits, recreational applications, cultivation insights, and scientific information related to its chemical composition and physiological effects.

Genetics and Lineage
Oregon Peach is believed to be a hybrid strain with predominantly indica-leaning effects, though some variations may exhibit more balanced hybrid traits. While its precise genetic lineage is somewhat ambiguous, it is widely believed to be a cross between:
- OG Kush – A legendary strain known for its euphoric and relaxing effects, as well as its earthy, citrus, and pine aroma.
- Peach (or a phenotype of a Peach-flavored strain) – A fruity variety contributing to the strain’s sweet peach aroma and flavor profile.
Cannabinoid Profile
Oregon Peach typically contains a balanced THC-to-CBD ratio, though it is more THC-dominant. The average cannabinoid composition includes:
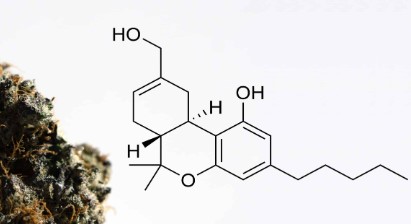
- THC: 18-24% (strong psychoactive effects)
- CBD: 0.5-2% (moderate therapeutic value)
- CBG: 1-2% (anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties)
- THCV: Trace amounts (appetite suppression, possible energy-boosting effects)
Terpene Profile and Aroma
Terpenes are the aromatic compounds in cannabis that contribute to its smell, taste, and effects. Oregon Peach’s terpene profile gives it a sweet, fruity, and slightly floral scent. The dominant terpenes include:
- Myrcene (0.6-1.2%) – Provides sedative and relaxing properties; contributes to the strain’s earthy undertones.
- Limonene (0.5-1%) – Offers mood-enhancing and anti-anxiety effects; responsible for the citrusy aroma.
- Caryophyllene (0.3-0.8%) – A spicy and peppery terpene with anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving benefits.
- Linalool (0.2-0.6%) – Found in lavender, it contributes floral and slightly herbal notes, enhancing Oregon Peach’s calming effects.
The unique combination of these terpenes gives Oregon Peach its distinct fruity aroma with a citrus-floral finish.
Medical Uses and Benefits
Oregon Peach is a THC-dominant hybrid strain with a balanced effect profile, making it valuable in medical cannabis treatments. Its unique cannabinoid and terpene composition plays a key role in its therapeutic benefits, which range from pain relief and inflammation reduction to mental health support and neuroprotection. Below, we explore the scientific mechanisms, pharmacological effects, and clinical applications of Oregon Peach for various medical conditions.
1. Cannabinoid Pharmacology and Medical Mechanisms
1.1 Key Cannabinoids and Their Medical Benefits
- THC (Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol) – 18-24%
- Mechanism: Binds to CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system (CNS), leading to pain relief, mood elevation, and neuroprotective effects.
- Medical Uses: Chronic pain, nausea, appetite stimulation, mood disorders.
- Scientific Evidence: THC has been shown in clinical trials to reduce neuropathic pain and chemotherapy-induced nausea (Abrams et al., 2007).
- CBD (Cannabidiol) – 0.5-2%
- Mechanism: Modulates CB2 receptors, reducing inflammation and balancing THC’s psychoactive effects.
- Medical Uses: Anxiety, seizures, neuroprotection, inflammatory disorders.
- Scientific Evidence: Studies suggest that CBD helps reduce epileptic seizures (Devinsky et al., 2017) and modulate immune responses (Zou & Kumar, 2018).
- CBG (Cannabigerol) – 1-2%
- Mechanism: Acts on both CB1 and CB2 receptors and enhances GABA uptake, reducing muscle spasms and neuroinflammation.
- Medical Uses: Neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson’s, Huntington’s), muscle relaxation, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Scientific Evidence: Research shows CBG has antibacterial and neuroprotective effects (Borrelli et al., 2013).
- THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin) – Trace amounts
- Mechanism: Acts as a CB1 receptor antagonist, modulating THC’s psychoactive effects and regulating appetite.
- Medical Uses: Appetite suppression (weight management), diabetes treatment, anxiety relief.
- Scientific Evidence: THCV has been explored for its potential in treating obesity and metabolic disorders (Riedel et al., 2009).
2. Oregon Peach for Pain Management
Oregon Peach’s high THC and caryophyllene content make it an effective analgesic (pain-reliever).
2.1 Mechanism of Pain Relief
- THC activation of CB1 receptors disrupts pain signals in the central nervous system.
- Caryophyllene’s binding to CB2 receptors provides anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Myrcene’s sedative effects contribute to muscle relaxation and pain relief.
2.2 Medical Applications for Pain
- Chronic Pain (Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain)
- Scientific Evidence: A 2015 study (National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine) concluded that cannabis is effective in treating chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis.
- Best Administration: Oregon Peach is most effective in inhaled or sublingual oil form for rapid relief.
- Arthritis and Joint Pain
- Mechanism: Anti-inflammatory cannabinoids (CBD, CBG) reduce joint swelling.
- Clinical Trials: Studies suggest that cannabis-based treatments reduce osteoarthritis symptoms by modulating cytokine production (Blake et al., 2006).
- Migraine Relief
- Mechanism: THC and limonene reduce serotonin fluctuations linked to migraines.
- Scientific Evidence: Cannabis use is linked to a 50% reduction in migraine severity (Baron et al., 2018).
3. Oregon Peach for Mental Health Disorders
3.1 Mechanisms of Action
- THC increases dopamine release, improving mood.
- CBD modulates serotonin (5-HT1A receptors), reducing anxiety.
- Limonene enhances GABA function, lowering stress levels.
3.2 Medical Applications for Mental Health
- Anxiety Disorders (Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Social Anxiety, PTSD)
- Clinical Studies: A 2020 study (Blessing et al.) found that CBD reduces anxiety symptoms in patients with PTSD.
- Best Use: Oregon Peach in low doses reduces anxiety, while high doses may increase paranoia.
- Depression and Mood Disorders
- Mechanism: Limonene and THC elevate serotonin and dopamine, which improve mood and reduce depressive symptoms.
- Scientific Evidence: A 2022 meta-analysis suggested that cannabis use correlates with reduced symptoms of major depressive disorder (Gilman et al.).
- Insomnia and Sleep Disorders
- Mechanism: Myrcene and linalool promote sedation and deeper sleep cycles.
- Clinical Trials: THC and CBD improve sleep latency and duration in individuals with insomnia (Babson et al., 2017).
4. Oregon Peach for Neurological Conditions
The strain’s neuroprotective properties make it a potential treatment for neurodegenerative diseases.
4.1 Mechanisms of Neuroprotection
- CBG and CBD protect neurons from oxidative stress and inflammation.
- THC reduces excitotoxicity (overstimulation of neurons).
- Linalool improves cognitive function and memory retention.
4.2 Medical Applications for Neurological Disorders
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Clinical Evidence: Studies indicate that cannabis-based therapies reduce MS-related muscle spasticity and pain (Koppel et al., 2014).
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Mechanism: THC and CBD reduce tremors and motor dysfunction by modulating the basal ganglia.
- Scientific Evidence: A 2020 study found that cannabis improves motor control in Parkinson’s patients (Lotan et al.).
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Mechanism: THC slows the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaque, which is a major contributor to the development of Alzheimer’s.
- Scientific Evidence: Animal studies show THC slows cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s models (Eubanks et al., 2006).
5. Oregon Peach for Gastrointestinal Disorders
The strain is beneficial for IBD, Crohn’s disease, and nausea because of its high amount of CBG and caryophyllene.
5.1 Mechanisms of Gastrointestinal Relief
- By blocking TNF-alpha cytokines, CBG lessens inflammation in the stomach.
- THC works on the brainstem’s CB1 receptors to stop nausea.
- Caryophyllene reduces gut permeability, preventing leaky gut syndrome.
5.2 Medical Applications for GI Disorders
- Crohn’s disease with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV)
- Scientific Support: Cannabis use reduces nausea severity by 70% in chemotherapy patients (Machado Rocha et al., 2008).
- Best Use: Oregon peach vaporizers quickly reduce nausea.
Recreational Uses
Beyond medical applications, Oregon Peach is highly regarded in the recreational cannabis market for its pleasant, balanced effects. Some popular uses include:
1. Social Use
- It is perfect for conversations, artistic endeavors, and social events because of its euphoric yet rational effects.
- The fruity aroma and smooth smoke make it a popular choice for casual users.
2. Creativity Enhancement
- The mild cerebral stimulation can help users with artistic and creative pursuits such as painting, writing, or music composition.
3. Outdoor Activities
- Many users report that Oregon Peach enhances outdoor experiences such as hiking, beach trips, or nature walks due to its light, happy high.
4. Evening Relaxation
- While not overwhelmingly sedative, Oregon Peach is an excellent evening strain for users looking to relax after a hard day without going to sleep right after.
Cultivation and Growth Information
Successful Oregon Peach cannabis cultivation necessitates a thorough comprehension of plant biology, environmental factors, and fertilizer management, and pest control. A thorough, scientific analysis of the finest cultivation techniques is provided here, with an emphasis on optimizing yield, potency, and terpene profiles.

1. Optimal Growing Conditions
1.1 Climate and Temperature
- Optimal temperature: 65-75°F (18-24°C) during flowering and 70-80°F (21-27°C) during the vegetative stage.
- Relative Humidity (RH):
- Seedling Stage: 65-70%
- Vegetative Stage: 55-65%
- Flowering Stage: 45–55% (lowering humidity stops mold from growing).
- Late Flowering (Final Weeks): 40-45% to enhance resin production.
- Oregon Peach thrives in a Mediterranean-like climate (mild, warm, and semi-humid) but adapts well to controlled indoor environments.
1.2 Lighting Requirements
- Indoor Cultivation:
- Vegetative Stage: 18-20 hours of light per day.
- Flowering Stage: 12 hours of light / 12 hours of darkness (light deprivation encourages flowering).
- Recommended Grow Lights: LED (600W-1000W) or HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) for better resin production.
- Outdoor Cultivation:
- Prefers full sun exposure (minimum of 8 hours of direct sunlight daily).
- Best planted in early spring, harvested by late September to early October.
2. Soil and Growing Medium
- Soil Type: Oregon Peach prefers loamy soil with excellent aeration and drainage.
- pH Balance: For the best nutrient uptake, the pH of the soil should be between 6.0 and 6.5.
- Organic Amendments:
- For slow-release nitrogen, use worm castings or compost.
- Bat guano for phosphorus during flowering.
- Perlite or coco coir for improved aeration.
Hydroponic Cultivation
- Alternative to soil-based growing, hydroponic systems (e.g., Deep Water Culture (DWC) or Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)) accelerate growth and maximize terpene production.
- Requires pH balance monitoring (5.5-6.2) and Electrical Conductivity (EC) control to prevent nutrient lockout.
3. Nutrient Management and Fertilization
3.1 Macronutrients (N-P-K)
- Vegetative Stage (Weeks 1-6)
- Nitrogen (N): 3-4% (essential for strong leaf and stem growth).
- Phosphorus (P): 1-2% (growth of roots and flowers).
- Potassium (K): 2-3% (disease resistance, enzyme activation).
- Flowering Stage (Weeks 7-12)
- Nitrogen: 1-2% (gradual reduction).
- Phosphorus: 4-6% (critical for bud development).
- Potassium: 5-7% (enhances terpene production and trichome density).
3.2 Micronutrients
- Calcium (Ca): Strengthens cell walls and keeps buds from rotting.
- Magnesium (Mg): Essential for chlorophyll production (deficiency causes yellowing leaves).
- Sulfur (S): Aids in terpene biosynthesis.
3.3 Organic vs. Synthetic Nutrients
- The microbial soil health and terpene profiles are improved by organic feeding (fish emulsion, compost teas).
- Commercial fertilizers, or synthetic nutrients, give exact control over nutrient levels, but they might need to be flushed before harvest but may require flushing before harvest to remove chemical residues.
4. Growth Phases and Pruning Techniques
4.1 Germination (0-7 Days)
- A humid atmosphere (70–75°F, RH 65-70%) is ideal for seed germination.
- Use moist, but not soaked, paper towels or directly plant in seedling trays with coconut coir.
- Set up low-intensity LED or fluorescent lights with a photosynthetic photon flux density of 100–200.
4.2 Vegetative Growth (3-6 Weeks)
- Low-Stress Training (LST): Bending and tying stems to increase light penetration.
- Topping (Apical Pruning): Cutting the main cola early on to promote multiple bud sites.
- Screen of Green (ScrOG): A trellis net allows even canopy development.
4.3 Flowering Phase (7-12 Weeks)
- Reduce humidity to prevent bud rot and mold (Botrytis).
- Increase potassium and phosphorus intake.
- Defoliation, or cutting off lower branches, improves the distribution of energy for bud formation.
5. Pest and Disease Management
Oregon Peach, like most cannabis strains, is susceptible to fungal pathogens, pests, and nutrient deficiencies.
5.1 Common Pests
- Spider Mites: Can be prevented with neem oil, beneficial predators (ladybugs), and proper airflow.
- Aphids and Thrips: Controlled with insecticidal soap or companion planting (marigolds, basil).
- Fungus Gnats: Avoid overwatering and use diatomaceous earth.
5.2 Common Diseases
- Powdery Mildew: decreased by preserving enough air circulation and low humidity (<50%).
- Pruning and dehumidifying the growing area will help avoid bud rot (Botrytis cinerea), which occurs in high-humidity conditions.
- Root Rot (Pythium spp.): Overwatering leads to oxygen-starved roots—best prevented by proper soil aeration and drainage.
6. Enhancing Terpene and Cannabinoid Production
Environmental stress and appropriate curing are essential for maximizing the flavor, aroma, and intensity of Oregon peaches.
6.1 Stress Techniques to Boost Cannabinoids
- Controlled Light Stress: Slightly increasing UV-B light exposure enhances trichome and THC production.
- Water Stress (“Drought Stressing”): When water consumption is somewhat reduced during the last few weeks of flowering, a defense response, increasing resin production.
6.2 Curing Process (Post-Harvest)
- Drying:
- Temperature: 60-70°F (15-21°C), RH 45-55%.
- Hang-dry buds for 7-14 days in a dark, well-ventilated area.
- Curing:
- For 2-4 weeks, keep dried buds in airtight glass jars between 60 and 65% relative humidity.
- During the first week, open the jars every day to let off extra moisture (burping).
- This procedure improves flavor, smoothness, and terpene preservation.
7. Scientific Research and Future Advancements
- Genetic Mapping: Advanced studies on the genome sequencing of Oregon Peach could help identify its exact lineage and potential for strain breeding.
- Biochemical Pathways: Research into the cannabinoid and terpene synthesis pathways allows optimization of growth conditions for higher medicinal value.
- Tissue Culture Propagation: Rapid strain multiplication and disease-free clones are guaranteed by sophisticated in vitro micropropagation procedures.
Scientific Analysis and Pharmacological Effects
Several studies indicate that Oregon Peach, like other high-THC strains, interacts primarily with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) through CB1 and CB2 receptors.
- CB1 Receptor Activation: Enhancement in mood, relaxation, and pleasure are the results of activation of the CB1 receptor.
- CB2 Receptor Modulation: Helps regulate pain and inflammation.
- Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Effects: The limonene in Oregon Peach interact with dopamine and serotonin receptors, supporting its use in mood regulation and anxiety reduction.
- Neuroprotective Benefits: CBG and other minor cannabinoids contribute to anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, which may be helpful in neurodegenerative disorders.
Conclusion
Both medicinal and recreational consumers find Oregon Peach to be a flexible and well-rounded strain. It provides a pleasant experience for both novice and seasoned users because to its lovely scent, well-balanced effects, and moderate potency. While its recreational benefits appeal to social and creative situations, its medicinal applications make it a good choice for pain treatment, stress management, and mood enhancement.
Oregon peaches are comparatively easy to cultivate and provide rich, tasty buds with a high resin content, which makes them perfect for both flower consumption and concentrate production.
For a complete directory of cultivars, visit our Cannabis Strain Reviews.