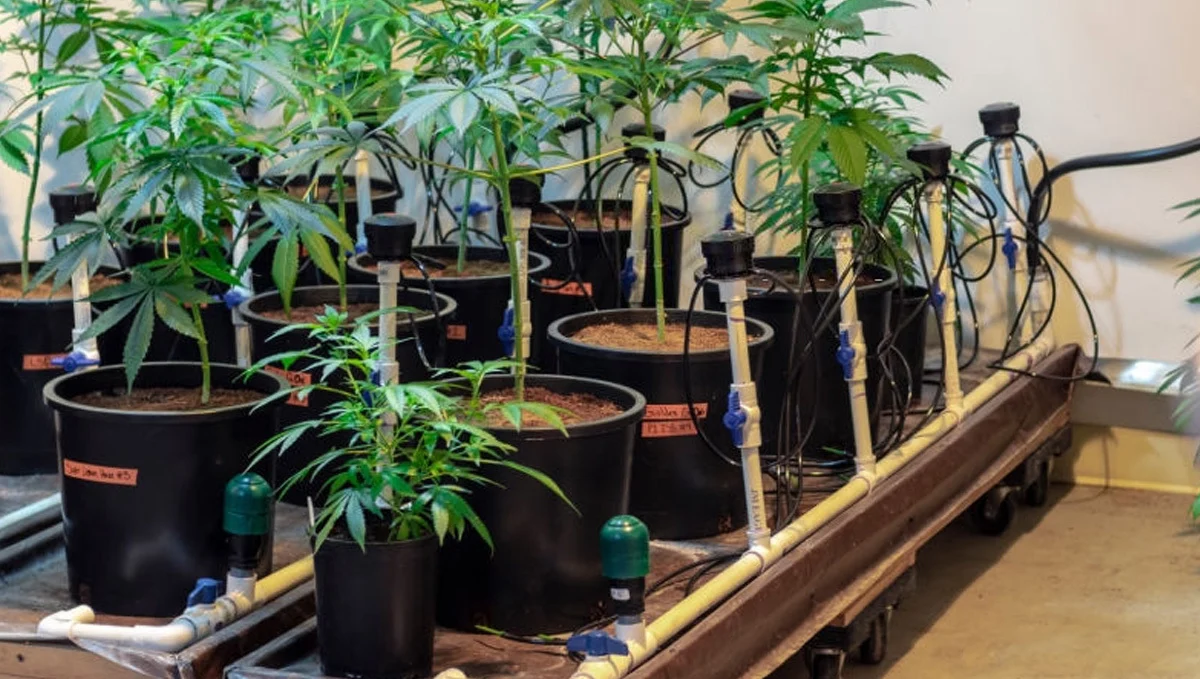

How to Install a Hydroponic Growing System for Medical Cannabis Plants
Introduction to Hydroponics
With the use of mineral fertilizer solutions in a water solvent, hydroponics is a cutting-edge technique for growing plants without soil. This approach allows plants to receive nutrients directly to their roots, leading to faster growth rates, higher yields, and more efficient resource use compared to traditional soil-based gardening. As a result, hydroponics has become an increasingly popular method for cultivating a wide variety of crops, including medical cannabis.
Historical Background

It is not a novel idea to grow plants without soil. Ancient civilizations like the Babylonians and Aztecs practiced early forms of hydroponics. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon and the floating gardens of the Aztecs are examples of early hydroponic systems. Modern hydroponics began to take shape in the 20th century, with significant advancements in the 1930s by Dr. William F. Gericke at the University of California, who coined the term “hydroponics” from the Greek words “hydro” (water) and “ponos” (labor).
Advantages of Hydroponics for Growing Medical Cannabis
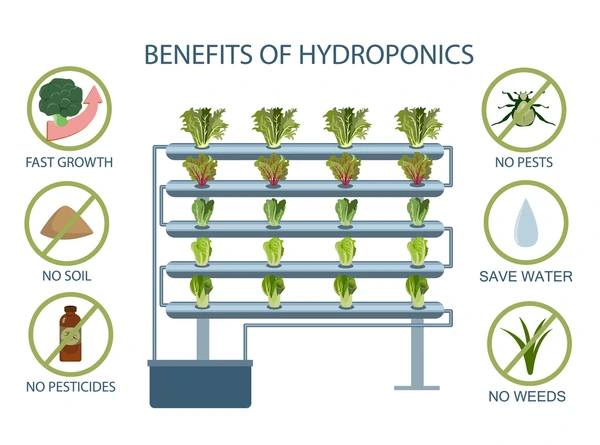
Hydroponics offers several advantages over traditional soil-based growing methods, making it a popular choice for cultivating medical cannabis. Here’s a detailed look at the benefits of hydroponics:
1. Faster Plant Growth
Direct Nutrient Delivery:
- Nutrients are supplied straight to the roots of plants in hydroponic systems by dissolving them in water and doing so instantly. This eliminates the need for roots to search through soil, accelerating growth.
Optimal Nutrient Uptake:
- Precise control over nutrient concentration and availability allows plants to absorb what they need when they need it, promoting faster and more efficient growth.
Improved Oxygenation:
- Systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC) and Aeroponics provide roots with high levels of oxygen, enhancing root health and overall plant vitality. Oxygenated roots can absorb nutrients more effectively, leading to rapid growth.
2. Higher Yields
Controlled Environment:
- Hydroponic systems are often used in controlled environments like grow tents or greenhouses, where factors such as light, temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels can be precisely regulated. This control creates optimal growing conditions, resulting in higher yields.
Maximized Space Utilization:
- Hydroponic setups can be designed to use vertical space efficiently, allowing for more plants to be grown in a given area. Techniques like vertical farming and stacked systems increase the number of plants per square foot.
Continuous Harvesting:
- With hydroponics, it’s possible to implement a perpetual harvest system, where plants are at different stages of growth. This ensures a continuous supply of mature plants ready for harvest, maximizing yield over time.
3. Water Efficiency
Recirculating Systems:
- Many hydroponic systems, such as Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and Ebb and Flow, recirculate water, significantly reducing water waste. Excess water is collected and reused, making these systems more sustainable.
Reduced Evaporation:
- In a controlled environment, water loss due to evaporation is minimized compared to outdoor soil-based growing. Hydroponics systems are designed to retain moisture, further conserving water.
Targeted Water Delivery:
- Water is sent straight to the roots of the plants, which minimizes runoff and guarantees that the plants get just the right amount of water, improving water efficiency.
4. Pest and Disease Control
Soilless Growing Medium:
- Without soil, many soil-borne pests and diseases are eliminated. This reduces the need for pesticides and minimizes the risk of root diseases like pythium (root rot).
Controlled Environment:
- Indoor hydroponic systems provide a controlled environment that is less accessible to pests. Using grow tents or greenhouses with proper filtration and entry protocols can significantly reduce pest infestations.
Easier Monitoring and Management:
- Hydroponic systems allow for easy monitoring of plant health. Any signs of pest or disease can be quickly identified and addressed, preventing widespread issues.
5. Nutrient Control and Efficiency
Precision Feeding:
- Cannabis plants have varied needs at different stages of growth, and growers can adjust the fertilizer solution to meet those needs. With this accuracy, plants are guaranteed to receive the ideal ratio of nutrients for their vegetative growth, flowering, and fruiting.
Minimized Nutrient Waste:
- Nutrients are delivered in a dissolved form, reducing the risk of nutrient lockout and ensuring efficient uptake by plants. Excess nutrients can be recirculated and reused, minimizing waste.
Customizable Nutrient Solutions:
- Hydroponic growers can easily adjust the nutrient solution composition to correct deficiencies or imbalances, ensuring plants remain healthy and productive.
6. Space Efficiency
Compact Systems:
- Hydroponic systems can be designed to fit into small or irregular spaces, making them ideal for urban environments or indoor growing.
Vertical Farming:
- Techniques such as vertical farming allow for the cultivation of multiple layers of plants within the same footprint, significantly increasing production capacity without expanding the grow area.
Scalability:
- Hydroponic systems can be easily scaled up or down to fit the available space and production needs, providing flexibility for growers of all sizes.
7. Environmental Benefits
Reduced Pesticide Use:
- The controlled environment and absence of soil reduce the need for chemical pesticides, leading to cleaner, more sustainable growing practices.
Lower Water Consumption:
- Hydroponics uses significantly less water than traditional soil-based growing, making it an environmentally friendly option, particularly in regions with water scarcity.
Sustainable Practices:
- Many hydroponic systems incorporate sustainable practices such as using renewable energy sources, recycling water, and composting plant waste, contributing to overall environmental conservation.
8. Year-Round Growing
Controlled Climate:
- No matter the outside weather, hydroponic systems can be installed indoors or in greenhouses to provide year-round growing. This ensures a consistent supply of medical cannabis.
Extended Growing Seasons:
- By manipulating light cycles and environmental conditions, growers can extend the growing season and produce multiple harvests per year, maximizing productivity.
9. Enhanced Plant Health
Optimal Root Environment:
- Hydroponic systems provide a consistently ideal environment for root growth, with proper oxygenation, moisture, and nutrient levels. Healthy roots lead to robust and resilient plants.
Stress Reduction:
- Plants grown hydroponically experience less stress from factors like drought, nutrient deficiencies, and soil compaction. Reduced stress translates to healthier, more vigorous plants.
Higher Cannabinoid Production:
- The controlled environment and optimized nutrient delivery in hydroponic systems can lead to higher levels of cannabinoids and terpenes in cannabis plants, enhancing their medicinal properties.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing a Hydroponic System for Medical Cannabis Plants
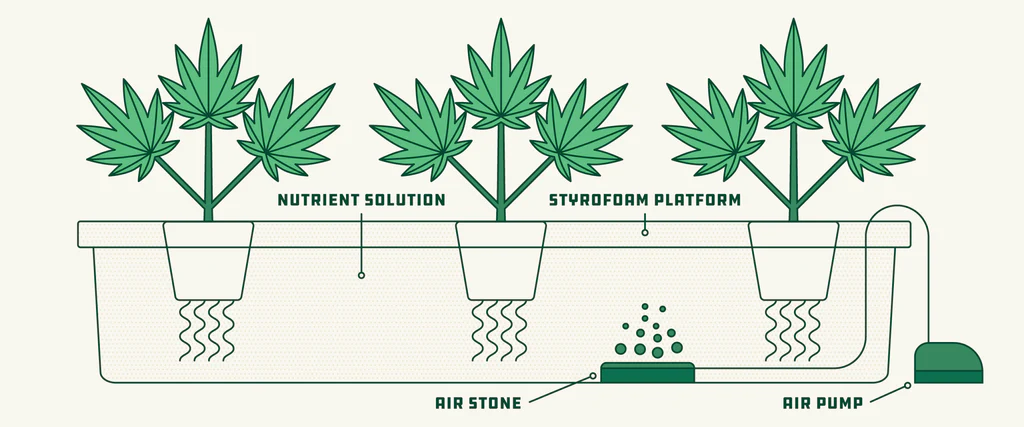
Setting up a hydroponic system for growing medical cannabis involves several critical steps. This detailed guide will take you through each phase, ensuring a successful installation and operation of your hydroponic system.
1. Choosing the Right Hydroponic System
Types of Hydroponic Systems:
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants’ roots are suspended in nutrient-rich water. Ideal for beginners due to its simplicity.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of nutrient solution flows over the roots. Suitable for small plants.
- Drip System: Every plant has a nutrient solution dripped onto its base. Versatile and supports larger plants.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain): Periodically floods the grow area with nutrient solution and then drains it away. Good for larger setups.
- Aeroponics: Roots are misted with nutrient solution while suspended in the air. Offers high oxygen levels and rapid growth but is more complex.
Recommended System for Beginners: Deep Water Culture (DWC)
2. Gathering Equipment and Supplies
Essential Equipment:
- Grow Tent or Grow Space: Choose a dedicated area or tent with enough space for plants and equipment. Grow tents offer a regulated setting.
- Lighting: LED grow lights are recommended due to their energy efficiency and full-spectrum light output.
- Hydroponic System Kit: Includes containers, air pumps, air stones, net pots, and growing medium.
- Nutrient Solution: Specifically formulated for cannabis, ensuring all essential nutrients are provided.
- pH and EC Meters: to keep an eye on and modify your nutrient solution’s pH and electrical conductivity.
- Ventilation System: Inline fans and carbon filters to manage temperature and odor.
- Timers: For automating light and nutrient cycles.
- Growing Medium: Options include clay pebbles, rockwool, and coco coir, depending on the system.
3. Setting Up the Grow Space
Step-by-Step Setup:
- Select a Location: Choose a secure, easy-to-clean space with access to electricity and water.
- Install the Grow Tent: Assemble the grow tent as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure it is stable and lightproof.
- Set Up Lighting: Hang LED grow lights inside the tent. Adjust the height to be 18-24 inches above the plants. Ensure the lights are adjustable to accommodate plant growth.
- Ventilation System: Install inline fans and carbon filters for proper airflow and odor control. Ensure there’s an intake and exhaust system to maintain optimal temperature (70-85°F) and humidity (40-60%).
- Hydroponic System Placement: Place the DWC setup inside the grow tent. Position air pumps and air stones to ensure proper oxygenation of the nutrient solution.
4. Preparing the Nutrient Solution
Mixing the Solution:
- Fill the Reservoir: Fill with water, preferably filtered or distilled, to avoid impurities.
- Add Nutrients: Follow the nutrient manufacturer’s instructions. Start with the base nutrients, then add any supplements as needed.
- Adjust pH: Cannabis prefers a pH range of 5.5-6.5. To monitor and change pH using pH up or down solutions, use a pH meter.
- Check EC: Ensure the electrical conductivity (EC) is within the recommended range for cannabis, usually between 1.2-2.0 mS/cm.
5. Planting and Growing Cannabis
Starting from Seeds or Clones:
- Seeds: Germinate seeds using the paper towel method or directly in rockwool cubes. Once sprouted, transfer to net pots filled with a growing medium like clay pebbles.
- Clones: Place clones directly into net pots with the growing medium.
Transferring to the Hydroponic System:
- Insert Net Pots: Place net pots into the DWC system, ensuring roots are exposed to the nutrient solution.
- Oxygenate Solution: Turn on air pumps and air stones to provide oxygen to the roots.
Growth Stages:
- Vegetative Stage: Provide 18-24 hours of light daily. Monitor and maintain nutrient levels, pH, and EC. Keep temperatures between 70-85°F and humidity around 60%.
- Flowering Stage: Switch to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness to induce flowering. Adjust the nutrient solution to support blooming. Lower humidity to 40-50%.
6. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular Maintenance:
- Daily Checks: Monitor pH, EC levels, water temperature, and plant health.
- Nutrient Solution: Change the solution every 1-2 weeks to prevent nutrient imbalances and pathogen growth.
- Clean Equipment: Regularly clean and sanitize the hydroponic system to prevent algae and bacteria buildup.
Common Issues and Solutions:
- pH Fluctuations: Regularly check and adjust pH levels to prevent nutrient lockout.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Identify and correct deficiencies by adjusting the nutrient mix.
- Root Rot: Ensure adequate oxygenation and maintain water temperature between 65-75°F to prevent root rot.
- Pests and Diseases: Inspect plants regularly and use appropriate treatments if issues arise.
7. Harvesting and Post-Harvest
Harvesting:
- Timing: Harvest cannabis when trichomes are milky white with some amber, indicating peak potency.
- Cutting: Use sterilized scissors to cut plants at the base.
Post-Harvest Processing:
- Trimming: Remove large fan leaves and trim sugar leaves.
- Drying: Hang trimmed plants upside down in a dark, well-ventilated area with 50-60% humidity and 60-70°F temperature.
- Curing: Place dried buds in glass jars, opening daily for the first two weeks to release moisture and then weekly. To improve flavor and potency, cure for a minimum of two to four weeks.
Detailed Steps
Step 1: Setting Up the Grow Tent
Assembling the Tent:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to assemble the grow tent. Typically, this involves connecting metal poles to form the frame and then attaching the fabric covering.
- Ensure all zippers and seams are properly closed to maintain a lightproof environment.
Positioning Equipment:
- Place the hydroponic system in the center of the tent.
- Hang LED lights from the top bars of the tent using adjustable ratchet hangers.
- Position the inline fan and carbon filter system at the top of the tent to manage airflow.
Step 2: Installing the Hydroponic System
Deep Water Culture (DWC) Setup:
- Reservoir Preparation:
- Clean the reservoir thoroughly before use.
- Fill the reservoir with water and mix the nutrient solution according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Use a submersible water pump to keep the solution well-mixed.
- Air System:
- Connect air stones to the air pump using airline tubing.
- Place air stones at the bottom of the reservoir to ensure even oxygen distribution.
- Turn on the air pump to start oxygenating the nutrient solution.
- Net Pots and Growing Medium:
- Fill net pots with the growing medium (e.g., clay pebbles).
- Place seedlings or clones into the net pots, ensuring roots are exposed to the nutrient solution.
Step 3: Lighting and Ventilation
LED Grow Lights:
- Hang the lights about 18-24 inches above the plant canopy.
- Adjust the height as plants grow to maintain the optimal distance.
Ventilation System:
- Connect the inline fan to the carbon filter using ducting.
- Position the fan and filter system to exhaust air outside the grow tent.
- Set up an intake fan or passive intake vents to bring fresh air into the tent.
- Use a hygrometer and thermometer to monitor humidity and temperature inside the tent.
Step 4: Monitoring and Adjusting the System
Daily Checks:
- pH Levels: Use a pH meter to check the nutrient solution daily. Adjust with pH up or down as needed.
- EC Levels: Monitor the electrical conductivity to ensure nutrient concentration is within the optimal range.
- Water Temperature: Keep the water temperature between 65-75°F using an aquarium heater or chiller if necessary.
- Plant Health: Inspect plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies, pests, or diseases.
Nutrient Solution Management:
- Change the nutrient solution every 1-2 weeks.
- Clean the reservoir and replace with fresh nutrient solution to prevent buildup of salts and pathogens.
Step 5: Managing Growth Stages
Vegetative Stage:
- Maintain a light cycle of 18-24 hours of light per day.
- Increase nutrient strength as plants grow.
- Prune plants to promote bushier growth and remove any dead or unhealthy leaves.
Flowering Stage:
- To encourage flowering, convert to a 12/12 light cycle (12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness).
- Adjust nutrient solution to focus on bloom nutrients.
- When you notice any indications of nutrient excess or deficiency, make the necessary adjustments.
Step 6: Harvesting and Curing
Harvest Timing:
- Examine trichomes with a microscope or magnifying lens.
- For maximum effectiveness, harvest when the majority of the trichomes are milky and some have become amber.
Post-Harvest Processing:
- Trimming:
- Trim large fan leaves and sugar leaves from the harvested plants.
- Trim close to the buds for a clean finish.
- Drying:
- Hang trimmed plants upside down in a dark, well-ventilated area.
- Maintain 50-60% humidity and 60-70°F temperature.
- Dry for 7-14 days until stems snap rather than bend.
- Curing:
- Place dried buds in glass jars, filling them about 75% full.
- Open jars daily for the first two weeks to release moisture, then weekly.
- Cure for at least 2-4 weeks to enhance flavor and potency.
Conclusion
Hydroponics represents a transformative approach to agriculture, fundamentally changing the way we cultivate plants by eliminating the need for soil and providing precise control over growing conditions. This method offers numerous advantages, making it particularly suitable for growing medical cannabis, where consistency, potency, and quality are paramount.
Key Benefits of Hydroponics:
- Faster Growth Rates:
- The direct delivery of nutrients to plant roots in a hydroponic system accelerates growth significantly. By optimizing the availability of essential nutrients and oxygen, plants can grow 30-50% faster than those grown in soil.
- Higher Yields:
- Controlled environments ensure that plants receive optimal light, temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels, leading to larger and more robust plants. This control translates to higher yields per plant and more efficient use of space.
- Water Efficiency:
- Hydroponic systems, especially recirculating ones, use less water than traditional soil-based gardening. Water is reused within the system, minimizing waste and making hydroponics a more sustainable option, particularly in areas with water scarcity.
- Pest and Disease Control:
- The risk of diseases and pests carried by soil is decreased when there is no soil. Furthermore, the hydroponic system’s regulated environment makes it simpler to monitor and manage plant health, which further minimizes the need for pesticides and herbicides.
- Precise Nutrient Management:
- Hydroponics allows growers to provide a balanced and customizable nutrient solution tailored to the specific needs of their plants. This precision ensures optimal plant health and growth, avoiding nutrient deficiencies and excesses that can occur in soil.
- Space Efficiency:
- Hydroponic systems can be designed to fit into compact or vertical spaces, maximizing the use of available area. This is particularly beneficial in urban environments or indoor growing setups where space is limited.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Hydroponics provides a more sustainable method of farming by allowing year-round cultivation, lowering the need for pesticides, and consuming less water. The capacity to cultivate food indoors also lessens the carbon footprint of distribution and transportation.
Hydroponics and Medical Cannabis:
For medical cannabis, hydroponics provides a reliable and efficient means of production. The precise control over environmental factors and nutrient delivery ensures that plants develop with consistent cannabinoid profiles and high medicinal quality. Hydroponic systems allow for the cultivation of medical cannabis in controlled indoor environments, ensuring a steady supply regardless of external weather conditions.
Installing a Hydroponic System:
Setting up a hydroponic system involves several key steps:
- Choosing the right type of hydroponic system based on your needs and expertise level.
- Gathering essential equipment, including grow tents, lighting, nutrient solutions, and monitoring tools.
- Setting up the grow space with proper ventilation, lighting, and positioning of the hydroponic system.
- Preparing and maintaining the nutrient solution, ensuring optimal pH and nutrient concentration.
- Planting and managing cannabis plants through their growth stages, from vegetative to flowering.
- keeping an eye on the system and doing routine maintenance to avoid problems like bug infestations, pH imbalances, and nutrient shortages.
- Harvesting and curing the cannabis to ensure maximum potency and quality.
Final Thoughts:
Hydroponics offers a highly efficient and sustainable method for growing medical cannabis. Through the utilization of this soilless growing method, cultivators can attain increased growth rates, better yields, and enhanced plant health. Whether you are a commercial producer or a home grower, hydroponics provides the tools and flexibility needed to cultivate high-quality medical cannabis consistently. With careful planning, setup, and maintenance, a hydroponic system can be a rewarding investment, delivering robust and potent plants while conserving resources and promoting sustainable growing practices.