How to Test c for Cannabis Nutrient Solution: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Growing cannabis involves meticulous attention to detail, and one critical factor in ensuring healthy growth and optimal yields is maintaining the correct pH level of the nutrient solution. The pH level affects nutrient availability, uptake by the plant, and overall plant health. This guide will provide an in-depth understanding of how to test and adjust the pH levels of your cannabis nutrient solution, ensuring you have the knowledge and tools to keep your plants thriving.
Understanding pH and Its Importance
What is pH?

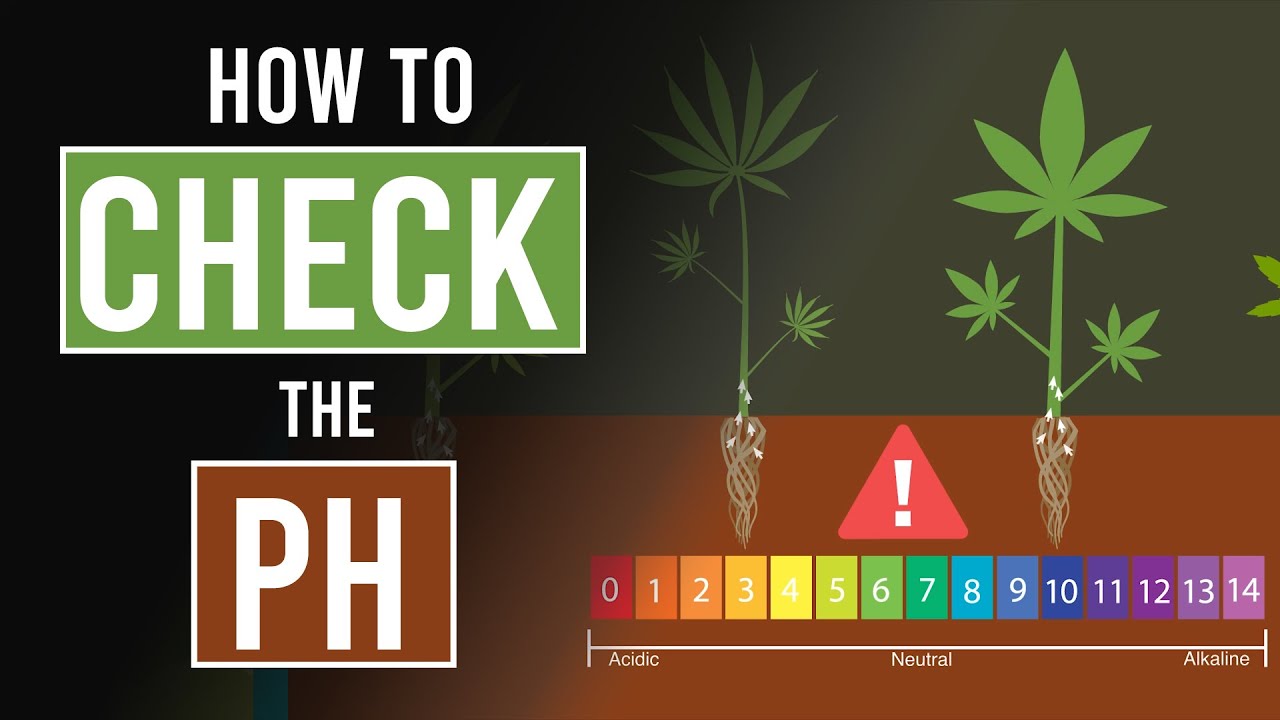
pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. It is an acronym for “potential of hydrogen”. The pH scale has a neutral pH of 7, and a range of 0 to 14. Alkalinity is indicated by numbers above 7, whereas acidity is indicated by values below 7. Because the scale is logarithmic, a tenfold increase or reduction in hydrogen ion concentration is represented by each whole number change. One can observe that, for instance, a pH of 6 is ten times more acidic than a pH of 7, and that a pH of 5 is 100 times more acidic still.
The Importance of pH for Cannabis Growth
pH plays a crucial role in the growth and development of cannabis plants. It has a direct impact on the accessibility and absorption of vital nutrients. If the pH is not within the optimal range, certain nutrients can become unavailable to the plant, leading to deficiencies and poor growth.
Optimal pH Ranges
For cannabis, the optimal pH range varies slightly depending on the growing medium:
- Soil-grown plants: The optimal pH range is 6.0 to 7.0. This range ensures that nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are readily available to the plant.
- Hydroponic and soilless media plants: The optimal pH range is slightly lower, from 5.5 to 6.5. This is because nutrient availability in these media is different from soil.
How pH Affects Nutrient Availability
Nutrients are most available to cannabis plants within specific pH ranges. Here’s a breakdown of how pH affects the availability of major and minor nutrients:
Macronutrients
- Nitrogen (N): Most available in the pH range of 5.5 to 8.0. vital to the general health of the plant and to its vegetative growth.
- Phosphorus (P): Best absorbed in the pH range of 6.0 to 7.5. Crucial for root development and flowering.
- Potassium (K): Most available between pH 6.0 and 8.5. Important for overall plant health and disease resistance.
Micronutrients
- Iron (Fe): Optimal availability in the pH range of 5.0 to 6.5. Necessary for chlorophyll production.
- Manganese (Mn): Best absorbed in the pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. Involved in photosynthesis and enzyme activity.
- Zinc (Zn): Available between pH 5.0 and 7.0. vital for the synthesis of growth hormone and the distance between internodes.
Tools Needed for Testing pH Levels
Testing the pH levels of your cannabis nutrient solution requires specific tools to ensure accuracy and consistency. Here’s a detailed guide on the tools you’ll need and how to use them.
1. pH Meter
Types of pH Meters:
- Digital pH Meter: Provides accurate readings and is easy to use. It requires calibration and proper maintenance.
- pH Pen: A portable version of a digital pH meter. Convenient for quick tests and portable use.
- Continuous pH Monitor: Ideal for hydroponic systems, it continuously monitors pH levels and alerts you to any fluctuations.
Using a Digital pH Meter:
- Calibration: Essential for accuracy. Use calibration solutions (usually pH 4.0 and pH 7.0) to calibrate the meter before use.
- Cleaning: Rinse the electrode with distilled water before and after each use to prevent contamination.
- Measurement: Insert the electrode into the nutrient solution, wait for the reading to stabilize, and record the pH value.
2. pH Test Strips
Types of pH Test Strips:
- Litmus Paper: Basic pH test strips that change color to indicate pH level. They are inexpensive but less precise.
- Advanced pH Test Strips: Provide a more accurate reading by using a broader color range.
Using pH Test Strips:
- Dipping: Dip the strip into the nutrient solution and remove it after the recommended time.
- Color Matching: Compare the strip’s color to the provided color chart to determine the pH level.
- Accuracy: Ensure the strips are stored properly and check expiration dates for accurate results.
3. Liquid pH Test Kits
Components:
- Test Tube: A small container to hold the nutrient solution sample.
- pH Indicator Solution: A liquid reagent that changes color based on the pH of the solution.
- Color Chart: A reference guide to match the resulting color to determine the pH level.
Using a Liquid pH Test Kit:
- Sample Collection: Fill the test tube with a sample of the nutrient solution.
- Adding Indicator: Add a few drops of the pH indicator solution to the sample.
- Mixing: Cap the test tube and shake it to mix the solution thoroughly.
- Color Comparison: Match the resulting color to the provided color chart to determine the pH level.
4. Calibration Solutions
Purpose: Calibration solutions are used to ensure the accuracy of your digital pH meter.
Types:
- pH 4.0 Buffer Solution: Used for acidic calibration.
- pH 7.0 Buffer Solution: Used for neutral calibration.
- pH 10.0 Buffer Solution: Used for alkaline calibration (optional, depending on the pH range you are measuring).
Using Calibration Solutions:
- Calibration Process: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibrating your pH meter. Typically, you will immerse the electrode in the buffer solution and adjust the meter to match the known pH value.
5. Storage Solution
Purpose: To keep the electrode of your pH meter hydrated and functioning properly.
Using Storage Solution:
- Storage: When not in use, store the pH meter electrode in the storage solution to prevent it from drying out.
- Maintenance: Regularly check and replenish the storage solution to ensure the electrode remains in good condition.
6. pH Up and pH Down Solutions
Purpose: To adjust the pH level of your nutrient solution.
Types:
- pH Up Solutions: Typically contain potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate and are used to raise the pH level.
- pH Down Solutions: Typically contain phosphoric acid or nitric acid and are used to lower the pH level.
Using pH Adjusters:
- Adding pH Up or Down: Add a small amount of pH Up or pH Down solution to the nutrient solution.
- Mixing: To guarantee uniform distribution, thoroughly stir the solution.
- Retesting: Test the pH level again after adjustment and repeat if necessary to reach the desired pH range.
7. Distilled Water
Purpose: Used for cleaning the pH meter electrode and for diluting nutrient solutions if needed.
Using Distilled Water:
- Cleaning: Rinse the pH meter electrode with distilled water before and after each use to prevent contamination.
- Dilution: Use distilled water to dilute concentrated nutrient solutions or to prepare calibration solutions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing pH Levels
Testing the pH levels of your cannabis nutrient solution is a crucial process that ensures your plants receive the optimal nutrients for growth. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of testing pH levels using various methods and tools.
1. Preparing Your Equipment
Calibration of pH Meter:
- Why: Calibration ensures the accuracy of your pH meter readings.
- How:
- Turn on the pH meter.
- Rinse the electrode with distilled water to remove any contaminants.
- Dip the electrode into a pH 7.0 buffer solution.
- Adjust the meter to read 7.0 using the calibration controls.
- Rinse the electrode again and dip it into a pH 4.0 buffer solution.
- Adjust the meter to read 4.0 (some meters may also require calibration with a pH 10.0 solution for a three-point calibration).
Checking pH Test Strips:
- Why: Ensure they are not expired and provide accurate readings.
- How:
- Check the expiration date on the test strips.
- Test a strip in a known pH solution to verify accuracy.
- Store strips properly in a cool, dry place.
2. Collecting the Nutrient Solution Sample
Steps:
- After making sure everything is clean, take a sample of your nutrient solution.
- Ensure the solution is well-mixed before taking a sample to get an accurate representation of the entire solution.
- Keep your hands and containers clean to prevent contamination.
3. Testing the pH Level
Using a Digital pH Meter:
- Turn on the meter and ensure it’s calibrated.
- Rinse the electrode with distilled water before use.
- Insert the electrode into the nutrient solution, ensuring it’s fully submerged.
- Stir gently and wait for the reading to stabilize.
- Record the pH reading.
- Rinse the electrode with distilled water after use.
Using pH Test Strips:
- Dip the strip into the nutrient solution for the recommended time (usually a few seconds).
- Remove the strip and wait for the color to develop (typically within 15-30 seconds).
- Compare the strip’s color to the provided color chart to determine the pH level.
- Record the pH reading.
Using a Liquid pH Test Kit:
- Fill the test tube with a small amount of the nutrient solution sample.
- Add the recommended number of drops of pH indicator solution to the test tube.
- Cap the test tube and shake it gently to mix the solution.
- Compare the color of the solution to the provided pH color chart.
- Record the pH reading.
Adjusting pH Levels

Once you have tested the pH levels of your cannabis nutrient solution, you may need to adjust it to ensure it falls within the optimal range for nutrient uptake. Maintaining healthy plant development and preventing nutritional deficits or toxicities need careful pH adjustment. Here’s a detailed guide on how to adjust pH levels effectively.
Understanding pH Adjusters
To adjust the pH of your nutrient solution, you will use pH Up and pH Down solutions. These solutions are designed to raise or lower the pH levels of your nutrient solution to the desired range.
pH Up Solutions:
- Composition: Typically contain potassium hydroxide (KOH) or potassium carbonate (K2CO3).
- Purpose: Used to raise the pH level of the nutrient solution when it is too acidic.
pH Down Solutions:
- Composition: Typically contain phosphoric acid (H3PO4), nitric acid (HNO3), or sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
- Purpose: Used to lower the pH level of the nutrient solution when it is too alkaline.
Steps to Adjust the pH of the Nutrient Solution
1. Test the pH Level:
Before making any adjustments, it is crucial to have an accurate pH reading. Follow the steps outlined in the previous section to test the pH level of your nutrient solution.
2. Calculate the Amount of pH Adjuster Needed:
Start with small increments to avoid over-adjusting. The amount of pH Up or pH Down needed will depend on the initial pH reading and the volume of the nutrient solution.
General Guidelines:
- pH Up: If the pH is slightly below the optimal range, add 1-2 drops of pH Up per gallon of nutrient solution. For larger adjustments, you may need more, but always start with a small amount.
- pH Down: If the pH is slightly above the optimal range, add 1-2 drops of pH Down per gallon of nutrient solution. For larger adjustments, you may need more, but always start with a small amount.
3. Add the pH Adjuster:
- For Liquid Solutions:
- Add a few drops of pH Up or pH Down to the nutrient solution.
- Stir the solution thoroughly to ensure even distribution.
- Retest the pH after a few minutes to see if it has reached the desired level.
- For Powdered Adjusters:
- Dissolve the powder in a small amount of water first to create a liquid solution.
- Add the dissolved solution to the nutrient mix in small increments.
- Stir thoroughly and retest the pH.
4. Mix Thoroughly:
After adding the pH adjuster, stir or agitate the nutrient solution well to ensure that the adjuster is evenly distributed throughout the solution.
5. Retest the pH Level:
Wait a few minutes after mixing, then retest the pH level of the nutrient solution. This step is crucial to ensure that the pH has been adjusted to the desired range.
- Desired pH Ranges:
- Soil-grown plants: 6.0 to 7.0
- Hydroponic and soilless media plants: 5.5 to 6.5
6. Repeat if Necessary:
If the pH level is still not within the desired range, repeat the process by adding small increments of pH Up or pH Down, mixing thoroughly, and retesting until the pH is correct.
Maintaining pH Balance
Maintaining the correct pH balance in your cannabis nutrient solution is crucial for ensuring optimal nutrient uptake and overall plant health. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to maintain pH balance effectively.
1. Regular Testing
To keep your nutrient solution’s pH balance constant, you must test its pH on a regular basis. This helps you detect any fluctuations early and make necessary adjustments before they impact plant health.
Frequency:
- Soil-grown plants: Test the pH every time you water or feed your plants.
- Hydroponic systems: Test the pH daily or every few days, as these systems can experience rapid pH changes.
Method:
- Use a reliable pH meter or pH test strips.
- Always calibrate your pH meter before use to ensure accurate readings.
2. Consistent Monitoring and Logging
Keeping a detailed log of your pH readings and any adjustments you make can help you track trends and anticipate potential issues.
Log Details:
- Date and time of pH testing.
- Initial pH reading.
- Any adjustments made (amount and type of pH Up or pH Down added).
- Final pH reading after adjustment.
3. Stable Nutrient Solution
Using high-quality, stable nutrient solutions designed specifically for cannabis can help maintain a consistent pH balance. These solutions are formulated to stay within the optimal pH range and provide all necessary nutrients.
Tips:
- Choose reputable brands known for producing stable nutrient solutions.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing and using the nutrient solution.
4. Water Quality
The quality of the water you use can significantly impact the pH balance of your nutrient solution. Using filtered or distilled water can help maintain a consistent pH.
Water Quality Tips:
- Filtered Water: Use water that has been filtered to remove impurities and contaminants that can affect pH.
- Distilled Water: Distilled water is free from minerals and other substances that can impact pH, making it a good option for mixing nutrient solutions.
- Avoid Hard Water: Hard water contains high levels of calcium and magnesium, which can affect pH stability.
5. Temperature Control
Temperature fluctuations can affect the pH of your nutrient solution. Maintaining a consistent temperature helps ensure stable pH levels.
Optimal Temperature Range:
- Nutrient Solution: Keep the nutrient solution temperature between 65°F and 75°F (18°C and 24°C).
- Growing Environment: Maintain a stable environment temperature to reduce stress on the plants and nutrient solution.
6. Use of Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions can help stabilize the pH of your nutrient solution, reducing the need for frequent adjustments.
Types of Buffer Solutions:
- Commercial Buffers: Products specifically designed to stabilize pH levels in nutrient solutions.
- Natural Buffers: Adding substances like dolomite lime to the growing medium can help buffer pH levels naturally.
7. Proper Mixing Techniques
Ensuring that your nutrient solution is thoroughly mixed can help maintain a consistent pH.
Mixing Tips:
- Even Distribution: Stir the nutrient solution thoroughly after adding nutrients or pH adjusters to ensure even distribution.
- Mixing Tools: Use clean, non-reactive tools to mix the solution, such as plastic or stainless steel.
Troubleshooting Common pH Issues
Maintaining the correct pH balance in your cannabis nutrient solution is essential for healthy plant growth. However, even with diligent monitoring, you may encounter pH issues that require troubleshooting. This is a thorough guide on recognizing and fixing typical pH issues.
1. pH Drifting
Symptoms:
- The pH level changes significantly between feedings or within a short period.
- Plants exhibit nutrient deficiency symptoms despite proper feeding.
Causes:
- Poor water quality.
- Unstable nutrient solution.
- Incorrect mixing techniques.
Solutions:
- Use High-Quality Water: Ensure you are using filtered or distilled water to prevent contaminants that can cause pH fluctuations.
- Stable Nutrient Solutions: Use reputable, high-quality nutrient solutions designed for cannabis to ensure stability.
- Proper Mixing: Thoroughly mix the nutrient solution to ensure even distribution. Stir the solution well after adding nutrients or pH adjusters.
- Buffer Solutions: Consider adding buffer solutions to stabilize the pH. Products like dolomite lime can help buffer pH levels naturally.
2. Inaccurate pH Meter Readings
Symptoms:
- Inconsistent pH readings.
- pH meter shows error messages or fails to stabilize.
Causes:
- Improper calibration.
- Dirty or damaged electrode.
- Expired calibration solutions.
Solutions:
- Regular Calibration: Calibrate your pH meter regularly using fresh calibration solutions. For precise calibration, adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Clean the Electrode: Rinse the electrode with distilled water before and after each use. For a deeper clean, soak the electrode in a pH electrode cleaning solution.
- Electrode Storage: Store the electrode in a storage solution when not in use to prevent it from drying out and becoming damaged.
3. pH Lockout
Symptoms:
- Nutrient deficiencies (yellowing leaves, stunted growth) despite adequate nutrient feeding.
- pH levels consistently outside the optimal range.
Causes:
- pH levels are too high or too low, causing nutrient lockout.
- Accumulation of salts or other contaminants in the growing medium.
Solutions:
- Flush the System: Flush the growing medium or hydroponic system with pH-balanced water to remove excess salts and contaminants.
- Re-adjust the pH: After flushing, re-adjust the nutrient solution to the correct pH range (6.0-7.0 for soil and 5.5-6.5 for hydroponics).
- Monitor Closely: Closely monitor pH levels after flushing and adjustment to ensure they remain within the optimal range.
4. pH Fluctuations in Hydroponic Systems
Symptoms:
- Rapid changes in pH levels within the hydroponic reservoir.
- Plants exhibit signs of stress or nutrient deficiencies.
Causes:
- Nutrient solution concentration changes.
- Water evaporation or addition.
- Introduction of new nutrients or additives.
Solutions:
- Regular Monitoring: Check pH levels daily in hydroponic systems, as they are more prone to rapid fluctuations.
- Consistent Nutrient Solution: Maintain a consistent concentration of the nutrient solution. Avoid sudden changes in the nutrient mix.
- Top Off with pH-Balanced Water: When topping off the reservoir, use pH-balanced water to minimize fluctuations.
5. Persistent pH Imbalances
Symptoms:
- Continuous difficulty maintaining pH within the optimal range.
- Chronic nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
Causes:
- Poor water quality.
- Inadequate nutrient solution.
- Incorrect use of pH adjusters.
Solutions:
- Assess Water Quality: Ensure you are using high-quality, pH-neutral water. Test the water source for contaminants that could affect pH.
- Evaluate Nutrient Solution: Use a balanced, high-quality nutrient solution specifically designed for cannabis.
- Proper Use of pH Adjusters: Use pH Up and pH Down solutions sparingly and in small increments. Thoroughly mix the solution after each adjustment and retest the pH.
6. Plant-Specific pH Issues
Symptoms:
- Specific plants in your grow space show pH-related issues while others do not.
- Localized nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
Causes:
- Differences in root zone conditions.
- Inconsistent watering practices.
- Variations in growing medium.
Solutions:
- Check Root Zone: Inspect the root zone of affected plants for signs of compacted soil, root rot, or other issues that could affect pH.
- Consistent Watering Practices: Ensure even and consistent watering practices across all plants.
- Uniform Growing Medium: Use a consistent and well-draining growing medium to ensure uniform pH conditions.
Advanced Techniques for pH Management
For serious cannabis cultivators, maintaining optimal pH levels can sometimes require more advanced techniques beyond regular testing and manual adjustments. Here are some advanced methods to help ensure precise and consistent pH management in your grow operation.
1. Automated pH Controllers
Automated pH controllers can continuously monitor and adjust the pH of your nutrient solution, providing a high level of accuracy and reducing the need for manual intervention.
Benefits:
- Continuous Monitoring: Automated systems provide real-time pH monitoring, alerting you to fluctuations as they happen.
- Automatic Adjustments: These systems can automatically add pH Up or pH Down solutions to maintain the desired pH level.
- Consistency: Ensures a stable pH environment, reducing stress on plants and promoting optimal nutrient uptake.
Popular Systems:
- Bluelab pH Controller: A reliable system that automatically adjusts pH levels in your reservoir.
- Autogrow IntelliDose: An advanced system that can manage both pH and nutrient levels, ideal for larger grow operations.
2. Use of Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions can help stabilize the pH of your nutrient solution, making it less prone to fluctuations. These solutions can maintain a more consistent pH level, reducing the need for frequent adjustments.
Types of Buffers:
- Commercial Buffers: Products specifically designed to maintain a stable pH in hydroponic systems.
- Natural Buffers: Substances like dolomite lime or silica, which can naturally buffer pH levels in soil and soilless media.
Application:
- Commercial Buffers: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for dosing and application.
- Natural Buffers: Add to your growing medium or nutrient solution as needed. For example, dolomite lime can be mixed into the soil to help maintain a stable pH.
3. pH Dosing Systems
pH dosing systems are similar to automated pH controllers but are often part of a more comprehensive nutrient management system. These systems can manage pH and nutrient concentrations simultaneously, providing a holistic approach to nutrient management.
Benefits:
- Integrated Management: Manages both pH and nutrient levels, ensuring they are balanced for optimal plant health.
- Scalability: Suitable for both small and large-scale operations.
- Efficiency: Reduces the labor and time required for manual monitoring and adjustments.
Popular Systems:
- Hydroponic Dosing Systems: Systems like the NutriDose or the HydroLogic pH Controller can automate nutrient and pH management.
- Customizable Solutions: Some systems allow for customization and integration with other environmental controls, providing a tailored approach to your specific needs.
4. Advanced pH Metering and Calibration
Using high-end pH meters with advanced features can improve the accuracy and reliability of your pH measurements.
Features to Look For:
- Automatic Calibration: Some advanced pH meters can automatically calibrate themselves using built-in buffer solutions.
- Temperature Compensation: Ensures accurate pH readings by accounting for temperature variations.
- Data Logging: Records pH readings over time, allowing for trend analysis and better decision-making.
Examples:
- Hanna Instruments HI9814: A portable pH, EC, and TDS meter with automatic calibration and temperature compensation.
- Bluelab Combo Meter: Measures pH, conductivity, and temperature, with options for data logging.
5. pH Stability Techniques
Implementing techniques to stabilize the pH can reduce the frequency of adjustments and improve plant health.
Techniques:
- Consistent Nutrient Solutions: Use high-quality, stable nutrient solutions specifically designed for cannabis.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean and maintain your hydroponic system regularly to prevent buildup of salts and other contaminants that can affect pH.
- Optimal Environmental Conditions: Maintain consistent temperature and humidity levels to reduce stress on plants and minimize pH fluctuations.
6. Use of Beneficial Microbes
Beneficial microbes can help stabilize the pH in the root zone by creating a more balanced microenvironment.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Nutrient Uptake: Microbes can improve nutrient availability and uptake, reducing the impact of minor pH fluctuations.
- Disease Resistance: Beneficial microbes can outcompete harmful pathogens, promoting healthier root systems.
- Natural pH Buffering: Some microbes can naturally buffer pH, creating a more stable root environment.
Application:
- Microbial Inoculants: Products like Great White or Mykos can be added to your growing medium or nutrient solution.
- Compost Teas: Brewed compost teas rich in beneficial microbes can be applied to the root zone.
Conclusion
Maintaining the correct pH level in your cannabis nutrient solution is a vital aspect of successful cultivation. The pH level influences the availability and uptake of essential nutrients, directly impacting plant health, growth, and yields. By understanding pH and its importance, using the right tools for testing, and following a systematic approach to testing and adjusting pH levels, you can ensure your plants receive the nutrients they need.
Regular pH testing and adjustment are fundamental practices. Utilizing tools such as digital pH meters, pH test strips, liquid pH test kits, and calibration solutions can help you obtain accurate readings. Proper adjustment using pH Up and pH Down solutions will ensure that your nutrient solution stays within the optimal range, which is crucial for nutrient uptake.
Maintaining pH balance involves consistent monitoring, logging pH readings, using high-quality water and nutrients, controlling the temperature, and employing buffer solutions to stabilize pH levels. Troubleshooting common pH issues like pH drifting, inaccurate readings, pH lockout, and persistent imbalances requires a good understanding of potential causes and solutions.
Advanced techniques for pH management, such as automated pH controllers, pH dosing systems, advanced pH meters with automatic calibration and temperature compensation, pH stability techniques, and the use of beneficial microbes, can provide more precise and consistent control over your growing environment. By ensuring a steady pH, these techniques lessen the need for frequent modifications and improve the general health of the plants.
Incorporating these practices and advanced techniques into your cannabis cultivation routine will lead to healthier plants, better nutrient uptake, and ultimately, higher yields. By staying vigilant and proactive in managing pH levels, you can achieve a successful and productive grow operation.