
How to Identify Sativa and Indica and Their Role in the Medical Field
Introduction
Cannabis, commonly known as marijuana, is a complex plant with a rich history and numerous applications. The two main types of cannabis, Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, exhibit distinct characteristics that influence their effects on the human body. Understanding these differences is crucial, especially in the medical field, where the correct strain can significantly impact treatment outcomes. This detailed guide explores the identification of Sativa and Indica strains and their specific roles in medical applications.
Historical Context and Origins
Cannabis Sativa
Cannabis sativa is believed to have originated in the equatorial regions such as Central America, Africa, and Southeast Asia. The warm climates and long growing seasons in these regions contributed to the development of tall, thin plants with long flowering periods.
Cannabis Indica
Cannabis indica, on the other hand, originated in the colder, mountainous regions of Central Asia, including Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India. The harsher climates and shorter growing seasons in these areas led to the evolution of shorter, bushier plants with shorter flowering periods.
Physical Characteristics

Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica plants exhibit distinct physical characteristics that make them recognizable and distinguishable from each other. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for growers, researchers, and medical professionals to identify and utilize the appropriate strain for various applications.
Cannabis Sativa
Appearance:
- Height and Structure:
- Sativa plants are known for their tall and lanky structure.
- They can grow up to 20 feet (6 meters) in height in optimal outdoor conditions.
- The plants have a more open, airy structure with long, thin branches.
- Leaves:
- Sativa leaves are characterized by their long and narrow shape.
- The leaves typically have a lighter green color compared to Indica.
- Each leaf can have between 5 to 13 leaflets, with serrated edges.
- Flowering and Buds:
- Sativa strains have a longer flowering period, usually taking between 10 to 16 weeks to fully mature.
- The buds of Sativa plants are often less dense and more elongated than those of Indica plants.
- The flowers are usually light and airy, allowing them to withstand humid climates better without mold issues.
Growth Patterns:
- Climate Suitability:
- Sativa plants thrive in warmer climates with long growing seasons.
- They are well-suited for regions near the equator, such as parts of Central America, Africa, and Southeast Asia.
- Yield:
- Due to their size, Sativa plants can produce a large yield, especially when grown outdoors in optimal conditions.
- The open structure allows for better light penetration and air circulation, promoting healthy growth.
Cannabis Indica
Appearance:
- Height and Structure:
- Indica plants are typically shorter and bushier compared to Sativa.
- They usually grow between 3 to 6 feet (1 to 2 meters) in height.
- The plants have a dense, compact structure with thick branches.
- Leaves:
- Indica leaves are broader and wider, with a darker green color.
- The leaves generally have fewer leaflets (5 to 9) than Sativa leaves, but they are wider and more robust.
- The leaflets also have serrated edges.
- Flowering and Buds:
- Indica strains have a shorter flowering period, typically taking between 8 to 12 weeks to mature.
- The buds are denser and more tightly packed compared to Sativa buds.
- Indica flowers tend to be resinous and sticky, often producing higher levels of cannabinoids.
Growth Patterns:
- Climate Suitability:
- Indica plants are well-suited for cooler climates with shorter growing seasons.
- They originated from regions with harsh conditions, such as the mountainous areas of Central Asia, including Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India.
- Yield:
- While Indica plants generally produce a lower yield per plant compared to Sativa, the dense buds often result in a high resin production, making them ideal for producing concentrates and extracts.
- The compact structure allows for efficient use of space, making Indica suitable for indoor growing environments.
Comparative Overview
| Feature | Cannabis Sativa | Cannabis Indica |
| Height | Up to 20 feet | 3 to 6 feet |
| Leaf Shape | Long, narrow leaves | Broad, wide leaves |
| Leaf Color | Lighter green | Darker green |
| Structure | Tall, lanky, open structure | Short, bushy, compact structure |
| Flowering Period | 10 to 16 weeks | 8 to 12 weeks |
| Bud Density | Less dense, more elongated buds | Dense, tightly packed buds |
| Climate Suitability | Warmer climates with long growing seasons | Cooler climates with shorter growing seasons |
| Yield | Higher yield per plant in optimal conditions | Lower yield per plant, but high resin production |
These physical characteristics provide a foundational understanding of how to differentiate between Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica. Recognizing these traits helps growers optimize cultivation techniques and allows medical professionals to identify and recommend the appropriate strain for specific therapeutic purposes.
Chemical Composition
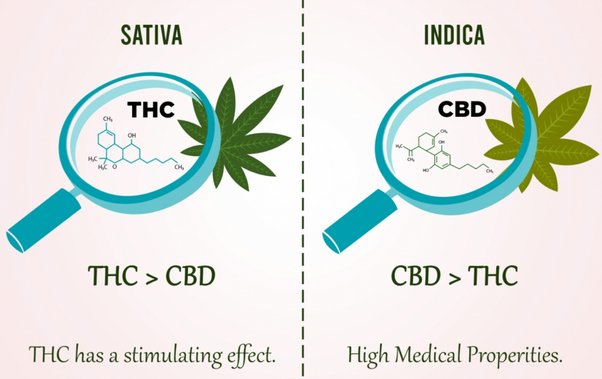
The chemical composition of cannabis is integral to its effects and therapeutic potential. The primary active compounds in cannabis are cannabinoids and terpenes. Understanding the differences in the chemical profiles of Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica is essential for identifying their respective medical benefits and applications.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are the most studied compounds in cannabis, with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) being the most well-known. These compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system in the human body, influencing various physiological processes.
Cannabis Sativa:
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol):
- THC concentration is usually higher in sativa strains.
- The main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, THC, is what gives users a “high.
- Higher THC levels in Sativa contribute to its stimulating and euphoric effects, making it suitable for treating conditions like depression, fatigue, and mood disorders.
- CBD (Cannabidiol):
- Sativa strains generally have lower CBD content compared to Indica strains.
- Being non-psychoactive, CBD has been linked to several possible medical advantages, including anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and anti-seizure qualities.
- The lower CBD content in Sativa strains means they are less likely to produce sedative effects, making them more suitable for daytime use.
Cannabis Indica:
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol):
- Indica strains tend to have lower THC levels compared to Sativa.
- Despite the lower THC content, Indica strains are still effective for pain relief and relaxation due to their overall chemical profile.
- CBD (Cannabidiol):
- Indica strains are typically richer in CBD.
- The higher CBD content enhances the therapeutic effects of Indica strains, particularly for conditions like chronic pain, insomnia, and anxiety.
- CBD can also counteract some of the psychoactive effects of THC, contributing to a more balanced and calming experience.
Terpenes
Aromatic substances called terpenes are what give cannabis its distinct flavor and aroma. They also contribute to the strain’s overall medicinal profile by regulating the effects of cannabinoids.
Common Terpenes in Sativa:
- Limonene:
- Aroma: Citrus.
- Effects: Uplifting, mood-enhancing, anti-anxiety.
- Medical Uses: Depression, anxiety, stress relief.
- Pinene:
- Terpinolene:
- Aroma: Floral, herbal.
- Effects: Energizing, uplifting, antioxidant.
- Medical Uses: Insomnia, antibacterial, antifungal.
Common Terpenes in Indica:
- Myrcene:
- Linalool:
- Aroma: Lavender.
- Effects: Calming, anti-anxiety, sedative.
- Medical Uses: Anxiety, depression, sleep disorders.
- Beta-Caryophyllene:
- Aroma: Spicy, peppery.
- Effects: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, gastroprotective.
- Medical Uses: Pain, inflammation, gastrointestinal issues.
Entourage Effect
The synergistic combination of terpenes and cannabinoids that enhances the overall medicinal effects of cannabis is known as the entourage effect. This concept is critical in understanding why whole-plant cannabis extracts may be more effective than isolated compounds.
Sativa Strains:
- The higher THC content and stimulating terpenes in Sativa strains work together to produce uplifting and energizing effects.
- This combination makes Sativa strains particularly effective for conditions like depression, ADHD, and fatigue, where increased energy and mood elevation are desired.
Indica Strains:
- The higher CBD content and calming terpenes in Indica strains produce relaxing and sedative effects.
- This synergy is beneficial for treating conditions like chronic pain, insomnia, and anxiety, where relaxation and pain relief are the primary goals.
Comparative Overview
| Component | Cannabis Sativa | Cannabis Indica |
| THC Content | Higher | Lower |
| CBD Content | Lower | Higher |
| Common Terpenes | Limonene, Pinene, Terpinolene | Myrcene, Linalool, Beta-Caryophyllene |
| Primary Effects | Stimulating, euphoric, uplifting | Relaxing, sedative, calming |
| Medical Uses | Depression, ADHD, fatigue, mood disorders | Chronic pain, insomnia, anxiety, muscle spasms |
Medical Applications

Cannabis, with its two primary strains, Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, has a wide range of medical applications due to its diverse chemical composition. The unique properties of each strain make them suitable for treating different medical conditions. This section explores the specific medical uses of Sativa and Indica strains and provides detailed insights into their therapeutic potential.
Cannabis Sativa
Mental Health Disorders:
- Depression:
- Effects: Sativa strains are known for their uplifting and mood-enhancing effects due to their higher THC content and stimulating terpenes like limonene.
- Application: Patients suffering from depression may benefit from Sativa strains as they can help elevate mood and provide a sense of well-being.
- ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder):
- Effects: The stimulating properties of Sativa strains can improve focus and concentration.
- Application: Sativa strains may be used to help patients with ADHD manage symptoms by increasing attention span and reducing hyperactivity.
- Anxiety:
- Effects: In small doses, Sativa strains can help manage anxiety by providing an uplifting effect. However, high doses may exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
- Application: Sativa strains can be used cautiously to treat anxiety, particularly in patients who respond well to THC.
Physical Health Disorders:
- Chronic Pain:
- Effects: Some Sativa strains have analgesic properties that can help reduce pain.
- Application: Patients experiencing chronic pain conditions such as arthritis or migraines may find relief with Sativa strains.
- Fatigue:
- Effects: The energizing effects of Sativa strains can combat fatigue and promote activity.
- Application: Sativa strains can be beneficial for patients dealing with fatigue, chronic fatigue syndrome, or conditions that cause low energy levels.
Other Uses:
- Appetite Stimulation:
- Effects: Sativa strains can stimulate appetite, which is beneficial for patients with eating disorders or those undergoing treatments like chemotherapy that reduce appetite.
- Application: Sativa strains can help patients maintain a healthy appetite and nutritional intake.
Cannabis Indica
Mental Health Disorders:
- Anxiety:
- Effects: Indica strains are known for their calming and sedative effects, primarily due to higher CBD content and terpenes like myrcene and linalool.
- Application: Patients with anxiety disorders can benefit from the relaxing effects of Indica strains, which help reduce stress and promote a sense of calm.
- Insomnia:
- Effects: Indica strains are highly effective for inducing sleep due to their sedative properties.
- Application: Patients suffering from insomnia or other sleep disorders can use Indica strains to improve sleep quality and duration.
- PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder):
- Effects: The relaxing effects of Indica strains can help manage PTSD symptoms by reducing anxiety and improving sleep.
- Application: Indica strains can be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for PTSD patients.
Physical Health Disorders:
- Chronic Pain:
- Effects: Indica strains are effective for pain relief due to their higher CBD content and overall sedative effects.
- Application: Patients with chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, or back pain can find relief with Indica strains.
- Muscle Spasms:
- Effects: The muscle-relaxant properties of Indica strains can alleviate spasms and cramps.
- Application: Indica strains are beneficial for patients with conditions like multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries that cause muscle spasms.
- Inflammation:
- Effects: The anti-inflammatory effects of CBD-rich Indica strains can reduce inflammation and associated pain.
- Application: Indica strains can be used to treat inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and other autoimmune disorders.
Other Uses:
- Appetite Stimulation:
- Effects: Indica strains can also stimulate appetite, similar to Sativa strains, but with a more calming effect.
- Application: Indica strains can be beneficial for patients with eating disorders, chemotherapy-induced anorexia, or other conditions that reduce appetite.
Comparative Overview
| Condition | Cannabis Sativa | Cannabis Indica |
| Depression | Uplifting, mood-enhancing effects | Less commonly used, can be sedative |
| ADHD | Stimulating, improves focus and concentration | Less commonly used |
| Anxiety | Uplifting in small doses, may exacerbate in high doses | Calming, reduces stress and anxiety |
| Chronic Pain | Analgesic properties, reduces pain | Effective for pain relief, higher CBD content |
| Fatigue | Energizing, combats fatigue | Not typically used, can be sedative |
| Insomnia | Not typically used | Induces sleep, improves sleep quality |
| PTSD | Less commonly used | Reduces anxiety, improves sleep |
| Muscle Spasms | Less commonly used | Muscle relaxant, alleviates spasms |
| Inflammation | Anti-inflammatory properties in some strains | Reduces inflammation, high in CBD |
| Appetite Stimulation | Stimulates appetite | Stimulates appetite, with calming effect |
Role in Specific Medical Conditions
Cancer:
- Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: Chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting can be lessened with the use of both Sativa and Indica strains. Sativa strains might be preferred during the day for their energizing effects, while Indica strains can be used at night for their sedative properties.
- Pain Management: Indica strains are often preferred for their superior pain-relieving properties due to higher CBD content.
- Epilepsy: High-CBD strains, often derived from Indica plants, are used to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Indica strains are effective in managing muscle spasms and pain associated with multiple sclerosis.
Autoimmune Disorders:
- Crohn’s Disease: Indica strains can reduce inflammation and pain associated with Crohn’s disease.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: The anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties of Indica strains make them suitable for treating rheumatoid arthritis.
Mental Health Conditions:
- Bipolar Disorder: Sativa strains can help manage depressive episodes by uplifting mood, while Indica strains can be used to alleviate anxiety and promote sleep during manic phases.
- Schizophrenia: CBD-rich strains, typically from Indica plants, are being studied for their potential antipsychotic properties.
Methods of Identification
Visual Inspection
Plant Structure:
- Sativa: Tall, less dense foliage, long and thin leaves.
- Indica: Short, bushy, broad leaves.
Leaf Characteristics:
- Sativa: Narrow, lighter green leaves.
- Indica: Broad, darker green leaves.
Chemical Analysis
Cannabinoid Profiling:
- Laboratory testing can determine the THC and CBD content in cannabis samples.
- Sativa strains typically show higher THC levels.
- Indica strains generally have higher CBD levels.
Terpene Profiling:
- Gas chromatography is used to identify the dominant terpenes in cannabis samples.
- Sativa strains have higher levels of terpenes like limonene and pinene.
- Indica strains are richer in terpenes like myrcene and linalool.
Genetic Testing
DNA Sequencing:
- Advanced genetic testing can accurately differentiate between Sativa and Indica strains by analyzing their genetic makeup.
Marker-Assisted Selection:
- This technique identifies specific genetic markers associated with Sativa or Indica traits, aiding in breeding programs to develop new strains with desired characteristics.
Practical Applications in the Medical Field
Patient Assessment
Symptom Evaluation:
- A detailed assessment of patient symptoms is crucial to determine the most suitable strain.
- It is crucial to take into account the patient’s overall health, current medications, and medical history.
Strain Selection:
- Based on the patient’s symptoms and desired effects, healthcare providers can select either a Sativa or Indica strain.
- Hybrid strains are another option; they combine traits from both Indica and Sativa.
Dosage and Administration
Titration:
- It’s typical practice to start with a low dose and increase it gradually until the desired benefits are obtained.
- Monitoring patient response is crucial for adjusting the dosage as needed.
Methods of Consumption:
- Smoking/Vaporizing: Provides quick onset of effects, suitable for acute symptom relief.
- Edibles: Offer longer-lasting effects, suitable for chronic conditions.
- Tinctures/Oils: Versatile administration methods that can be taken sublingually or added to food.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular Check-Ups:
- Scheduling follow-up appointments to monitor patient progress and adjust treatment as necessary is important.
- Assessing any side effects or adverse reactions ensures the safety and efficacy of treatment.
Patient Education:
- Educating patients on the differences between Sativa and Indica strains and their potential effects is crucial.
- Providing guidance on safe consumption practices and potential interactions with other medications helps ensure patient safety.
Challenges and Considerations
Legal and Regulatory Issues
Legality:
- Cannabis laws vary by country and state, impacting access to and use of medical cannabis.
- Ensuring compliance with local regulations is crucial when prescribing or recommending cannabis.
Quality Control:
- Variability in strain quality and consistency due to differences in cultivation practices is a significant challenge.
- Sourcing cannabis from reputable, licensed producers helps maintain quality and safety.
Individual Variability
Patient Response:
- Individual differences in metabolism, endocannabinoid system, and tolerance can affect response to cannabis.
- Tailored therapy regimens are necessary to maximize results.
Side Effects:
- Impaired cognitive function, dry mouth, and lightheadedness are possible adverse effects.
- Long-term use should take the possibility of reliance and withdrawal symptoms into account.
Future Directions
Research and Development
Clinical Trials:
- Continued research into the medical applications of Sativa and Indica strains is necessary.
- Large-scale clinical trials can provide robust evidence for their efficacy and safety.
Strain Development:
- Breeding programs aim to develop new strains with specific therapeutic properties.
- Genetic engineering can enhance cannabinoid and terpene profiles for targeted medical applications.
Integration into Mainstream Medicine
Education and Training:
- Incorporating cannabis education into medical school curricula and continuing education programs is crucial.
- Training healthcare providers on the safe and effective use of medical cannabis ensures better patient outcomes.
Standardization:
- Developing standardized dosing guidelines and treatment protocols is necessary for consistency and safety.
- Implementing quality control measures ensures the reliability of medical cannabis products.
Conclusion
Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, the two primary strains of cannabis, have distinct characteristics that influence their medical applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing their therapeutic potential.
Physical Characteristics
Sativa and Indica plants can be distinguished by their physical attributes. Sativa plants are tall and lanky with long, narrow leaves, thriving in warmer climates. In contrast, Indica plants are shorter, bushier, and have broader leaves, well-suited for cooler climates.
Chemical Composition
The chemical profiles of Sativa and Indica strains differ significantly, primarily in their cannabinoid and terpene content. Sativa strains typically have higher THC levels and lower CBD levels, resulting in stimulating and euphoric effects. They contain terpenes such as limonene and pinene, which further contribute to their uplifting nature. Indica strains, on the other hand, have higher CBD levels and lower THC levels, leading to more relaxing and sedative effects. Terpenes like myrcene and linalool in Indica strains enhance their calming properties.
Medical Applications
The distinct chemical compositions of Sativa and Indica strains make them suitable for treating different medical conditions:
- Sativa Strains: Effective for mental health disorders such as depression and ADHD, as well as physical conditions like chronic pain and fatigue. They are also beneficial for appetite stimulation.
- Indica Strains: Suitable for anxiety, insomnia, PTSD, chronic pain, muscle spasms, and inflammation. Indica strains are often used for their sedative and pain-relieving properties.
Identification Methods
Identifying Sativa and Indica strains involves visual inspection, chemical analysis, and genetic testing. These methods help ensure that the correct strain is used for medical purposes, optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
Practical Applications
In the medical field, proper patient assessment and strain selection are crucial. Dosage and administration methods, such as smoking, vaporizing, edibles, and tinctures, should be tailored to individual needs. In order to modify treatment and guarantee patient safety, routine monitoring and follow-up are necessary.
Challenges and Considerations
Legal and regulatory issues, individual variability in response to cannabis, and potential side effects pose challenges. Ensuring quality control and compliance with local regulations is crucial. Personalized treatment plans and patient education are key to maximizing benefits and minimizing risks.
Future Directions
Continued research and development are vital for advancing the medical use of cannabis. Clinical trials will provide robust evidence for efficacy and safety. Strain development and genetic engineering will enhance therapeutic properties. Integrating cannabis education into medical training and developing standardized dosing guidelines will further optimize its use in mainstream medicine.
Final Thoughts
Differentiating between Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica is essential for harnessing their full therapeutic potential. By understanding their physical characteristics, chemical compositions, and specific medical applications, healthcare providers can make informed decisions to better address patient needs. As research progresses and the legal landscape evolves, the medical community must stay informed and adapt to incorporate cannabis into treatment protocols effectively. The continued exploration of cannabis will undoubtedly unlock new possibilities for improving patient care and outcomes.