Table of Contents
How to grow marijuana
Growing cannabis from seed to harvest is both an art and a science. While the timeline varies based on strain, environment, and grower preferences, the process generally spans 10 to 32 weeks depending on the type of seed (photoperiod vs. autoflowering), growing conditions, and cultivation methods.
This guide breaks down each growth stage, details the time required, and explains the biological, environmental, and genetic factors that influence plant development.
Growers who want a broader understanding of the full grow lifecycle—from germination through harvest—can reference our cannabis seed growing guides before focusing on indoor timelines and optimization.
Growth Timeline Overview
| Growth Stage | Duration (Photoperiod) | Duration (Autoflower) |
|---|---|---|
| Germination | 1–7 days | 1–7 days |
| Seedling | 1–3 weeks | 1–2 weeks |
| Vegetative | 4–8+ weeks (flexible) | 2–4 weeks |
| Flowering | 6–12+ weeks | 5–8 weeks |
| Harvest & Curing | 2–6 weeks | 2–6 weeks |
| Total | 13–32 weeks | 8–16 weeks |
Germination (1–7 Days)
Scientific Basis
Germination is the process by which a cannabis seed develops into a seedling. When exposed to moisture, the seed’s embryonic root (radicle) emerges. This process is governed by phytohormones such as gibberellins, which activate the metabolism of stored food in the seed.

Factors Affecting Germination:
- Humidity: Optimal around 70%
- Temperature: 21–26°C (70–79°F)
- Medium: Paper towel, starter cubes, or directly in soil
Common Techniques
- Paper towel method (sterile and controlled)
- Direct soil sowing (preferred for minimal transplant shock)
Seedling Stage (1–3 Weeks)
Physiological Development
- Cotyledons (seed leaves) appear first
- True leaves begin to develop in sets of 3, then 5, and so on
- Rapid root development below the surface
Light Requirements
- 18–24 hours of light per day
- Light intensity: 200–400 µmol/m²/s (PPFD)
Nutrient Needs
- Low nutrient demand (high risk of nutrient burn)
- Emphasis on phosphorus and calcium for root development
Humidity & Temperature
- Humidity: 65–80%
- Temperature: 22–26°C (72–79°F)
Vegetative Stage (2–8+ Weeks)
This is the phase of vigorous growth where the plant develops stems, leaves, and branches but not flowers.
Duration
- Photoperiod strains: 4–8+ weeks (can be extended indefinitely until light schedule is changed)
- Autoflowers: 2–4 weeks (fixed; transition automatically)
Key Developments
- Rapid increase in biomass
- Pre-flowering (sex organs) may begin to appear
- Photosynthetic efficiency increases with leaf area
Environmental Conditions
- Light: 18–24 hrs/day
- Temperature: 22–28°C (72–82°F)
- Humidity: 50–70%
- Nutrients: High nitrogen demand
Training Techniques
- Topping: Cutting the apical meristem to promote bushy growth
- Low-Stress Training (LST): Bending stems to expose lower branches to light
- Screen of Green (ScrOG): Using a screen to even canopy height
Flowering Stage (5–12+ Weeks)
Initiation
Triggered in photoperiod strains when light exposure is reduced to 12 hours/day. Autoflowers transition automatically after the vegetative phase due to their Cannabis ruderalis genetics.
Phases of Flowering
- Week 1–2 (Transition): Stretching and development of pistils
- Week 3–4: Buds begin to form
- Week 5–7: Trichomes develop; peak resin production begins
- Week 8+: Maturation of cannabinoids and terpenes
Biological Mechanisms
- Flower induction involves phytochrome regulation due to changes in red/far-red light ratios.
- Trichome glands (capitate-stalked) begin secreting THC, CBD, and terpenes as a defense mechanism and to attract pollinators.
Optimal Conditions
- Light: 12/12 cycle (photoperiod)
- PPFD: 600–1000 µmol/m²/s
- Temperature: 20–26°C (68–78°F)
- Humidity: 40–50%
- Nutrients: Lower nitrogen, higher potassium and phosphorus
Length Variability by Genetics
- Indica strains: 6–9 weeks
- Sativa strains: 10–14+ weeks
- Hybrids: 8–10 weeks
- Autoflowers: 5–8 weeks
Harvesting and Curing (2–6 Weeks)
Harvest Timing
Determined by examining trichome maturity under magnification:
- Clear trichomes: Immature
- Cloudy: Peak THC
- Amber: Increased CBN, sedative effects
Post-Harvest Process
- Drying: 7–14 days, 18–22°C, 50–60% RH
- Curing: 2–6 weeks in airtight containers burped daily
Why Curing Matters
Curing stabilizes cannabinoids and improves terpene profile through:
- Enzymatic degradation of chlorophyll
- Oxidation of monoterpenes into more stable aromatic compounds
Photoperiod vs. Autoflower Cannabis Growth Time
| Feature | Photoperiod | Autoflower |
|---|---|---|
| Dependent on light | Yes (12/12 to flower) | No (flowers by age) |
| Total time to harvest | 13–32 weeks | 8–16 weeks |
| Vegetative control | Full (can extend phase) | Minimal (2–4 weeks max) |
| Yield potential | Higher (usually) | Moderate |
| Suitability | Indoor/controlled grows | Outdoor/stealth grows |
Environmental Factors Affecting Growth Duration
Light Intensity and Spectrum
- High light intensity speeds growth
- Red spectrum promotes flowering
- Blue spectrum enhances vegetative structure
Temperature and Humidity

- Extremes can slow metabolism
- Ideal VPD (Vapor Pressure Deficit) during:
- Veg: 0.8–1.2 kPa
- Flower: 1.2–1.5 kPa
Soil vs. Hydroponics vs. Aeroponics
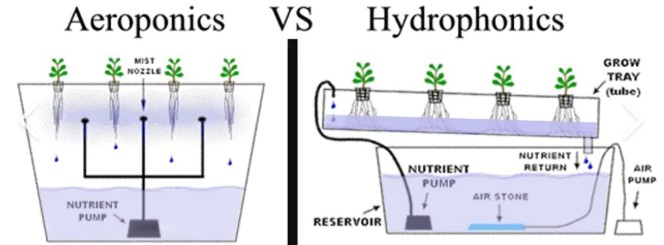
- Soil: Slower, more forgiving
- Hydroponics: Faster growth, more control
- Aeroponics: Fastest, but high maintenance
Genetic Factors Influencing Growth Time
Species and Subspecies
- Indica: Shorter lifecycle, bushy
- Sativa: Longer lifecycle, tall
- Ruderalis: Autoflower traits, fastest lifecycle
Strain-Specific Traits
- Breeders often select for faster flowering
- High-CBD strains tend to flower longer in some cases
Phenotypic Variability
Even seeds from the same strain can vary significantly due to:
- Heterozygosity
- Stress-induced phenotypic changes
Cultivation Techniques That Alter Growth Duration
Cloning
- Cuts 1–3 weeks off early growth
- No germination or seedling stage
Sea of Green (SOG)

- Short veg time, many small plants
- Harvest possible in 8–10 weeks total
Monster Cropping
- Cloning a flowering plant to re-veg
- Extends overall time but improves yield
Real-World Examples
Outdoor Photoperiod Cultivation
- Germinate in April
- Transplant outdoors in May
- Vegetative phase lasts until July
- Flowering from August to October
- Harvest in late October
- Total time: ~28 weeks
Indoor Autoflower Cultivation
- Germinate and grow under 18/6 light
- Automatic flowering after 3–4 weeks
- Harvest in ~10 weeks
- Total time: ~10–12 weeks
Advanced Grower Tips
- Avoid transplant shock by starting in final containers or using biodegradable pots.
- Optimize root oxygenation using air pots or fabric pots to speed vegetative growth.
- Use mycorrhizal fungi and beneficial bacteria to enhance nutrient uptake and shorten growth time.
- Flush nutrients 1–2 weeks before harvest to improve flavor and smoke quality.
Conclusion
The total time required to grow a cannabis plant from seed to harvest varies significantly depending on genetics, environmental control, and cultivation methods. Here’s a quick summary:
- Autoflowers: 8–16 weeks from seed to harvest
- Photoperiod strains: 13–32 weeks, depending on how long you veg
- Fastest route: Clone + SOG + Hydro = ~8–10 weeks
- Longest route: Sativa photoperiod outdoors = up to 32 weeks