How to Grow Cannabis from Seed
Introduction
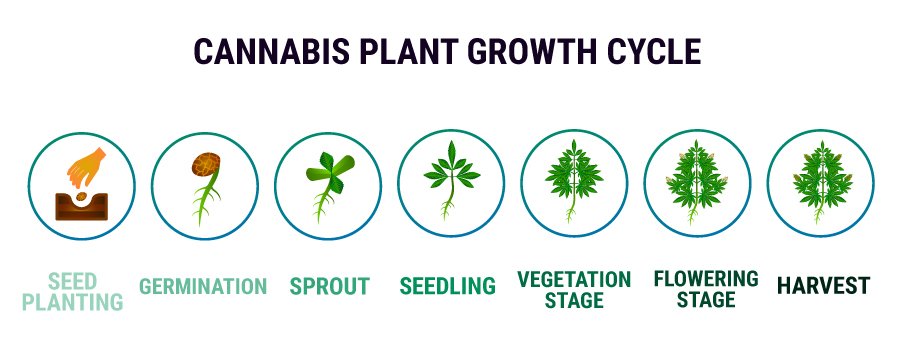
Growing cannabis from seed can be a rewarding and satisfying endeavor, whether for personal use, medicinal purposes, or as a hobby. The process requires careful attention to detail and a good understanding of the plant’s life cycle. This guide will cover everything you need to know to successfully grow cannabis from seed, from selecting the right seeds to harvesting your plants.
Choosing the Right Seeds
Types of Cannabis Seeds
- Regular Seeds: These can produce either male or female plants. Growers often prefer female plants for their bud-producing capabilities, while male plants are used for breeding purposes.
- Feminized Seeds: These are bred to produce only female plants, ensuring that every plant will yield buds.
- Autoflowering Seeds: These plants transition from vegetative to flowering stage based on age rather than light cycles. They are great for beginners and those who want to harvest several crops in a single season.
Seed Quality
High-quality seeds are vital for a successful grow. Look for dark-brown seeds with a glossy surface. Avoid seeds that are white, green, or cracked. Buying from reputable seed banks can ensure the quality and genetic stability of your seeds.
Germination
Methods
- Paper Towel Method: Place seeds between damp paper towels, keep them in a warm place, and wait for the taproot to emerge.
- Direct Soil Planting: Plant seeds directly in moist soil, about 1/4 inch deep.
- Water Soaking: Soak seeds in water for 24-48 hours until they crack open and the taproot emerges.
Environment
Keep the seeds in a warm, dark place with a temperature between 70-85°F (21-29°C). Ensure that the environment remains moist but not waterlogged.
Planting the Seedlings
Soil Preparation
Use a well-draining soil mix with a pH of 6.0-7.0. Adding perlite or vermiculite can improve soil aeration. Cannabis plants thrive in nutrient-rich soil, so consider using organic compost.
Planting
Once the seeds have germinated and the taproot is visible, plant them in small pots or directly into the ground. Make a small hole about 1/4 inch deep, place the seed root-down, and cover it lightly with soil.
Vegetative Stage
Lighting
Cannabis plants require 18-24 hours of light every day throughout their vegetative stage. To ensure appropriate illumination, use full-spectrum LED grow lights or high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps.
Watering
Water the plants thoroughly but allow the soil to dry out between watering sessions. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other issues.
Nutrients
Feed the plants with a balanced fertilizer high in nitrogen, which is essential for vegetative growth. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid nutrient burn.
Training Techniques
- Topping: Cutting the top of the plant to encourage bushier growth.
- Low-Stress Training (LST): Bending and tying down branches to expose more bud sites to light.
- ScrOG (Screen of Green): Using a screen to spread out the plant canopy for even light distribution.
Flowering Stage
Light Cycle
Switch to a 12-hour light and 12-hour dark cycle to induce flowering. Ensure that the dark period is uninterrupted, as light leaks can stress the plants and cause hermaphroditism.
Nutrients
During flowering, switch to a fertilizer with higher phosphorus and potassium levels. These nutrients support bud development and enhance yield.
Environment
Maintain a temperature between 65-80°F (18-26°C) and humidity levels around 40-50%. Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent mold and mildew.
Monitoring and Maintaining Health
Pests and Diseases
Regularly inspect plants for signs of pests like spider mites, aphids, and whiteflies. Use organic insecticides or natural predators like ladybugs for pest control. Prevent diseases by maintaining good air circulation and avoiding overwatering.
pH Levels
Keep the soil pH within the optimal range (6.0-7.0) to ensure nutrient availability. Use pH up or down products to adjust the levels as needed.
Harvesting
Timing
Harvesting at the right time is crucial for optimal potency and flavor. Trichomes (tiny resin glands) should be milky white with some amber-colored ones. Use a magnifying glass or microscope to inspect them.
Method
- Flushing: Stop feeding nutrients 1-2 weeks before harvest and flush the plants with plain water to remove any chemical residue.
- Cutting: Cut the plants at the base and remove large fan leaves.
- Drying: Hang the plants upside down in a dark, well-ventilated room with a temperature of 60-70°F (15-21°C) and humidity around 50%.
- Curing: Place dried buds in airtight jars, opening them daily to release moisture. Cure for at least two weeks for improved flavor and potency.
Advanced Tips
Cloning
Instead of starting from seed every time, you can take cuttings from a healthy mother plant and root them to create clones. This ensures genetic consistency and can speed up the growing process.
Hydroponics
Growing cannabis hydroponically involves using a nutrient-rich water solution instead of soil. This method can result in faster growth and higher yields but requires more equipment and knowledge.
SCROG and SOG
- SCROG (Screen of Green): This technique involves using a screen to train plants to grow horizontally, optimizing light exposure and increasing yields.
- SOG (Sea of Green): This method involves growing many small plants closely together, forcing them into flowering quickly to produce numerous small buds.
Legal Considerations
Before starting your cannabis grow, ensure that it is legal in your area. Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the number of plants you can grow, the allowable size, and any necessary permits or licenses.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Nutrient Deficiencies
- Nitrogen Deficiency: Yellowing leaves starting from the bottom.
- Phosphorus Deficiency: Dark, dull, and sometimes purple-tinged leaves.
- Potassium Deficiency: Yellowing edges and tips, with browning in severe cases.
Pests
- Spider Mites: Tiny, spider-like pests that create fine webbing on the plants.
- Aphids: Small, green insects that cluster on new growth.
- Fungus Gnats: Small, black flies that lay eggs in the soil.
Environmental Stress
- Heat Stress: Leaves curling upwards and developing brown edges.
- Light Burn: Bleached or yellowing leaves directly under grow lights.
- Overwatering: Drooping leaves and soggy soil.
Conclusion
Growing cannabis from seed is a multifaceted endeavor that combines elements of science, art, and patience. It is a journey that can yield not only high-quality cannabis but also a deep sense of accomplishment and understanding of plant biology. Let’s recap the critical aspects of this process to ensure you are well-equipped for a successful grow.
The Seed Selection
Choosing the appropriate seeds is the cornerstone of a successful cannabis cultivation. High-quality seeds from reliable suppliers guarantee genetic stability and viability. Whether you opt for regular, feminized, or autoflowering seeds, understanding the characteristics of each type helps tailor your grow to meet specific goals, whether for medicinal use, high yields, or unique flavor profiles.
Germination and Planting
The germination stage is where the magic begins. Ensuring a warm, moist environment for your seeds to sprout sets the stage for healthy growth. The methods—such as the paper towel technique, direct soil planting, or water soaking—each have their benefits. Selecting the method that suits your setup and experience level is crucial.
Nurturing the Seedlings
Once the seeds have sprouted, the seedling stage requires careful attention to light, water, and nutrients. Providing a stable environment helps these young plants establish strong roots and robust initial growth. Using well-draining, nutrient-rich soil and maintaining appropriate light cycles are essential steps.
Vegetative Stage Care
In the vegetative stage, the focus shifts to promoting vigorous growth and preparing the plants for flowering. Adequate lighting, balanced nutrition, and training techniques like topping or low-stress training (LST) can significantly influence plant structure and future yields. Understanding the plant’s response to these techniques helps optimize growth and bud production.
Transitioning to Flowering
The flowering stage is where the plant’s efforts culminate in bud development. Adjusting the light cycle to 12 hours on and 12 hours off initiates this phase. Nutrient needs change, with a higher emphasis on phosphorus and potassium. Maintaining an optimal environment—temperatures between 65-80°F and humidity around 40-50%—ensures healthy bud formation and reduces the risk of mold and pests.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest
Knowing when and how to harvest is a skill honed through observation and experience. Monitoring trichomes for the right balance of milky white and amber colors indicates peak potency and flavor. The process of flushing, cutting, drying, and curing is meticulous but crucial for ensuring the final product is free of harsh chemicals and has the best possible aroma and taste.
Advanced Techniques
As you gain experience, exploring advanced growing techniques like cloning, hydroponics, and SCROG or SOG can further enhance your cultivation skills and yields. Cloning ensures genetic consistency, hydroponics can speed up growth, and SCROG/SOG techniques maximize space and light efficiency.
Troubleshooting and Continuous Improvement
Challenges are an inevitable part of cannabis cultivation. From pests and diseases to nutrient deficiencies and environmental stresses, being proactive and responsive is key. Regular monitoring and prompt action can prevent small issues from becoming major problems. Continuous learning and adapting based on your experiences and latest industry developments will help refine your growing techniques.
Final Thoughts
Growing cannabis from seed is a fulfilling experience that combines the joy of gardening with the satisfaction of generating your own high-quality cannabis. It needs commitment, attention to detail, and a willingness to learn and adapt. The end result is not just the buds you harvest but the knowledge and experience you gain along the way.
Understanding and executing the principles and strategies mentioned in this article will help you create successful grows that produce potent, tasty, and high-quality cannabis. Whether you are growing for personal use, medicinal purposes, or simply for the love of the plant, the journey from seed to harvest is filled with learning opportunities and personal growth.
Embrace the process, celebrate the milestones, and enjoy the fruits of your labor. Happy growing!