
How is CBD Oil Extracted from Cannabis Plants to Use it Medically?
Introduction
Cannabidiol (CBD) oil, a non-psychoactive compound derived from cannabis plants, has garnered significant attention for its potential therapeutic benefits. Used in managing conditions like chronic pain, anxiety, epilepsy, and more, CBD oil’s efficacy and safety depend heavily on the quality of its extraction process. Understanding the methods used to extract CBD oil is crucial for appreciating its medicinal value and ensuring its purity and potency.
Overview of CBD Oil Extraction
The cannabis plant yields cannabidiol (CBD) oil, which is well known for its potential medicinal advantages, which include pain relief, anti-inflammatory qualities, and anxiety reduction. The quality, efficacy, and safety of CBD oil are largely determined by the extraction process used to obtain it. This overview explores the primary methods of CBD oil extraction, highlighting their procedures, advantages, and disadvantages.
Primary Methods of CBD Oil Extraction
1. Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction uses chemical solvents to dissolve the cannabinoids and other desirable compounds from the cannabis plant material. Common solvents include ethanol, butane, propane, and isopropyl alcohol.
Ethanol Extraction:
- Process:
- The cannabis plant material is ground finely.
- It is soaked in ethanol, which dissolves the cannabinoids and other compounds.
- The solution is filtered to remove the plant material.
- Ethanol is evaporated, leaving a concentrated extract.
- Advantages: Safe, efficient, and cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: Ethanol may extract chlorophyll, imparting a bitter taste.
Butane and Propane Extraction:
- Process:
- The plant material is prepared similarly to ethanol extraction.
- It is exposed to butane or propane, which dissolve the cannabinoids.
- The solution is filtered to remove plant material.
- The solvent is evaporated to leave a concentrated extract.
- Advantages: Efficient and produces a highly concentrated extract.
- Disadvantages: Highly flammable and requires strict safety protocols; potential residual solvents.
2. CO₂ Extraction
Supercritical CO₂ extraction utilizes carbon dioxide under high pressure and varying temperatures to extract CBD. It is a sophisticated method known for producing high-quality, pure extracts.
Process:
- Cannabis plant material is finely ground.
- CO₂ is pressurized to a supercritical state and passed through the plant material.
- Cannabinoids and terpenes are dissolved in the CO₂.
- The CO₂ and dissolved compounds are passed through a separator, where pressure is reduced, allowing the CO₂ to revert to gas and leaving the extracted compounds behind.
- Further purification may be done to enhance potency.
Advantages: Produces high-quality, pure extracts; non-toxic and leaves no residue; adjustable parameters allow for selective extraction. Disadvantages: Expensive and requires specialized equipment and technical expertise.
3. Oil Infusion
Oil infusion is a traditional method that uses carrier oils such as olive oil, coconut oil, or hemp seed oil to extract cannabinoids.
Process:
- Cannabis plant material is decarboxylated (heated to activate cannabinoids).
- The decarboxylated plant material is mixed with a carrier oil and heated to extract cannabinoids.
- The mixture is filtered to remove plant material, leaving an infused oil.
Advantages: Simple, safe, and uses natural ingredients. Disadvantages: Lower concentration of CBD compared to other methods; shorter shelf life due to the perishable nature of oils.
Solvent Extraction
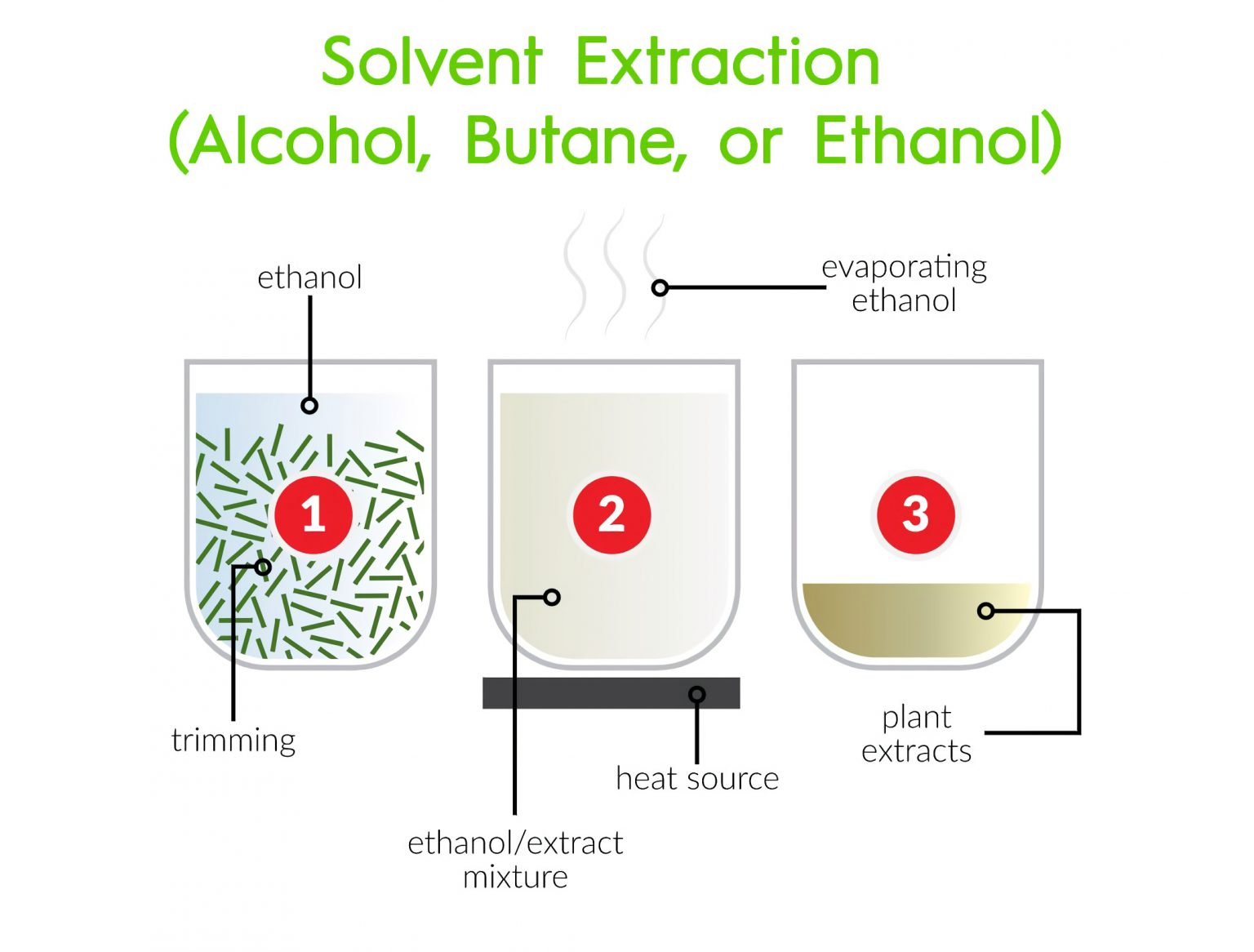
1. Ethanol Extraction
Ethanol extraction is one of the safest and most efficient methods for extracting CBD. Ethanol is a polar solvent, which means it can dissolve both water-soluble and fat-soluble substances, making it highly effective at extracting a wide range of cannabinoids and terpenes.
Process:
- Plant Preparation: The cannabis plant material is finely ground to increase the surface area for extraction.
- Soaking: The ground plant material is soaked in ethanol. The solvent dissolves the cannabinoids, terpenes, and other desirable compounds.
- Filtration: The mixture is filtered to remove the solid plant material, resulting in a liquid solution containing the dissolved compounds.
- Evaporation: The ethanol is evaporated using heat and vacuum, leaving behind a concentrated extract of cannabinoids and terpenes.
Advantages:
- In general, the FDA considers ethanol to be safe (GRAS).
- It efficiently extracts a broad spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes.
- The process is relatively simple and cost-effective.
Disadvantages:
- Chlorophyll can also be extracted with ethanol, which could give the finished product a bitter flavor.
- Because of its flammability, it needs to be handled and stored carefully.
2. Butane and Propane Extraction
Butane and propane extraction are hydrocarbon-based methods known for producing highly concentrated extracts. These solvents are non-polar, which means they selectively extract cannabinoids and terpenes without dissolving water-soluble substances like chlorophyll.
Process:
- Plant Preparation: The cannabis plant material is finely ground.
- Extraction: The ground plant material is placed in an extraction vessel, and butane or propane is passed through it. The terpenes and cannabinoids are dissolved by the solvents.
- Filtration: The solution is filtered to remove the plant material.
- Evaporation: The solvent is evaporated under controlled conditions, typically using a vacuum oven, leaving behind a concentrated extract.
Advantages:
- Produces a highly concentrated extract.
- Non-polar solvents do not extract chlorophyll, resulting in a cleaner taste.
Disadvantages:
- Highly flammable and requires strict safety protocols and equipment.
- Possibility of hazardous residual solvents in the finished product if they are not adequately purged.
CO₂ Extraction
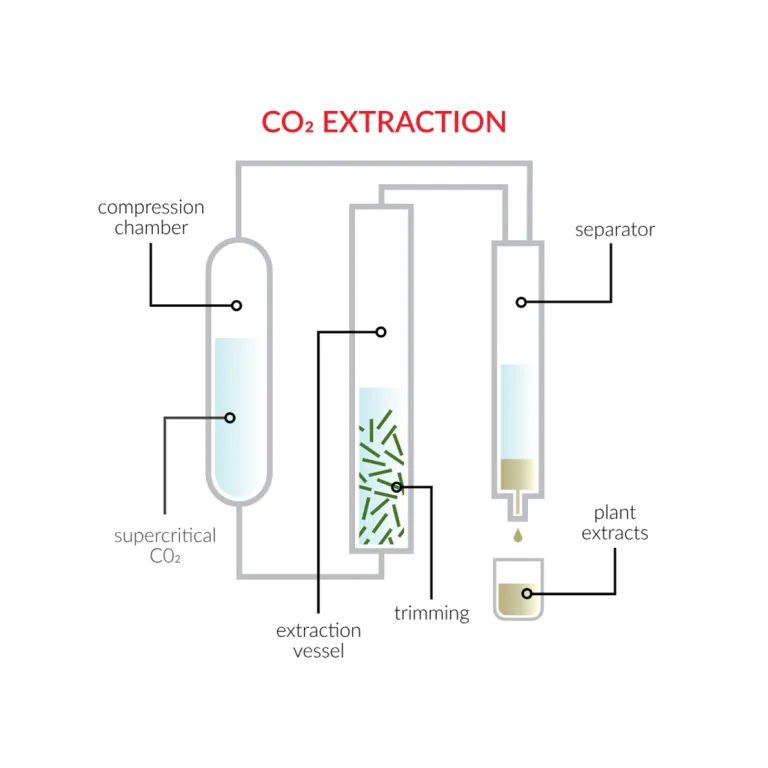
Principles of CO₂ Extraction
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) can exist in various states—solid, liquid, and gas—depending on the temperature and pressure. When CO₂ is subjected to conditions above its critical temperature (31.1°C) and critical pressure (73.8 bar), it enters a supercritical state where it exhibits properties of both a liquid and a gas. In this state, CO₂ can diffuse through the cannabis plant material like a gas and dissolve compounds like a liquid, making it an excellent solvent for extracting cannabinoids and terpenes.
Process of Supercritical CO₂ Extraction
The CO₂ extraction process involves several key steps:
1. Plant Preparation
The cannabis plant material is dried and finely ground to increase the surface area, facilitating more efficient extraction. Next, the extracted material is placed into the extraction vessel.
2. Supercritical CO₂ Application
- Pressurization: CO₂ is pressurized and heated to reach its supercritical state. The specific temperature and pressure settings can be adjusted depending on the desired compounds to be extracted.
- Extraction: The supercritical CO₂ is passed through the cannabis plant material in the extraction vessel. As it moves through the plant, it dissolves the cannabinoids, terpenes, and other valuable compounds.
3. Separation
- Collection: The CO₂-cannabinoid solution is transferred to a separator vessel where the pressure is reduced. This causes the CO₂ to return to its gaseous state, separating from the extracted compounds.
- Recycling: The gaseous CO₂ is recycled back into the system for reuse, making the process environmentally sustainable.
4. Post-Extraction Processing
- Winterization: The crude extract may undergo winterization to remove fats, waxes, and lipids. This involves mixing the extract with ethanol, chilling it to sub-zero temperatures, and filtering out the precipitated impurities.
- Decarboxylation: The extract is heated to convert acidic cannabinoids (e.g., CBDA) into their active forms (e.g., CBD), maximizing their therapeutic potential.
- Distillation: Further refinement through short path or fractional distillation separates cannabinoids from other compounds based on their boiling points, resulting in a highly purified product.
Advantages of CO₂ Extraction
- High Purity and Quality: CO₂ extraction produces a clean, high-quality extract free from chlorophyll and other undesirable compounds.
- Non-Toxic and Safe: CO₂ is non-toxic, non-flammable, and leaves no harmful residues, ensuring the safety of the final product.
- Precision and Control: The ability to adjust temperature and pressure allows for selective extraction of specific cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Environmentally Friendly: CO₂ is a natural, recyclable solvent that minimizes environmental impact.
Disadvantages of CO₂ Extraction
- High Initial Investment: The equipment required for supercritical CO₂ extraction is expensive and involves significant upfront costs.
- Complex Process: The method requires technical expertise and precise control over operating conditions, making it more complex compared to other extraction methods.
- Operational Costs: Although CO₂ itself is inexpensive, the high pressure and temperature conditions result in higher operational costs.
Oil Infusion Method of CBD Oil Extraction
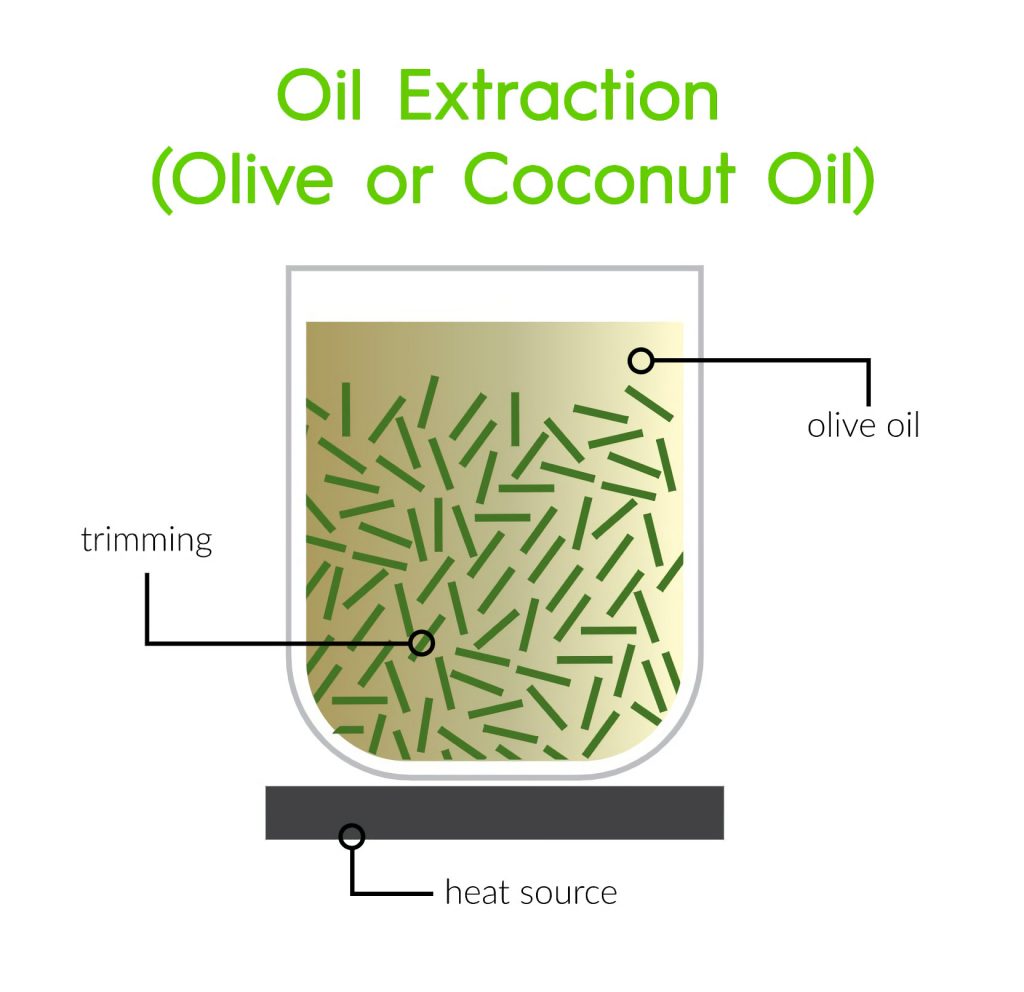
Principles of Oil Infusion
Oil infusion leverages the solubility of cannabinoids in fats to extract them from the plant material. Carrier oils, such as olive oil, coconut oil, or hemp seed oil, are used to dissolve and capture the active compounds from the cannabis plant. The process typically involves heating the plant material with the carrier oil to facilitate the transfer of cannabinoids and other desirable compounds into the oil.
Process of Oil Infusion
The oil infusion process involves several key steps:
1. Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is an essential process that activates the cannabinoids in cannabis plant material by heating it. Raw cannabis contains cannabinoids in their acidic forms (e.g., CBDA), which need to be converted into their active forms (e.g., CBD) to exert their therapeutic effects.
- Process:
- Preheat the oven to 220-240°F (105-120°C).
- Spread the cannabis plant material evenly on a baking sheet.
- Bake the material for 30-45 minutes, checking and stirring occasionally to ensure even heating.
- Once the plant material turns a light brown color, remove it from the oven and let it cool.
2. Infusion
The decarboxylated cannabis is then mixed with a carrier oil and gently heated to infuse the cannabinoids into the oil.
- Process:
- Combine the decarboxylated cannabis with the carrier oil in a suitable container. The ratio of cannabis to oil can vary, but a common ratio is 1 ounce of cannabis to 2 cups of oil.
- Heat the mixture gently using a double boiler, slow cooker, or a saucepan over low heat. The temperature should be kept between 200-245°F (93-118°C) to avoid degrading the cannabinoids.
- Allow the mixture to simmer for 2-3 hours, stirring occasionally. Ensure the temperature remains consistent and does not exceed the desired range.
- After the infusion period, remove the mixture from heat and let it cool slightly.
3. Filtration
Filtering the infused oil removes the plant material, resulting in a clear, cannabinoid-rich oil.
- Process:
- Line a fine mesh strainer or cheesecloth over a clean container.
- To remove the plant particles from the oil, pour the infused oil through a cheesecloth or sieve.
- To get as much oil as you can out of the plant material, squeeze the strainer or cheesecloth.
- To store the filtered oil, move it to a sanitized, sealed container.
Advantages of Oil Infusion
- Simplicity: The process is straightforward and does not require specialized equipment, making it accessible for small-scale and home producers.
- Safety: Oil infusion uses food-safe ingredients, eliminating the risk of harmful solvent residues.
- Natural Ingredients: The use of natural carrier oils enhances the final product’s nutritional profile, adding beneficial fatty acids and other nutrients.
Disadvantages of Oil Infusion
- Lower Concentration: Oil infusion typically produces a less concentrated extract compared to other methods like CO₂ or solvent extraction.
- Shelf Life: The final product has a shorter shelf life due to the perishable nature of the carrier oils, which can degrade over time.
- Heat Sensitivity: Maintaining the correct temperature is crucial, as excessive heat can degrade cannabinoids and other beneficial compounds.
Post-Extraction Processes for CBD Oil
Key Post-Extraction Processes
1. Winterization
Fats, waxes, and lipids are eliminated from the crude extract using the purifying process known as winterization. These unwanted compounds can affect the texture, taste, and quality of the final CBD oil.
Process:
- Mixing: The crude CBD extract is mixed with ethanol or another suitable solvent. The typical ratio is 1 part extract to 10 parts ethanol.
- Freezing: The mixture is placed in a freezer or cold environment, typically at temperatures between -20°C and -30°C (-4°F to -22°F), for 24-48 hours. This causes the fats and waxes to precipitate out of the solution.
- Filtration: The cold mixture is passed through a fine filter, such as a Buchner funnel or fine mesh strainer, to separate the solid fats and waxes from the liquid.
- Evaporation: The filtered solution is gently heated to evaporate the ethanol, leaving behind a purified CBD extract.
Advantages:
- Removes unwanted fats and waxes, improving the quality of the final product.
- Enhances the clarity and stability of the CBD oil.
Disadvantages:
- Requires additional time and equipment.
- Involves handling and evaporating flammable solvents.
2. Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is the process of converting acidic cannabinoids (e.g., CBDA) into their active forms (e.g., CBD) through the application of heat. This step is crucial for maximizing the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids.
Process:
- Preparation: The crude extract or cannabis plant material is spread evenly on a baking sheet or placed in a suitable container.
- Heating: The material is heated in an oven or a decarboxylation machine at a temperature between 220-240°F (105-120°C) for 30-60 minutes. The precise time and temperature depend on the desired level of decarboxylation.
- Cooling: After heating, the decarboxylated material is allowed to cool before proceeding to further processing or usage.
Advantages:
- Activates cannabinoids, making them more bioavailable and effective for therapeutic use.
- Essential for producing potent CBD oil.
Disadvantages:
- Requires precise control of temperature and time to avoid degrading cannabinoids.
- Can be an additional step in the extraction process.
3. Distillation
Distillation is used to further refine the CBD extract by separating cannabinoids from other compounds based on their boiling points. This process can produce highly purified and concentrated CBD oil.
Types of Distillation:
Short Path Distillation:
- Setup: The crude extract is placed in a flask connected to a distillation apparatus under a vacuum.
- Heating: The extract is gently heated, causing the cannabinoids to vaporize at their specific boiling points.
- Condensation: The vaporized cannabinoids pass through a condenser, where they are cooled and collected in separate fractions.
- Collection: The different fractions are collected, resulting in a highly purified CBD concentrate.
Fractional Distillation:
- Setup: Similar to short path distillation, but with multiple fractionating columns to separate compounds more precisely.
- Heating and Condensation: The process involves repeated vaporization and condensation cycles, allowing for more refined separation of cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Collection: The final product is collected in highly purified fractions, each containing specific cannabinoids.
Advantages:
- Produces highly purified and potent CBD oil.
- Makes it possible to isolate and separate particular terpenes and cannabinoids.
Disadvantages:
- Requires specialized equipment and technical expertise.
- Can be time-consuming and costly.
Ensuring Quality and Safety of CBD Oil
Source of Cannabis
The quality of CBD oil begins with the source of the cannabis plants used for extraction. Several factors influence the quality of the raw material:
Organic Cultivation
- Organic Farming: Cannabis should be grown using organic farming practices, without the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers. Organic cultivation reduces the risk of contaminating the final product with harmful chemicals.
- Soil Health: Healthy, nutrient-rich soil promotes the growth of robust cannabis plants. Testing the soil for contaminants such as heavy metals is essential to prevent these from entering the plants.
Strain Selection
- High-CBD Strains: Selecting cannabis strains known for their high CBD content and low THC levels ensures the extraction of oil with the desired cannabinoid profile. ACDC, Harlequin, and Charlotte’s Web are a few of the widely used strains.
- Genetic Stability: Using genetically stable strains helps maintain consistent cannabinoid and terpene profiles across different batches of CBD oil.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for producing high-quality CBD oil. GMP guidelines cover various aspects of production to ensure safety and consistency:
Facility Standards
- Clean Environment: Production facilities should maintain high standards of cleanliness to prevent contamination.
- Controlled Environment: Temperature, humidity, and air quality should be controlled to protect the integrity of the cannabis material and extracts.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Documentation: Detailed SOPs should be in place for every step of the production process, from cultivation to extraction and packaging. This ensures consistency and traceability.
- Employee Training: Staff should be well-trained in GMP and SOPs to maintain high standards of quality and safety.
Third-Party Testing
Independent third-party testing is critical for verifying the quality, potency, and safety of CBD oil. These tests should be conducted by accredited laboratories and cover several key aspects:
Cannabinoid Profile
- Potency Testing: Accurate measurement of CBD and THC content ensures that the product is labeled correctly and meets legal requirements. Testing for other cannabinoids, such as CBG and CBN, provides a comprehensive profile.
Terpene Profile
- Flavor and Aroma: Terpenes contribute to the flavor, aroma, and therapeutic effects of CBD oil. Testing for terpene content ensures that the product maintains its expected sensory qualities and potential benefits.
Contaminant Testing
- Pesticides: Testing for pesticide residues ensures that the final product is free from harmful chemicals used during cultivation.
- Heavy Metals: Cannabis plants can absorb heavy metals from the soil. Testing for metals such as lead, arsenic, cadmium, and mercury is essential for safety.
- Microbial Contaminants: Testing for bacteria, mold, and yeast ensures that the CBD oil is free from microbial contamination.
- Residual Solvents: For products extracted using solvents, testing for residual solvents ensures that they are within safe limits.
Compliance with Regulations
CBD oil production must comply with local, national, and international regulations to ensure safety and efficacy. Key regulatory considerations include:
Legal Requirements
- THC Limits: In many regions, CBD oil must contain less than 0.3% THC to be considered legal. Compliance with THC limits is essential to avoid legal issues and ensure product safety.
- Labeling Standards: Accurate labeling of CBD content, ingredients, and usage instructions is required to inform consumers and meet regulatory standards.
Certifications
- GMP Certification: Obtaining GMP certification demonstrates adherence to high manufacturing standards and enhances consumer trust.
- Organic Certification: Organic certification ensures that the cannabis used in production meets organic farming standards, adding an extra layer of quality assurance.
Quality Control Measures
Strong quality control procedures are used at every stage of production to ensure the reliability and security of CBD oil.
Batch Testing
- Consistency: Each batch of CBD oil should be tested to ensure consistent potency and purity. Batch testing helps identify and address any variations in the final product.
- Traceability: Keeping detailed records of each batch, including source material and test results, ensures traceability and accountability.
Storage and Packaging
- Proper Storage: CBD oil should be stored in a cool, dark place to prevent degradation. Exposure to light, heat, and air can reduce the potency and shelf life of the product.
- Secure Packaging: Using airtight, UV-protected packaging helps preserve the quality of CBD oil. Child-resistant packaging ensures safety in households with children.
Consumer Education
Educating consumers about CBD oil helps them make informed decisions and use the product safely:
Product Information
- Usage Instructions: Clear instructions on dosage and usage methods help consumers use CBD oil effectively.
- Potential Effects: Information about potential benefits and side effects ensures that consumers have realistic expectations and can monitor their response to the product.
Transparency
- Lab Results: Providing access to third-party lab results for each batch enhances transparency and builds consumer trust.
- Source Information: Sharing details about the source of cannabis and production methods fosters confidence in the quality and safety of the product.
Applications of CBD Oil in Medicine

1. Chronic Pain Management
CBD oil is widely used for its analgesic properties, making it effective in managing chronic pain conditions.
Mechanism of Action
CBD has an impact on the endocannabinoid system (ECS), an important mechanism that controls immunological responses, inflammation, and pain. By modulating the activity of ECS receptors (CB1 and CB2), CBD can reduce pain and inflammation.
Clinical Applications
- Arthritis: Studies have shown that CBD can reduce pain and inflammation in patients with arthritis. Topical application of CBD has been particularly effective in relieving joint pain.
- Multiple Sclerosis: CBD oil can alleviate symptoms of multiple sclerosis, including muscle spasms and neuropathic pain. Sativex, a spray containing CBD and THC, is approved in several countries for treating MS-related spasticity.
- Fibromyalgia: Patients with fibromyalgia have reported significant improvements in pain and quality of life with CBD oil use.
2. Anxiety and Depression
CBD oil has shown promise in treating anxiety and depression, offering a safer alternative to traditional pharmaceuticals.
Mechanism of Action
CBD affects serotonin receptors in the brain, which play a key role in mood regulation. It also influences the hippocampus, an area involved in emotion and memory, promoting neurogenesis (growth of new neurons).
Clinical Applications
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Research indicates that CBD can reduce anxiety in individuals with GAD. People with social anxiety disorder showed significant reductions in anxiety after just one dose of CBD, according to a study.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): CBD oil has been effective in reducing symptoms of PTSD, including nightmares and anxiety. Its anti-anxiety effects can help patients cope with trauma-related stress.
- Depression: Animal studies have shown that CBD exhibits antidepressant-like effects. While human research is ongoing, initial findings are promising.
3. Epilepsy
One of the most well-documented medical applications of CBD oil is in the treatment of epilepsy, particularly treatment-resistant forms.
Mechanism of Action
CBD’s anti-epileptic properties are believed to result from its interaction with various receptors and ion channels involved in neuronal excitability and neurotransmitter release.
Clinical Applications
- Dravet Syndrome: It has been demonstrated that CBD considerably lowers the frequency of seizures in people with Dravet syndrome, a severe kind of epilepsy. This disorder is treated with Epidiolex, an FDA-approved medication that includes CBD.
- Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome (LGS): Epidiolex is also approved for treating seizures associated with LGS, another severe epileptic condition. Clinical trials have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing seizure frequency.
4. Inflammation and Autoimmune Disorders
CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties make it beneficial for treating various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions.
Mechanism of Action
CBD modulates the immune system by interacting with ECS receptors and other pathways involved in inflammation and immune responses. It reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhances the activity of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Clinical Applications
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): CBD can help manage symptoms of IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, by reducing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: CBD oil’s anti-inflammatory effects can alleviate pain and inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder affecting the joints.
- Lupus: While research is still in its early stages, CBD shows potential in managing lupus symptoms by modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation.
5. Neuroprotection
CBD oil has neuroprotective properties, making it a potential therapeutic option for neurodegenerative diseases.
Mechanism of Action
CBD’s neuroprotective effects are mediated through its antioxidant properties, reduction of inflammation, and modulation of neuroinflammatory pathways.
Clinical Applications
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Preclinical studies suggest that CBD may help reduce cognitive decline and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. It may also improve symptoms such as agitation and aggression.
- Parkinson’s Disease: CBD has been shown to alleviate motor symptoms and improve quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Its antioxidant properties may protect against neurodegeneration.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): While research is limited, CBD may help manage symptoms of ALS by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
6. Skin Conditions
CBD oil is increasingly used in dermatology for its potential benefits in treating various skin conditions.
Mechanism of Action
CBD interacts with the skin’s ECS, influencing the production of sebum and modulating inflammatory responses.
Clinical Applications
- Acne: CBD’s anti-inflammatory and sebostatic properties can help reduce acne by decreasing sebum production and inflammation in the skin.
- Psoriasis: CBD oil may alleviate symptoms of psoriasis by reducing inflammation and slowing down the proliferation of skin cells.
- Eczema: Topical application of CBD can relieve itching and inflammation associated with eczema, improving skin hydration and barrier function.
7. Cancer-Related Symptoms
CBD oil can help manage symptoms related to cancer and its treatment, such as pain, nausea, and loss of appetite.
Mechanism of Action
CBD interacts with ECS receptors and other pathways involved in pain perception, nausea, and appetite regulation.
Clinical Applications
- Pain Management: CBD oil can alleviate cancer-related pain, particularly neuropathic pain caused by nerve damage.
- Nausea and Vomiting: CBD, in combination with THC, has been effective in reducing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
- Appetite Stimulation: CBD can help stimulate appetite in cancer patients experiencing cachexia (wasting syndrome), improving their nutritional intake and overall health.
Conclusion
The extraction of CBD oil from cannabis plants and its subsequent application in medicine represents a significant advancement in natural therapeutics. Understanding the various extraction methods—solvent extraction, CO₂ extraction, and oil infusion—provides insight into the processes that determine the quality, potency, and safety of the final product. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, influencing the choice based on desired outcomes and available resources.
Post-extraction processes such as winterization, decarboxylation, and distillation are crucial for refining the crude extract and ensuring a high-quality end product. These processes remove impurities, activate cannabinoids, and enhance the purity and potency of CBD oil, making it suitable for medical use.
Ensuring the quality and safety of CBD oil involves careful sourcing of cannabis, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), rigorous third-party testing, and compliance with regulatory standards. High-quality CBD oil is free from contaminants, accurately labeled, and consistently potent, providing a reliable and effective therapeutic option.
The medical applications of CBD oil are vast and supported by growing scientific evidence. CBD oil has shown efficacy in managing chronic pain, anxiety, depression, epilepsy, inflammation, autoimmune disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, skin conditions, and cancer-related symptoms. Its non-psychoactive nature makes it an attractive option for patients seeking relief without the “high” associated with THC.
As research continues to uncover more about CBD’s mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential, the future of CBD oil in medicine looks promising. Ensuring the highest standards of quality, safety, and transparency will be essential for maximizing its benefits and improving patient outcomes. Through ongoing scientific exploration and adherence to best practices, CBD oil can continue to be a valuable and versatile tool in modern medicine, offering natural relief and enhancing the quality of life for many patients.