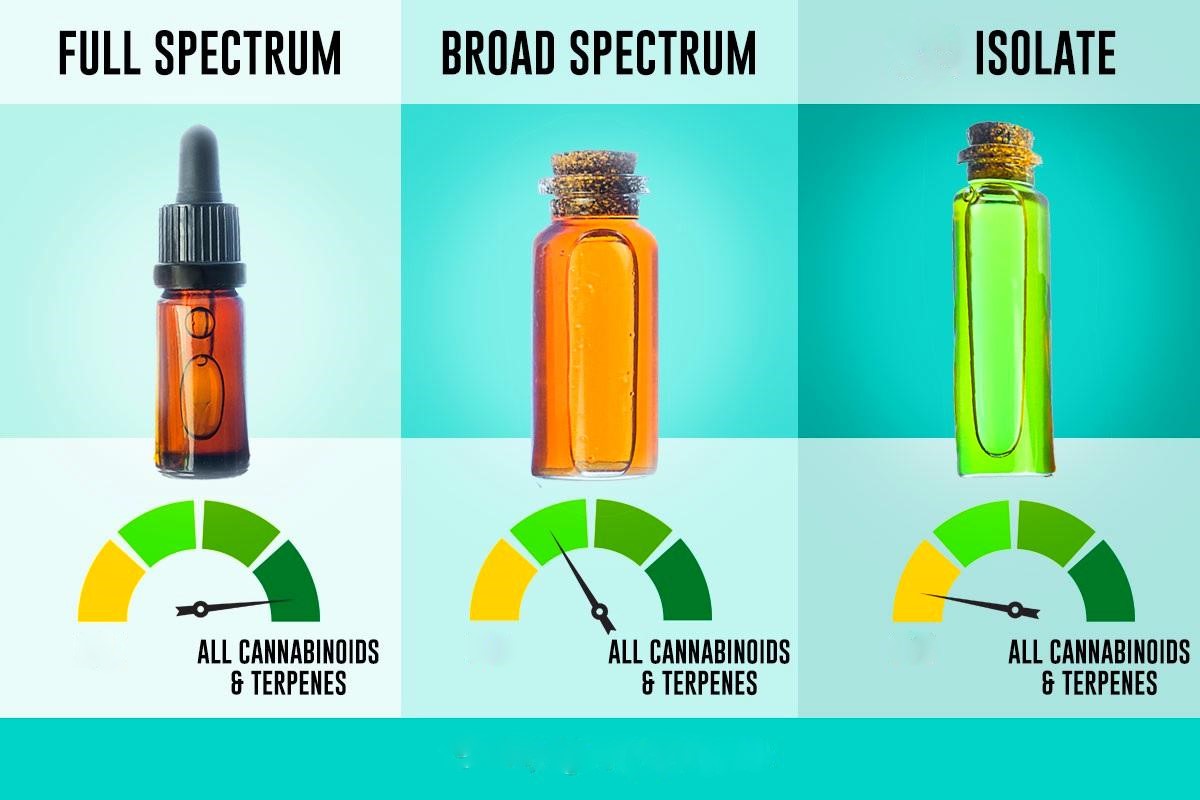

Understanding Full-Spectrum, Broad-Spectrum, and Isolate Products in Medical Applications
The advent of cannabinoid-based therapies has brought about a sophisticated understanding of how different formulations—full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate products—can be tailored to suit specific medical conditions. These three categories are foundational in cannabis and hemp-derived medical products and are differentiated by their composition, pharmacological profiles, and mechanisms of action in the body. This analysis dives deep into their potential applications in the medical field, focusing solely on therapeutic uses and excluding recreational contexts or discussions around consumption methods.
Full-Spectrum Products: A Synergistic Approach to Medical Applications

Full-spectrum products contain all the naturally occurring compounds in the cannabis or hemp plant, including cannabinoids (such as CBD, THC, CBG, and CBN), terpenes, flavonoids, and trace minerals. This “whole-plant” approach emphasizes the therapeutic potential of what is known as the entourage effect, a hypothesis suggesting that the combined action of multiple plant compounds produces greater therapeutic efficacy than isolated cannabinoids.
Therapeutic Benefits and Medical Applications
- Chronic Pain Management
Full-spectrum products are frequently utilized in the management of chronic pain due to their diverse cannabinoid profile. Cannabidiol (CBD) acts as a potent anti-inflammatory agent, while tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), present in varying degrees, has analgesic properties. Together, these compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) to modulate pain signals. Additionally, terpenes such as myrcene (known for its sedative properties) and beta-caryophyllene (a selective CB2 receptor agonist) enhance the pain-relieving effects of cannabinoids.
For conditions such as arthritis, neuropathy, and fibromyalgia, full-spectrum products offer a comprehensive approach by addressing both inflammation and nociceptive pain. Patients often report improved outcomes compared to single-molecule therapies like CBD isolates, likely due to the complementary interaction between cannabinoids and terpenes. - Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
While isolated CBD has gained recognition (e.g., FDA-approved Epidiolex for seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome), full-spectrum CBD products may provide additional benefits in seizure control. Research suggests that the inclusion of minor cannabinoids such as cannabigerol (CBG) and cannabinol (CBN), alongside terpenes like linalool and limonene, may enhance the anticonvulsant properties of CBD through the entourage effect.
Full-spectrum formulations are particularly promising for treatment-resistant epilepsy, where the synergistic interaction of cannabinoids appears to reduce seizure frequency and severity more effectively than isolates. - Anxiety and PTSD
The interplay of cannabinoids and terpenes in full-spectrum products also supports their use in managing anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The anxiolytic effects of CBD are complemented by THC’s ability to modulate serotonin activity, albeit at low doses to avoid psychoactive side effects. Meanwhile, terpenes such as linalool and limonene act as natural anxiolytics by enhancing GABAergic activity in the brain.
PTSD patients, in particular, benefit from the calming effects of these compounds. Studies indicate that THC can reduce hyperarousal symptoms and nightmares, while CBD mitigates stress-related responses. - Neurodegenerative Diseases
Full-spectrum products show potential in addressing conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis (MS). Cannabinoids such as CBD and THC exhibit neuroprotective properties by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and excitotoxicity, key contributors to neuronal damage in these disorders. Terpenes like pinene (a cognitive enhancer) and limonene may further augment these effects.
In MS patients, full-spectrum formulations have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating spasticity and neuropathic pain, enhancing overall quality of life. - Cancer Symptom Management
Full-spectrum products are frequently prescribed to manage symptoms associated with cancer and its treatments. THC provides relief from chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV), while CBD helps counteract inflammation and neuropathy. Additionally, preliminary studies suggest that the combination of cannabinoids and terpenes may exhibit antitumor properties by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting tumor growth pathways.
Beyond direct effects on cancer cells, these products improve appetite, reduce pain, and enhance mood, making them invaluable in palliative care.
Broad-Spectrum Products: A THC-Free Alternative
Broad-spectrum products are similar to full-spectrum products in that they contain a wide array of cannabinoids and terpenes, but they are devoid of THC. This absence of THC makes them an attractive option for patients who need the therapeutic benefits of cannabis-derived compounds but must avoid THC due to legal, occupational, or personal reasons.
Therapeutic Benefits and Medical Applications
- Anxiety and Sleep Disorders
Broad-spectrum products excel in treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and insomnia without the risk of THC-related psychoactive effects. CBD remains the primary active compound, promoting relaxation and improving sleep onset and quality. The presence of calming terpenes, such as myrcene and linalool, contributes to their efficacy.
For individuals with sensitivity to THC or for those in high-stakes professions where THC use is prohibited, broad-spectrum products provide a safe and effective alternative. - Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders
Conditions such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and lupus often involve immune dysregulation and chronic inflammation. Broad-spectrum products leverage CBD’s immunomodulatory properties, supported by the anti-inflammatory effects of terpenes like beta-caryophyllene. The absence of THC is particularly beneficial for patients with autoimmune conditions that could be aggravated by THC’s immunosuppressive properties.
Additionally, broad-spectrum formulations are often recommended for pediatric and geriatric patients, who may benefit from the absence of psychoactive compounds. - Neuropathy and Pain Management
Broad-spectrum products provide effective relief from neuropathic pain associated with diabetic neuropathy, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, and other conditions. While they lack THC’s direct analgesic properties, the presence of minor cannabinoids like CBG and terpenes such as limonene may compensate by enhancing CBD’s efficacy.
These products are also suited for patients who require long-term treatment without the potential dependency or cognitive side effects associated with THC-containing medications. - Post-Surgical Recovery
Broad-spectrum formulations are increasingly being used in post-operative care to manage pain and inflammation. CBD’s anti-inflammatory effects help reduce swelling and promote healing, while the inclusion of terpenes with antimicrobial properties, such as pinene and eucalyptol, may lower the risk of infections. The absence of THC ensures that patients can resume daily activities without cognitive impairment.
Isolate Products: Precision and Purity in Medical Use

Isolate products are composed of a single cannabinoid, most commonly CBD, in its purest form. These formulations are entirely devoid of other cannabinoids, terpenes, or flavonoids. This high level of purity makes isolates ideal for specific medical applications where precise dosing and consistency are critical.
Therapeutic Benefits and Medical Applications
- Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
CBD isolates have been extensively studied for their efficacy in treating epilepsy, culminating in the FDA approval of Epidiolex. By targeting specific receptors in the ECS and modulating ion channels, pure CBD reduces the hyperexcitability of neurons responsible for seizure activity.
Isolates are particularly valuable in pediatric epilepsy cases, where precision dosing and the absence of psychoactive THC are paramount. - Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Isolate-based topical formulations have shown promise in treating conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and acne. CBD’s anti-inflammatory and sebostatic properties reduce redness, swelling, and sebum production. The purity of isolates ensures minimal risk of skin irritation, making them suitable for patients with hypersensitive skin. - Pharmaceutical Drug Development
In clinical and research settings, isolates are often used to develop cannabinoid-based drugs due to their consistency and predictability. By isolating specific cannabinoids, researchers can better understand their pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, leading to targeted therapies for conditions like neuropathic pain and spasticity. - Pediatric Applications
For children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), severe anxiety, or epilepsy, isolates are preferred due to their controlled composition and absence of THC. These products minimize the risk of adverse effects while delivering therapeutic benefits. - Drug Sensitivity and Allergies
Patients with sensitivities to terpenes or other plant compounds may benefit from isolates, as they eliminate the risk of allergic reactions or adverse interactions. This is especially important for individuals with compromised immune systems or multiple chemical sensitivities. - Research into Cannabinoid-Specific Effects
CBD isolates serve as a foundation for understanding cannabinoid-specific effects in isolation from other compounds. This knowledge is critical for advancing medical applications and tailoring treatments to individual patient needs.
Comparative Analysis: Choosing the Right Product for Medical Use
The choice between full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate products depends on several factors, including the patient’s medical condition, sensitivity to THC, and the desired therapeutic outcome.
- Efficacy: Full-spectrum products often provide the most potent therapeutic effects due to the entourage effect, making them ideal for complex conditions like chronic pain or neurodegenerative diseases. Broad-spectrum products, while slightly less potent, offer similar benefits without THC. Isolates, on the other hand, are suitable for conditions requiring high-dose, targeted therapy.
- Safety: Broad-spectrum and isolate products are preferred for patients with THC sensitivities or those who must avoid THC for legal or professional reasons. Isolates are also ideal for individuals with allergies to terpenes or flavonoids.
- Population-Specific Needs: Pediatric and geriatric patients often benefit from broad-spectrum or isolate formulations due to their safety profiles. Full-spectrum products may be reserved for adults with severe or treatment-resistant conditions.
- Regulatory Considerations: In regions with strict THC regulations, broad-spectrum and isolate products provide compliant alternatives for medical use.
The Future of Cannabinoid-Based Medicine
As research into cannabinoids and their therapeutic applications expands, the medical community is gaining a deeper understanding of how full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate products can be harnessed to address a wide range of conditions. Innovations in extraction technology, formulation, and clinical research are likely to refine these products further, enhancing their efficacy, safety, and accessibility.
For now, the choice between these formulations should be guided by evidence-based practice, patient preferences, and the specific medical needs at hand. The availability of diverse cannabinoid products ensures that patients can receive personalized care, opening new possibilities in the treatment of chronic illnesses, neurological disorders, and beyond.
Restrictions on Using Cannabis Components in the Medical Field and Their Role as a Last Resort
Cannabis-derived products have gained significant attention in the medical field due to their therapeutic potential. However, strict regulations and clinical guidelines are necessary to ensure their safe and effective use. These restrictions aim to address concerns surrounding the psychoactive effects of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the ethical considerations of cannabis-based treatments, and the prioritization of traditional therapeutic methods. Furthermore, the careful monitoring of THC levels in medical formulations is critical to prevent unintended psychoactive effects, especially in vulnerable populations. This article examines the restrictions on cannabis components in the medical field and their status as a last-resort treatment option.
The Controlled Use of Cannabis in Medicine
Cannabis and its components, particularly cannabinoids like cannabidiol (CBD) and THC, are subject to stringent regulation in most countries. Medical cannabis is often reserved for patients with conditions that have proven resistant to conventional therapies, such as chronic pain, epilepsy, or chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. These restrictions stem from the need to balance the potential therapeutic benefits with public health and safety concerns.
Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), require robust evidence of safety and efficacy before approving cannabis-based medications. For instance, the FDA has approved only a few cannabinoid-based drugs, such as Epidiolex (CBD) for rare seizure disorders and Dronabinol (synthetic THC) for nausea and appetite stimulation. This careful oversight underscores the necessity of using cannabis components only in well-defined medical contexts.
Additionally, many healthcare systems require patients to exhaust all other treatment options before considering cannabis-based therapies. For example, in the management of chronic pain, physicians often explore non-opioid analgesics, physical therapy, and psychological interventions before recommending cannabinoids. Similarly, in neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis or epilepsy, cannabis-derived treatments are prescribed only after first-line and second-line medications fail to achieve adequate symptom control.
Monitoring THC Levels to Prevent Psychoactive Effects
THC, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, poses unique challenges in the medical field due to its potential to cause altered perception, cognitive impairment, and dependency. To mitigate these risks, strict regulations govern the allowable THC content in medical formulations.
- Low-THC or THC-Free Products
Medical cannabis products often emphasize CBD as the primary therapeutic agent due to its non-psychoactive properties and broad safety profile. In many jurisdictions, medical formulations are categorized based on their THC content. For example, low-THC products are often capped at less than 0.3–1% THC, while some countries only allow THC-free formulations for medical use. These restrictions ensure that patients can benefit from cannabinoids like CBD without experiencing psychoactive side effects.
Pediatric and geriatric patients, in particular, are prescribed low-THC or THC-free products due to their heightened sensitivity to psychoactive compounds. This approach minimizes the risk of cognitive side effects, such as confusion, memory impairment, or disorientation, while still providing therapeutic benefits. - Dosing Guidelines
Medical professionals are required to adhere to strict dosing guidelines when prescribing THC-containing products. Microdosing, which involves administering minimal doses of THC to achieve therapeutic effects, is often employed to minimize psychoactive effects. For example, in palliative care, low doses of THC may be used to improve appetite or alleviate pain without inducing euphoria or intoxication. - Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
Patients using THC-containing medications are typically monitored closely to assess efficacy and side effects. This monitoring includes regular follow-ups, blood tests to evaluate THC levels, and cognitive assessments to ensure that the treatment does not adversely affect mental function. If psychoactive effects are observed, the dosage is adjusted or the patient is transitioned to a low-THC or THC-free alternative.
Ethical Considerations and the Role of Cannabis as a Last Resort
The use of cannabis-derived treatments as a last-resort option reflects the ethical principle of beneficence—ensuring that the patient’s well-being is prioritized while minimizing potential harm. Physicians must consider the risk-benefit ratio of cannabis-based treatments and exhaust other evidence-based options first.
For instance, in the treatment of epilepsy, cannabinoids like CBD are prescribed only when standard antiepileptic drugs fail to control seizures. Similarly, in cancer care, cannabinoids are used to manage treatment-related side effects, such as chemotherapy-induced nausea and neuropathy, only after other antiemetic or analgesic drugs prove ineffective.
Restricting cannabis components to last-resort use also addresses concerns about normalization and overuse. By maintaining cannabis-based treatments as a secondary or tertiary option, healthcare systems reinforce the importance of using these therapies judiciously and within clinically validated frameworks.
Conclusion
The use of cannabis-derived products in the medical field represents a promising yet tightly regulated frontier in healthcare. Full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and isolate products each offer unique therapeutic benefits tailored to different medical conditions. Full-spectrum formulations leverage the entourage effect, broad-spectrum provides a THC-free alternative, and isolates ensure precision and purity for specific applications. These distinctions allow for highly individualized treatments that cater to the specific needs of patients.
However, the use of cannabis-based treatments is often reserved as a last-resort option. This reflects the prioritization of conventional therapies and the need for a robust risk-benefit analysis before turning to cannabinoid-based medicine. Medical cannabis is typically prescribed only when all other evidence-based treatments have proven ineffective, underscoring its use as a secondary or tertiary intervention.
Strict monitoring of THC levels is paramount to prevent psychoactive side effects, particularly in vulnerable populations such as pediatric or geriatric patients. By employing low-THC or THC-free formulations, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of cognitive impairment while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Close adherence to dosing guidelines and regular patient monitoring further ensure the safety of THC-containing medications in clinical practice.
These carefully calibrated restrictions ensure that cannabinoids are integrated responsibly into modern medicine. By enforcing stringent safety protocols and ethical care practices, healthcare professionals can harness the therapeutic potential of cannabis-based treatments, offering hope for patients with treatment-resistant conditions without compromising safety or clinical integrity.