Table of Contents
How to Flower a Cannabis Plant?
The flowering stage marks a critical juncture in the cannabis plant’s life cycle, signifying a pivotal shift from vegetative growth to the production of buds. These buds serve as the main reservoir of cannabinoids, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), which are accountable for the plant’s therapeutic and psychoactive effects. The importance of these compounds in both medical and recreational contexts underscores the need for exceptional care and precision in environmental management during this stage, aiming to nurture the development of cannabinoid-rich buds.
To achieve successful cultivation during this phase, an in-depth understanding of the cannabis plant’s requirements is essential. This includes a meticulous approach to managing key factors like lighting, which must mimic natural seasonal changes to trigger flowering. Nutrition also plays a crucial role; the plant demands a specific balance of nutrients, differing from its vegetative stage, to support the budding process effectively.
Moreover, the control of ambient environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, is paramount. These conditions significantly impact the quality of the final product, influencing not only the cannabinoid potency but also the terpene profile, which affects the buds’ aroma and flavor. Additionally, this phase sees an increased risk of pests and diseases, necessitating close monitoring and proactive measures to safeguard the developing flowers.
This comprehensive examination aims to deepen the understanding of the flowering stage’s importance in the cannabis plant’s growth cycle. It provides cultivators, whether beginners or seasoned, with practical insights and strategies for optimizing the growing environment. The primary objective is to cultivate cannabis plants that produce high-quality, potent buds, thereby maximizing their therapeutic and recreational value.
Through meticulous care and knowledgeable practices, growers have the potential to significantly influence their cannabis crop’s outcome. This involves not just ensuring a bountiful harvest but also achieving a product of superior quality. By adhering to these advanced cultivation strategies, cultivators can ensure their efforts culminate in a harvest that meets the highest standards of potency and quality.
The flowering stage is one phase within the full cannabis life cycle, which is outlined in our complete cannabis cultivation framework before each stage is explored in depth.
Understanding the Flowering Stage
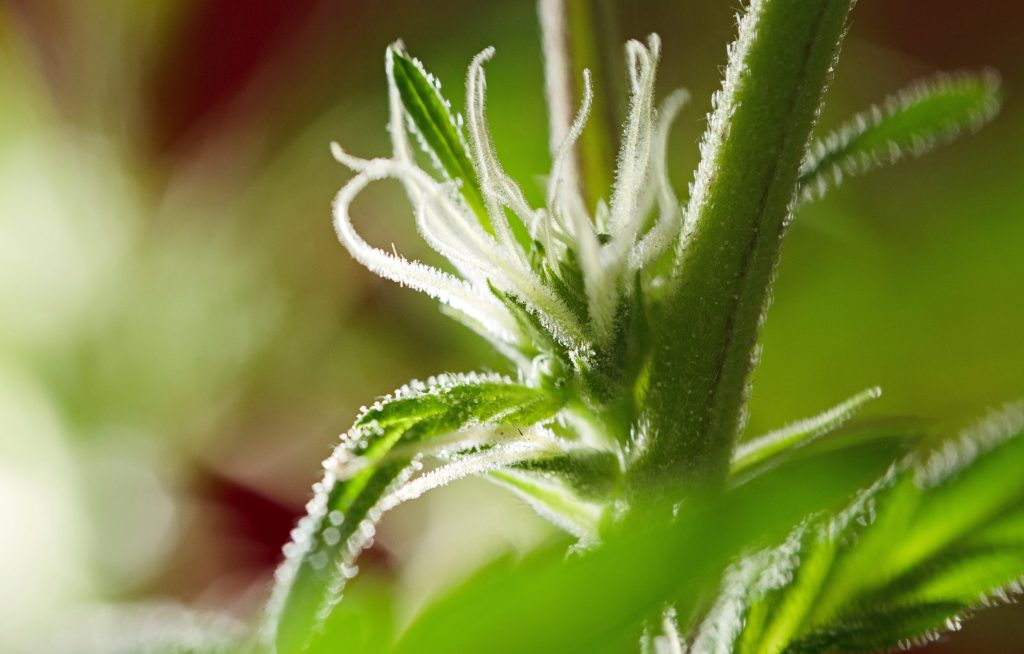

The flowering stage in the life cycle of a cannabis plant represents a significant transition from the vegetative phase, a period characterized by rapid growth and the establishment of a strong foundational structure. During the vegetative phase, the cannabis plant dedicates its energy primarily to developing a robust root system, expanding its foliage, and increasing its overall size and stature. This groundwork is essential for supporting the subsequent reproductive phase known as the flowering stage.
The onset of the flowering stage is predominantly initiated by changes in light exposure, signifying an intricate relationship between the plant’s growth patterns and environmental cues. Specifically, a reduction in the number of light hours the plant receives signals the commencement of this reproductive phase. This adaptation is a survival mechanism that evolved over millennia, allowing cannabis plants to align their reproductive efforts with the most favorable environmental conditions.
Once triggered, the plant shifts its focus from vegetative growth to the development of reproductive organs, namely flowers or buds. These structures are the site of cannabinoid synthesis, including compounds such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), which are of significant interest for their medicinal and recreational properties. The flowers are also crucial for the plant’s reproduction, containing the necessary genetic material for the propagation of future generations.
The duration of the flowering stage, as well as its specific characteristics, can exhibit considerable variation among different cannabis strains. This diversity is a reflection of the plant’s genetic background and its adaptation to various environmental conditions encountered across its natural and cultivated range. Certain strains may finish the flowering stage within as brief a period as six weeks, whereas others might necessitate up to twelve weeks or even longer. This variance not only influences the cultivation strategies required for different strains but also affects the timing and yield of the harvest.
Moreover, the behavior of the plant during the flowering stage is influenced by several factors, including light spectrum, temperature, and humidity. These conditions can affect the development and quality of the flowers, making it imperative for cultivators to monitor and adjust environmental parameters carefully to optimize the growth and potency of the buds.
In conclusion, the flowering stage is a critical and complex phase in the cannabis plant’s life cycle, necessitating a deep understanding of plant physiology and environmental interactions. Cultivators must pay meticulous attention to the specific needs and responses of their plants during this time to ensure a successful and bountiful harvest.
Indica vs. Sativa vs. Hybrid
Indica Strains: A Swift Journey to Flowering
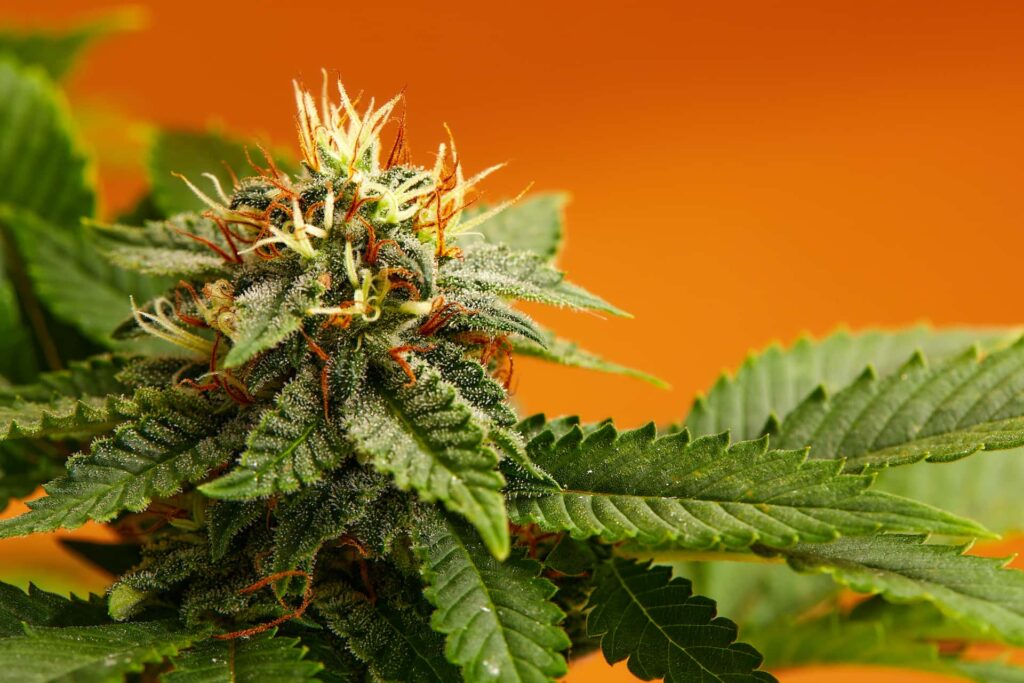

Indica strains of cannabis are celebrated for their notably shorter flowering periods, typically ranging between eight to nine weeks. This expedited path to maturity is a distinguishing feature that renders Indica varieties particularly appealing to cultivators aiming for rapid turnover rates in their cultivation cycles. The genetic lineage of Indica strains, originating from the harsh and unpredictable climates of regions like the Hindu Kush, has instilled in them an evolutionary advantage. This adaptation ensures their survival by enabling a swift reproductive cycle, thus avoiding the onset of adverse weather conditions. The compact stature and robust nature of Indica plants are reflections of their origin, designed to withstand the environmental challenges they face.
Sativa Strains: The Extended Bloom
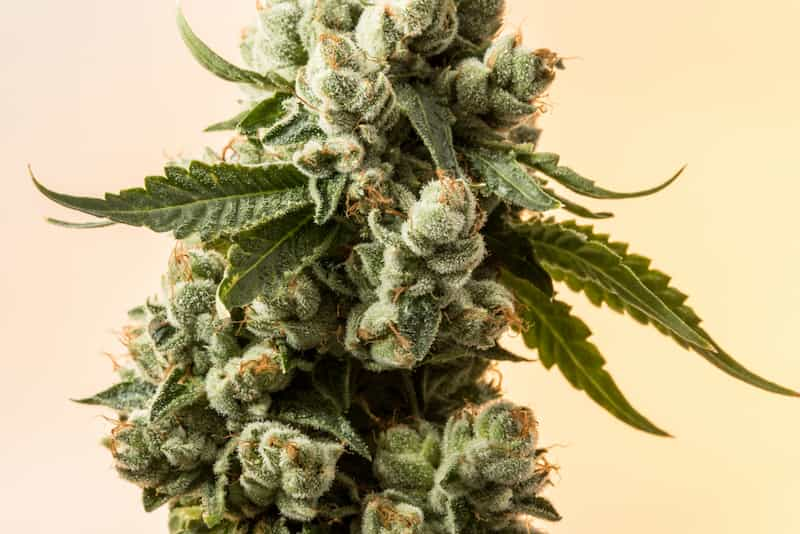

Contrastingly, Sativa strains demand a more extended flowering period, with some varieties requiring as long as ten to twelve weeks to fully mature. This prolonged developmental phase is deeply rooted in the genetic heritage of Sativa strains, which hail from equatorial regions characterized by consistent daylight hours and a generous supply of sunlight. The natural habitat of Sativa strains promotes a longer vegetative growth period, allowing these plants to achieve greater heights with a leaner structure and wider internodal spacing. The resulting larger, airier buds are a hallmark of Sativa strains, distinguishing them from the denser flowers of their Indica relatives.
Hybrid Strains: Bridging the Genetic Divide
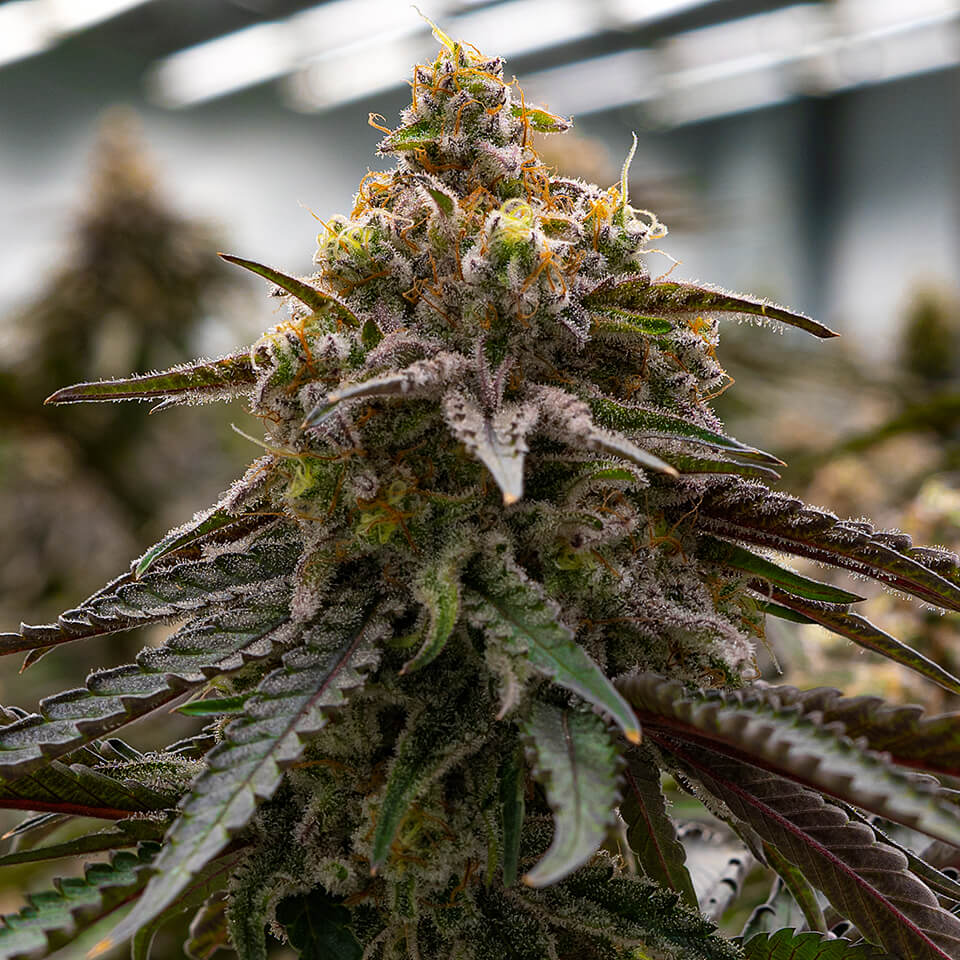

Hybrid strains emerge as a genetic cross between Indica and Sativa varieties, embodying characteristics from both lineages. The flowering times of these hybrids generally occupy a middle ground, contingent upon their dominant genetic influences. This intermediate flowering phase allows cultivators and consumers to enjoy the best of both worlds, combining the quick maturation of Indica strains with the desirable growth traits and bud structure of Sativa varieties. The development of hybrid strains is a testament to the advanced techniques and selective breeding practices employed in cannabis cultivation, aiming to produce strains that meet specific aesthetic, therapeutic, and cultivation efficiency criteria.
Tailoring Cultivation to Flowering Timelines
Understanding the distinct flowering periods across Indica, Sativa, and Hybrid strains is imperative for cultivators to align their practices with the growth patterns and needs of their chosen varieties. This knowledge facilitates the optimization of environmental factors — including lighting schedules, temperature control, and humidity management — throughout the cultivation process. Adjusting these variables to suit the specific flowering timeline of a strain can significantly influence the yield, potency, and overall quality of the cannabis harvest. Cultivators must employ strategic planning and continuous monitoring to ensure that each plant reaches its full potential during the crucial flowering phase, thereby achieving a successful and bountiful crop.
Transitioning to Flowering
The flowering stage in cannabis cultivation begins with a critical adjustment to the plant’s light exposure, shifting from long periods of light to a balanced 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. This change mimics the natural shift from summer to autumn, triggering the plant to start its reproductive phase. This process, based on the principle of photoperiodism, requires precise control in indoor setups to ensure uninterrupted darkness during the dark phase. Such precision is essential as any light exposure can disrupt flowering, affecting yield and quality.
Indoor cultivation benefits from this light cycle manipulation, offering control over the flowering stage and allowing for multiple harvests annually, unlike outdoor cultivation, which is restricted by natural seasons. This control is crucial for producing cannabis that meets specific standards in quality and potency, showcasing the blend of botanical science and environmental management in optimizing plant growth.
Ultimately, manipulating the light cycle to initiate the flowering stage is a key strategy in cannabis cultivation, underlining the importance of a well-managed environment to achieve high-quality cannabinoid production.
Lighting Considerations
Understanding Light Intensity and Spectrum in Flowering Cannabis

The flowering stage of cannabis cultivation is a phase that requires not only meticulous control over environmental conditions but also a thorough comprehension of the plant’s requirements. Among these, the intensity and spectrum of light play pivotal roles. During this critical phase, cannabis plants thrive under high-intensity lighting, which is essential for the synthesis of sugars through photosynthesis, fueling growth and development. However, it is not just the intensity of the light that matters but also its spectrum.
The light spectrum pertains to the array of wavelengths emitted by a light source. For flowering cannabis plants, light that leans towards the red wavelengths proves to be particularly beneficial. This preference is rooted in the plant’s natural adaptation to the seasonal changes in sunlight, with the red spectrum mimicking the warm, late-summer sun that signals the approach of the flowering season in nature. Red wavelengths encourage the formation of buds by stimulating certain photoreceptors within the plant, which in turn trigger the flowering response.
LED vs. HPS: A Comparative Analysis for Flowering Cannabis

When it comes to indoor cannabis cultivation, the choice of lighting technology can significantly influence the growth, health, and yield of the plants. Two commonly chosen options are LED (Light Emitting Diode) and HPS (High-Pressure Sodium) lights, each presenting its distinct advantages and disadvantages.
LED Lights: Efficiency and Spectrum Control
LED lights have been increasingly favored in modern horticulture for their energy efficiency and longevity. These lights generate less heat compared to traditional lighting options, reducing the risk of heat stress on the plants and the need for additional cooling systems in the cultivation environment. Furthermore, LED technology empowers cultivators to personalize the light spectrum, allowing for a customized approach to address the precise requirements of cannabis plants at every stage of growth. For the flowering stage, LEDs can be adjusted to emphasize red wavelengths, thereby optimizing bud development and potentially enhancing cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
HPS Lights: Proven Effectiveness in Flowering
High-Pressure Sodium lights have long been the standard in cannabis cultivation, particularly noted for their effectiveness in promoting robust flower growth and density. HPS lights emit a spectrum abundant in yellow and red wavelengths, closely matching the natural requirements of plants during the flowering phase. This spectral composition has been proven to encourage dense, resinous bud formation, a key goal for many cultivators. However, the high heat output of HPS lights and their less efficient energy use present challenges, requiring careful management of the cultivation environment to prevent excessive heat and ensure optimal growth conditions.
Conclusion: Tailoring Lighting to Cannabis Needs
The choice between LED and HPS lighting for cannabis cultivation during the flowering stage involves a balance of factors, including energy efficiency, heat management, spectrum control, and the specific growth characteristics desired in the final harvest. While LEDs offer advanced control and efficiency, HPS lights provide a tried-and-true solution for maximizing flower growth and density. Ultimately, the decision should be informed by a comprehensive understanding of the plant’s requirements, cultivation objectives, and the environmental conditions of the grow space. This ensures that the chosen lighting technology aligns with the overarching goals of quality, yield, and efficiency in cannabis production.
Nutrient Requirements
Nutritional Shifts During the Flowering Stage

As cannabis plants progress from the vegetative to the flowering stage, their nutritional needs experience substantial shifts. This shift is essential to support the plant’s altered growth focus, moving from leaf and stem development to the production of flowers or buds. Understanding and addressing these changing nutritional needs is paramount for cultivators aiming to optimize plant health and maximize yield.
The Vital Role of Phosphorus in Bud Development

Phosphorus plays a pivotal role in the flowering stage, primarily by facilitating critical plant processes such as energy transfer and photosynthesis. This macronutrient is a key component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells, which supports various functions, including the synthesis of nucleic acids and the metabolism of carbohydrates. During the flowering phase, the demand for phosphorus spikes as the plant channels its energy towards producing buds.
Moreover, phosphorus is integral to the process of photosynthesis, enabling the transformation of light energy into chemical energy, which fuels plant growth and development. A sufficient supply of phosphorus ensures that cannabis plants can efficiently produce the energy needed for robust bud formation. This makes phosphorus supplementation a critical consideration for cultivators looking to enhance the quality and quantity of their harvest.
Potassium: Strengthening Plants from Within

Potassium is another crucial nutrient that supports cannabis plants during their flowering stage. It plays a vital role in strengthening cellular walls, which not only contributes to the overall structural integrity of the plant but also helps in the development of dense and healthy buds. Strong cellular walls are essential for protecting the plant against pathogens and environmental stresses, thereby ensuring optimal growth conditions.
In addition to its role in fortifying plant cells, potassium is key to the regulation of water and nutrient transport within the plant. It facilitates the opening and closing of stomata, and the pores on the surface of leaves, which control both water loss through transpiration and the intake of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Efficient regulation of these processes is crucial for maintaining the plant’s water balance and ensuring the availability of essential nutrients for bud development.
Conclusion: Tailoring Nutrition for Flowering Cannabis
The flowering stage presents a unique set of nutritional demands that are critical to the plant’s ability to produce high-quality buds. Providing adequate levels of phosphorus and potassium during this phase is essential for supporting the plant’s increased energy requirements and structural needs. Cultivators must carefully monitor and adjust their nutrient feedings to cater to these changes, ensuring that plants have access to the resources they need to thrive. By understanding and responding to the nutritional shifts during the flowering stage, growers can significantly impact the health, vitality, and yield of their cannabis plants, ultimately leading to a successful and rewarding harvest.
Environmental Conditions
Key Environmental Conditions for Flowering Cannabis

As cannabis enters its flowering stage, achieving the right environmental balance becomes crucial for the plant’s health and the quality of the buds produced. Optimal temperature, humidity, and air circulation are vital components that need careful attention to ensure robust growth and potent bud formation.
Temperature Needs
Temperature plays a critical role in cannabis flowering, with ideal daytime temperatures ranging from 68-77°F (20-25°C) to support essential plant processes. A slight decrease in nighttime temperatures mimics natural conditions and may enhance bud quality, but extreme fluctuations should be avoided to mitigate stress.
Managing Humidity
Proper humidity levels are essential, with a recommendation to maintain relative humidity between 40-50% during flowering. This prevents mold and encourages resin production, contributing to the potency and aroma of the buds.
Air Circulation Importance
Effective ventilation and air movement prevent stagnant air, reducing mold and pest risks while ensuring even CO2 distribution. Good air circulation is critical for maintaining the desired temperature and humidity levels, supporting healthy plant growth.
Conclusion
Optimal environmental control during the flowering stage is key to cannabis cultivation success. By managing temperature, humidity, and air circulation, cultivators can greatly influence plant health, yield, and bud quality, showcasing the precision required in modern cannabis cultivation.
Watering Practices

As cannabis plants transition into the bud development phase, their physiological demands evolve, notably in terms of water requirements. This stage of growth is marked by an increase in the plant’s need for water, a vital component for various biological functions including nutrient transport, photosynthesis, and the maintenance of cellular structure. Water plays an integral role in the development of healthy, robust buds, acting as a carrier for essential nutrients from the soil or growing medium to the plant’s vascular system, where they are distributed to support growth and flowering.
However, the increased need for water during this critical phase of growth introduces the risk of overwatering, a common pitfall that can have detrimental effects on plant health. Overwatering can result in a saturated growing medium, which significantly reduces the availability of oxygen to the root system. Roots require oxygen to respire and when deprived of this essential element, their efficiency in nutrient uptake is compromised, potentially leading to stunted growth and diminished health of the plant.
Moreover, consistently wet conditions around the roots create an environment conducive to the proliferation of fungi and other pathogens, among which root rot is particularly notorious. Root rot is a condition that can devastate cannabis plants, characterized by the decay of root tissues and resulting in the inability of the plant to absorb water and nutrients effectively. This can lead to symptoms such as wilting, yellowing leaves, and ultimately, the death of the plant if not addressed promptly.
Given these considerations, it is of utmost importance for cultivators to carefully monitor the moisture level of the growing medium. This can be accomplished through different methods, including utilizing moisture meters, which offer accurate measurements of moisture content, or employing traditional techniques like the finger test, where the cultivator inserts a finger into the growing medium to assess its moisture level. Based on these assessments, watering schedules can be adjusted to ensure that the plants receive the necessary hydration to support bud development without becoming waterlogged.
Adjusting watering schedules is not a one-size-fits-all approach, as the optimal frequency and volume of water will vary depending on factors such as the size of the plant, the stage of growth, the type of growing medium, and the specific environmental conditions of the cultivation area. It is critical for cultivators to remain vigilant and responsive to the changing needs of their plants, adapting their watering practices to maintain an ideal balance of moisture that promotes healthy growth and maximizes the potential for a bountiful, high-quality harvest.
Monitoring and Managing Plant Health

During the intricate flowering stage of cannabis cultivation, the vigilance of the grower is paramount. This period is characterized by the plant’s increased susceptibility to a variety of stressors, including pests, diseases, and nutritional imbalances. Consistent and comprehensive monitoring becomes a crucial practice to protect the health of the plant and ensure the quality of the eventual harvest.
Pests pose a constant threat to cannabis plants, with common culprits including spider mites, aphids, and whiteflies. These tiny invaders can inflict considerable damage, feeding on the plant’s sap and weakening its structural integrity. Beyond the immediate physical damage, pests often act as vectors for disease, introducing viruses and bacteria that can further compromise plant health.
Likewise, diseases like powdery mildew and root rot can quickly establish themselves within the cultivation environment. These ailments, often fungal, thrive in conditions of excessive humidity and poor air circulation. Once established, they can rapidly spread throughout a crop, affecting the vitality of the plants and diminishing the yield and quality of the buds.
Nutritional deficiencies represent another critical area of concern during the flowering stage. Cannabis plants necessitate a precise equilibrium of nutrients to facilitate their growth and progression. Insufficiencies in essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium may result in diverse symptoms, such as leaf discoloration, inhibited growth, and diminished bud production. Conversely, an excess of nutrients can induce toxicity, causing various detrimental impacts on plant health.
The significance of early detection and intervention cannot be emphasized enough. Many issues, if identified promptly, can be addressed with minimal impact on the overall health of the plant. Regular inspections of the leaves stems, and buds can reveal early signs of pest infestation or disease, allowing for timely corrective measures. Similarly, a keen observation of plant growth and development can indicate nutritional imbalances before they escalate into more severe problems.
Implementing preventive measures can also play a crucial role in maintaining plant health during the flowering stage. Strategies such as maintaining optimal environmental conditions, employing integrated pest management (IPM) practices, and ensuring a balanced and timely delivery of nutrients can mitigate the risk of pests, diseases, and deficiencies.
In conclusion, the flowering stage demands a proactive approach to plant care. Through diligent monitoring and the early identification of potential issues, cultivators can implement effective interventions to protect their plants. This careful stewardship is essential for nurturing the development of high-quality cannabis buds, ultimately securing a successful and rewarding harvest.
The Final Weeks and Harvest Preparation
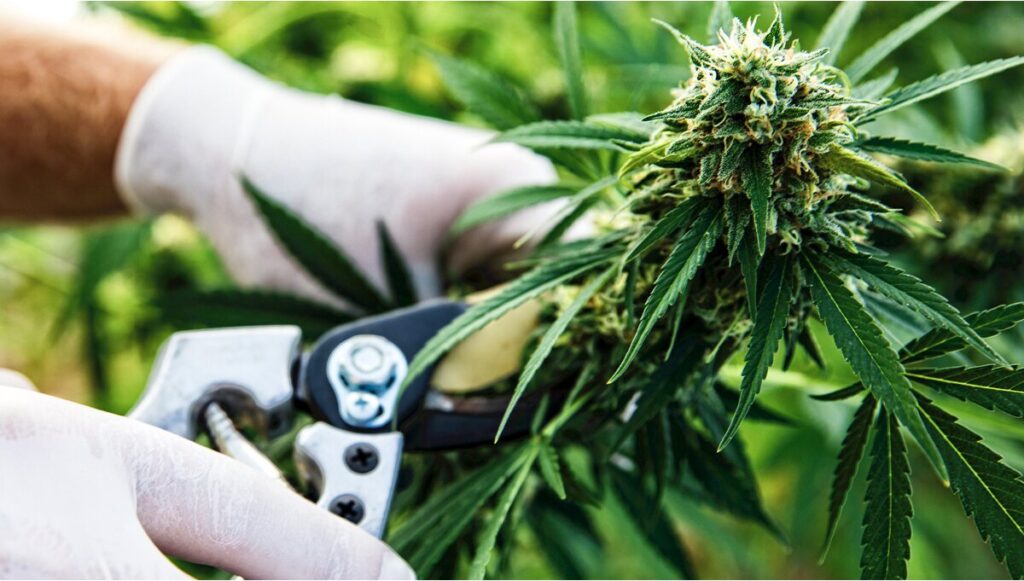

As the cannabis plants approach the culmination of the flowering stage, the attention of cultivators intensifies towards preparing for the impending harvest, a critical phase that significantly influences the final quality and potency of the cannabis buds. This preparation phase involves a series of meticulously planned steps designed to ensure the plants are in optimal condition for harvest, thereby maximizing the therapeutic and recreational attributes of the buds.
One key practice during these final weeks is the process known as flushing. This technique involves halting the application of nutrients to the plants and switching to pure water for irrigation purposes. The rationale behind flushing is to allow the plants to deplete the residual nutrients present within their tissues. These excess nutrients, if not adequately purged, can detract from the quality of the buds by imparting a harshness to the smoke and affecting the purity of the flavors and aromas. By flushing the plants, cultivators facilitate the removal of these surplus nutrients, thereby enhancing the smoothness, taste, and overall sensory experience of the final product.
Moreover, the observation of trichome development on the surface of the buds serves as a crucial indicator for determining the optimal timing for harvest. Trichomes, the minuscule, crystal-like structures adorning the surface of the buds, serve as the primary reservoir of cannabinoids and terpenes—the substances accountable for the psychoactive effects and aromatic characteristics of cannabis. As the flowering stage progresses, these trichomes change in appearance, transitioning from clear to cloudy and eventually to amber in color.
The predominance of cloudy trichomes with a proportion of amber ones is widely regarded as a sign of peak THC concentration within the plant, signaling that the buds have reached their maximum potency. Harvesting at this juncture ensures that the cannabis flowers are collected at the zenith of their cannabinoid and terpene production, offering an optimal balance between potency and effect. Conversely, harvesting too early or too late can result in a product that falls short of its potential, either in terms of strength or in the desired psychoactive and medicinal properties.
In conclusion, the final weeks of the flowering stage demand a strategic and observant approach to cultivation practices. Through the methodical flushing of plants and the careful monitoring of trichome maturation, cultivators can fine-tune the harvest timing to secure cannabis buds of superior quality. These steps, though seemingly simple, are pivotal in enhancing the desirability and efficacy of the harvest, underscoring the complexity and artistry inherent in cannabis cultivation.
Conclusion

Achieving proficiency in the flowering phase of cannabis growth is a blend of artistic skill and scientific knowledge, necessitating insight, perseverance, and careful observation. Through meticulous regulation of light patterns, nutritional intake, ambient conditions, and vigilant health checks of the plants, growers can enhance the caliber and strength of their cannabis buds. This holistic strategy boosts not only the harvest volume but also secures a fruitful and successful gathering of crops, symbolizing the peak of dedication poured into the entire growth cycle of the plant.