
Delta-8 THC vs. Delta-9 THC: Why It Matters in the Medical Field
Introduction
The cannabis plant is a complex organism with numerous compounds that interact with the human body in various ways. Among these compounds, cannabinoids have garnered significant attention for their therapeutic potential. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-9 THC) is the most well-known cannabinoid, primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis. However, Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Delta-8 THC), a close relative, is emerging as a significant compound with distinct properties and medical applications. This article delves into the differences between Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC, their medical implications, and why understanding these differences is crucial in the medical field.
Chemical Structure and Pharmacology
Delta-9 THC
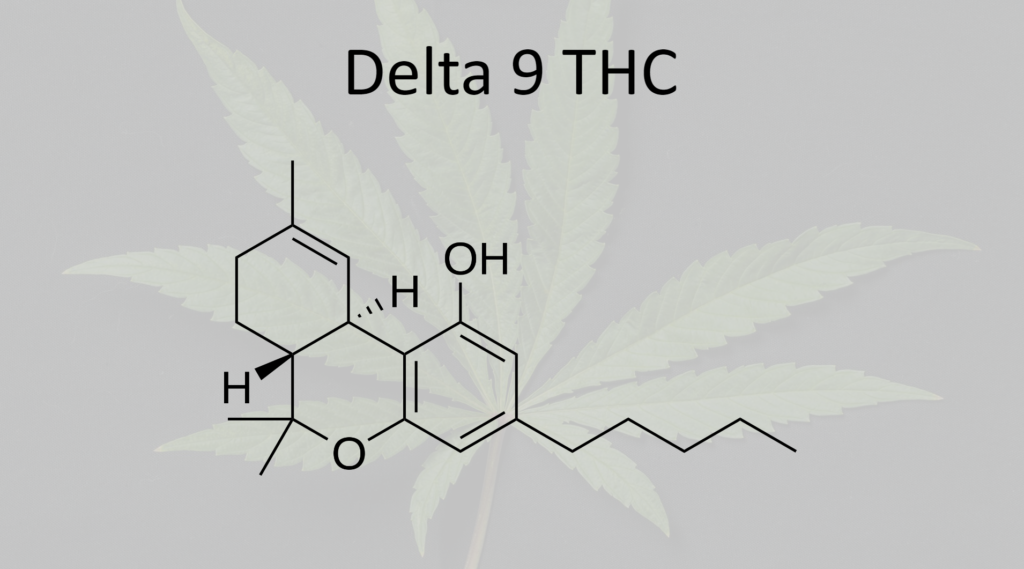
The main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis is delta-9 THC. It is well-known for its ability to induce euphoria, relaxation, and altered sensory perception. The chemical structure of Delta-9 THC is characterized by a double bond located at the ninth carbon atom in the cyclohexane ring. This specific placement is what gives Delta-9 THC its potent psychoactive properties.
Delta-9 THC binds predominantly to the CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system, leading to its psychoactive effects. It also interacts with CB2 receptors, which are more common in the peripheral organs and immune system. The binding to these receptors influences various physiological and psychological processes, including pain perception, appetite, mood, and memory.
Delta-8 THC
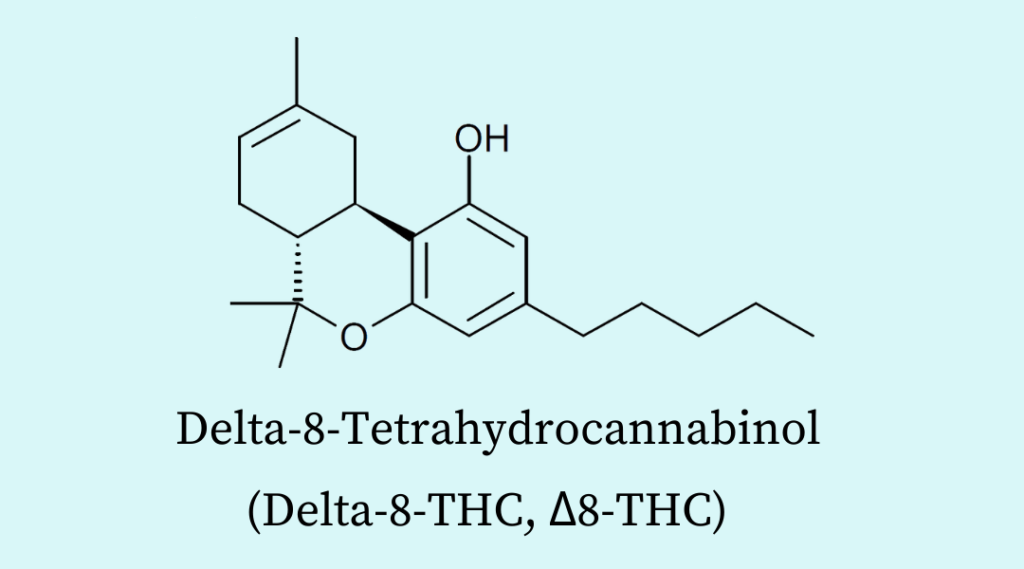
Because Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC are isomers, their molecular structures are similar but differ slightly. Instead of the ninth carbon atom, the double bond is found at the eighth one in delta-8 THC. This subtle variation drastically changes how it interacts with the body.
Similar to Delta-9 THC, Delta-8 THC binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors, but with less affinity. As a result, the psychoactive effect is lessened. Usually present in lower amounts, delta-8 THC is less common in cannabis plants and can be chemically changed into CBD (cannabidiol).
Medical Benefits and Applications of Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC
The distinct chemical structures and interactions with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) of Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC confer unique therapeutic benefits. Understanding these benefits and applications is crucial for leveraging these cannabinoids in medical treatments.
Pain Management
Delta-9 THC
Mechanism: Delta-9 THC is a potent analgesic that interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain and spinal cord. These interactions modulate pain signaling pathways, making it effective for various types of pain.
Applications:
- Chronic Pain: Rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain are a few chronic pain illnesses that are treated by delta-9 THC. Its effectiveness in lessening the severity of pain and enhancing quality of life has been extensively studied.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Delta-9 THC can alleviate muscle spasticity and pain associated with multiple sclerosis, providing significant relief for patients.
- Cancer Pain: It is also beneficial for managing pain in cancer patients, often in conjunction with other pain management strategies.
Delta-8 THC
Mechanism: Delta-8 THC has a similar, though less potent, interaction with CB1 and CB2 receptors, contributing to its analgesic effects. Its lower affinity for these receptors results in a milder psychoactive effect, which can be advantageous for patients sensitive to Delta-9 THC.
Applications:
- Arthritis: Delta-8 THC can reduce inflammation and pain in arthritis patients, offering an alternative for those who experience adverse effects from Delta-9 THC.
- Neuropathic Pain: Preliminary studies suggest that Delta-8 THC can effectively manage neuropathic pain, with fewer psychoactive side effects.
- Post-Surgical Pain: Its mild analgesic properties make it suitable for managing post-surgical pain, providing relief without significant cognitive impairment.
Nausea and Appetite Stimulation
Delta-9 THC
Mechanism: Delta-9 THC interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain and gastrointestinal tract, reducing nausea and stimulating appetite. Its effectiveness in this area has been recognized since the 1980s.
Applications:
- Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV): Delta-9 THC is highly effective in reducing CINV, improving patient comfort and adherence to cancer treatment protocols.
- HIV/AIDS: It helps in managing wasting syndrome by stimulating appetite and promoting weight gain in HIV/AIDS patients.
- Anorexia: Delta-9 THC can stimulate appetite in patients with anorexia and other eating disorders, aiding in nutritional intake and recovery.
Delta-8 THC
Mechanism: Delta-8 THC’s interaction with the ECS also helps reduce nausea and stimulate appetite, with a lower risk of severe psychoactive effects.
Applications:
- Pediatric Oncology: A study from 1995 demonstrated that Delta-8 THC effectively reduced nausea in children undergoing chemotherapy, with minimal side effects.
- Postoperative Recovery: Delta-8 THC can stimulate appetite and reduce nausea after surgery, aiding in recovery and nutritional intake.
- Geriatric Care: Its mild psychoactivity makes it suitable for elderly patients who need appetite stimulation without intense psychoactive effects.
Anxiety and Mental Health
Delta-9 THC
Mechanism: Delta-9 THC’s biphasic effects on anxiety mean it can reduce anxiety at low doses but potentially exacerbate it at higher doses due to its interaction with CB1 receptors and the subsequent modulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
Applications:
- PTSD: Delta-9 THC can help manage symptoms of PTSD, including reducing nightmares and hyperarousal.
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Some patients find relief from GAD symptoms with low doses of Delta-9 THC.
- Insomnia: Its relaxing effects can improve sleep quality, benefiting those with anxiety-related insomnia.
Delta-8 THC
Mechanism: Delta-8 THC’s lower psychoactivity and consistent anxiolytic effects make it a promising option for anxiety management. It modulates the ECS similarly to Delta-9 THC but with reduced risk of anxiety induction.
Applications:
- Anxiety Disorders: Delta-8 THC can provide consistent relief from anxiety disorders, including GAD and social anxiety disorder, without the risk of paranoia.
- Panic Attacks: Its calming effects may help manage acute panic attacks, providing a soothing alternative to traditional anxiolytics.
- Mood Disorders: Delta-8 THC can help stabilize mood, benefiting those with mood disorders such as bipolar disorder.
Neuroprotective Properties
Delta-9 THC
Mechanism: Delta-9 THC’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties contribute to its neuroprotective effects. It promotes neuronal health and shields brain cells from harm.
Applications:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Delta-9 THC can reduce inflammation and beta-amyloid plaque formation, potentially slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Parkinson’s Disease: It helps alleviate symptoms such as tremors and muscle rigidity, improving quality of life for Parkinson’s patients.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Delta-9 THC can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress following TBI, promoting recovery and reducing long-term damage.
Delta-8 THC
Mechanism: Delta-8 THC also exhibits neuroprotective properties, with studies showing its ability to reduce brain damage and improve cognitive function.
Applications:
- Stroke Recovery: Delta-8 THC can support recovery after a stroke by reducing inflammation and promoting neuronal repair.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Its neuroprotective effects may benefit patients with neurodegenerative diseases, potentially slowing disease progression.
- Cognitive Function: Delta-8 THC can help improve cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment or age-related cognitive decline.
Cancer Treatment
Delta-9 THC
Mechanism: Delta-9 THC can induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor growth through its interaction with the ECS and other cellular pathways.
Applications:
- Tumor Reduction: Delta-9 THC has shown promise in reducing the size and growth rate of various tumors, including those in breast and lung cancers.
- Supportive Care: It helps manage cancer-related symptoms such as pain, nausea, and loss of appetite, improving overall patient comfort and quality of life.
Delta-8 THC
Mechanism: Delta-8 THC’s anti-cancer properties are similar to Delta-9 THC, with the ability to induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor growth.
Applications:
- Research and Trials: While still in the early stages, research suggests Delta-8 THC could be an effective anti-cancer agent, providing a less psychoactive alternative to Delta-9 THC.
- Complementary Therapy: Delta-8 THC can be used alongside conventional cancer treatments to manage symptoms and potentially enhance treatment efficacy.
Safety and Side Effects of Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC

Both Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC have therapeutic potential, but their safety profiles and side effects differ. Understanding these differences is crucial for clinicians to make informed decisions about their use in medical treatments.
Delta-9 THC
Delta-9 THC is the most studied cannabinoid, and while it offers numerous therapeutic benefits, it also comes with a range of side effects, particularly at higher doses.
Cognitive Impairment
The euphoric effects of delta-9 THC are well-known, and they can affect cognitive abilities like:
- Short-term memory: Users often report difficulty in retaining new information while under the influence of Delta-9 THC.
- Attention and concentration: Delta-9 THC can reduce the ability to focus, making tasks that require sustained attention challenging.
- Judgment and decision-making: Altered judgment can lead to risky behaviors and impaired decision-making.
Psychiatric Effects
Delta-9 THC has a biphasic effect on mental health:
- Anxiolytic effects at low doses: At low doses, Delta-9 THC can reduce anxiety and provide a calming effect.
- Anxiety and paranoia at high doses: Higher doses are associated with increased anxiety, paranoia, and in some cases, panic attacks. This is particularly true for individuals with a predisposition to anxiety disorders.
Cardiovascular Effects
Delta-9 THC can influence cardiovascular function:
- Increased heart rate: Acute use of Delta-9 THC can cause tachycardia (increased heart rate), which can be uncomfortable for some users and potentially risky for individuals with heart conditions.
- Blood pressure changes: Delta-9 THC can cause temporary increases in blood pressure, followed by a drop in blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension), leading to dizziness and fainting in some cases.
Dependency and Tolerance
Long-term use of Delta-9 THC can lead to:
- Tolerance: As time goes on, users might need larger doses to have the same results, which would demand more intake.
- Dependency: Some users may develop a dependency on Delta-9 THC, characterized by withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, insomnia, and appetite disturbances when not using the substance.
Other Side Effects
Additional common side effects include:
- Dry mouth (xerostomia): Delta-9 THC reduces saliva production, leading to a dry mouth.
- Red eyes: It may result in enlarging blood vessels in the eyes, giving the appearance of bloodshot or red eyes.
- Increased appetite: Often referred to as “the munchies,” Delta-9 THC can stimulate appetite, which can be beneficial for certain medical conditions but undesirable in others.
Delta-8 THC
Delta-8 THC is similar to Delta-9 THC but tends to have a milder side effect profile due to its lower psychoactive potency.
Cognitive Effects
Delta-8 THC can cause cognitive effects, though typically less intense than those caused by Delta-9 THC:
- Mild euphoria: Users may experience a gentle sense of euphoria and well-being.
- Cognitive clarity: Many users report that Delta-8 THC provides relaxation without significant impairment of cognitive function.
Psychiatric Effects
Delta-8 THC is generally associated with a lower risk of psychiatric side effects:
- Reduced anxiety: Users often report a calming effect without the anxiety or paranoia that can accompany high doses of Delta-9 THC.
- Mood enhancement: Delta-8 THC can improve mood and reduce stress, making it a potentially useful tool for managing mild anxiety and mood disorders.
Cardiovascular Effects
The cardiovascular effects of Delta-8 THC are generally less pronounced than those of Delta-9 THC:
- Mild increase in heart rate: Some users may experience a slight increase in heart rate, but it is usually less intense than the effects of Delta-9 THC.
- Stable blood pressure: Delta-8 THC tends to have a more stable effect on blood pressure, reducing the risk of orthostatic hypotension.
Dependency and Tolerance
While Delta-8 THC can lead to tolerance and dependency, the risk is generally lower compared to Delta-9 THC:
- Tolerance development: Users may develop a tolerance over time, but the process tends to be slower than with Delta-9 THC.
- Dependency risk: The risk of developing a dependency on Delta-8 THC is present but considered lower, with milder withdrawal symptoms reported.
Other Side Effects
Common side effects of Delta-8 THC include:
- Dry mouth and eyes: Similar to Delta-9 THC, Delta-8 THC can cause dry mouth and eyes.
- Dizziness: Some users may experience dizziness, especially at higher doses.
- Increased appetite: Delta-8 THC can also stimulate appetite, though to a lesser extent than Delta-9 THC.
Legal Status and Accessibility
Delta-9 THC
According to the Controlled Substances Act, delta-9 THC is categorized as a Schedule I drug in the US, which means that the federal government does not recognize its significant potential for abuse and lacks any recognized medical use. But a patchwork of laws has resulted from the legalization of marijuana in many jurisdictions for both medical and recreational use.
Delta-8 THC
Delta-8 THC occupies a legal gray area. Derived from hemp, which is legal under the 2018 Farm Bill, Delta-8 THC is technically legal in many states if it contains less than 0.3% Delta-9 THC. However, some states have moved to explicitly ban Delta-8 THC, citing concerns over its psychoactive effects and lack of regulation.
The legal ambiguity affects accessibility and research opportunities. While Delta-8 THC products are available in many states, the lack of consistent regulation can lead to variability in product quality and safety.
Implications for the Medical Field
Research and Development
The distinct properties of Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC present unique opportunities for research and development in the medical field. Understanding the nuances of each cannabinoid can lead to more targeted therapies for various conditions.
Delta-9 THC
Delta-9 THC’s well-documented effects make it a valuable compound for research, especially in pain management, oncology, and neurology. However, its psychoactive properties and legal restrictions can limit clinical trials and broader applications.
Delta-8 THC
Delta-8 THC’s milder psychoactivity and potential therapeutic benefits position it as an exciting candidate for further research. Areas of interest include its role in pain relief, anti-nausea treatments, and neuroprotection. The relative legal accessibility of Delta-8 THC can facilitate more extensive clinical trials and studies.
Personalized Medicine
The differences between Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC highlight the potential for personalized medicine in cannabinoid therapy. Patients respond differently to each cannabinoid, and understanding these responses can lead to more effective and individualized treatment plans.
Safety and Regulation
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of cannabinoid-based treatments requires robust regulation and standardization. The varying legal statuses of Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC complicate this process. Establishing clear guidelines for production, testing, and labeling can enhance patient safety and trust in these therapies.
Education and Awareness
Healthcare providers need comprehensive education on the differences between Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC to make informed decisions about patient care. This includes understanding the pharmacology, potential benefits, side effects, and legal considerations associated with each cannabinoid.
Conclusion
The therapeutic potential of cannabinoids, specifically Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC, holds significant promise for a wide range of medical applications. These two compounds, while chemically similar, exhibit distinct pharmacological profiles and therapeutic benefits, making them valuable tools in the medical field.
Comparative Analysis
Delta-9 THC:
- Potency: Delta-9 THC is the more potent of the two, with strong psychoactive effects that can be both a benefit and a limitation.
- Applications: It is highly effective in managing chronic pain, chemotherapy-induced nausea, appetite stimulation, and has neuroprotective properties that can aid in conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- Side Effects: The intense psychoactivity of Delta-9 THC can lead to cognitive impairment, anxiety, paranoia, increased heart rate, and potential dependency with long-term use.
- Regulatory Status: Delta-9 THC remains a Schedule I substance in the United States, with varied legality across different states, complicating its medical use.
Delta-8 THC:
- Mild Psychoactivity: Delta-8 THC provides similar therapeutic benefits with milder psychoactive effects, making it a safer alternative for many patients.
- Applications: It is effective for pain relief, reducing nausea, stimulating appetite, and has anxiolytic and neuroprotective properties, potentially offering benefits in pediatric and geriatric care, and in patients with anxiety disorders.
- Side Effects: Delta-8 THC’s side effects are generally milder, including dry mouth, red eyes, dizziness, and increased appetite, with a lower risk of severe cognitive or psychiatric effects.
- Regulatory Status: Delta-8 THC occupies a legal gray area, being technically legal under federal law if derived from hemp but facing bans in some states. This inconsistency affects its accessibility and the standardization of products.
Implications for Medical Practice
The differences between Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC have significant implications for their use in medical practice. Delta-9 THC’s potency and wide range of applications make it a powerful option for severe conditions, but its side effects necessitate careful dosing and patient selection. In contrast, Delta-8 THC’s milder profile makes it suitable for patients requiring long-term management of symptoms without intense psychoactive effects, offering a broader therapeutic window and potentially greater safety.
Research and Development:
- Delta-9 THC: Continued research into its applications and side effect management is crucial, particularly in pain management, oncology, and neurology.
- Delta-8 THC: Expanding research into Delta-8 THC’s therapeutic potential, particularly in anxiety, neuroprotection, and pediatric care, can enhance its utility and integration into medical practice.
Personalized Medicine: The distinct effects and side effects profiles of Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC underscore the importance of personalized medicine in cannabinoid therapy. Tailoring treatments based on individual patient needs, conditions, and responses can optimize therapeutic outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
Regulatory Considerations: Harmonizing regulatory frameworks for both Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC is essential to ensure product quality, safety, and accessibility. Clear guidelines and standards for production, testing, and labeling can build patient trust and facilitate the integration of these cannabinoids into mainstream medical practice.
Education and Awareness: Healthcare providers need comprehensive education on the pharmacology, benefits, and risks associated with Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC. This knowledge is crucial for making informed clinical decisions and effectively communicating the potential benefits and risks to patients.
Future Directions
The future of cannabinoid-based medicine is promising, with Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC playing pivotal roles. As research advances, new therapeutic applications and improved formulations will likely emerge, expanding the scope of conditions that can be treated with these cannabinoids. The ongoing evolution of legal frameworks will also play a critical role in shaping their accessibility and integration into medical care.
In conclusion, Delta-8 THC and Delta-9 THC offer distinct and complementary benefits in medical treatment. Understanding their differences and therapeutic potential is essential for optimizing patient care and advancing the field of cannabinoid medicine. With continued research, education, and regulatory support, these cannabinoids can significantly enhance the landscape of medical treatments, providing new options for patients and clinicians alike.