CBD Oil for Eczema: Benefits, Effectiveness, Dosage
Understanding Eczema: A Chronic Skin Condition
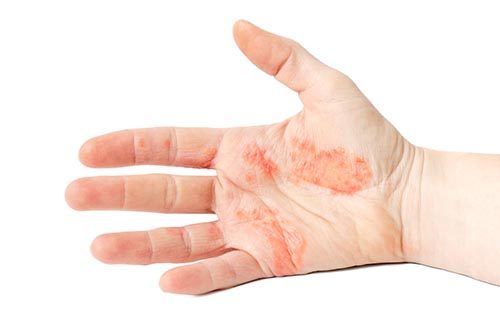
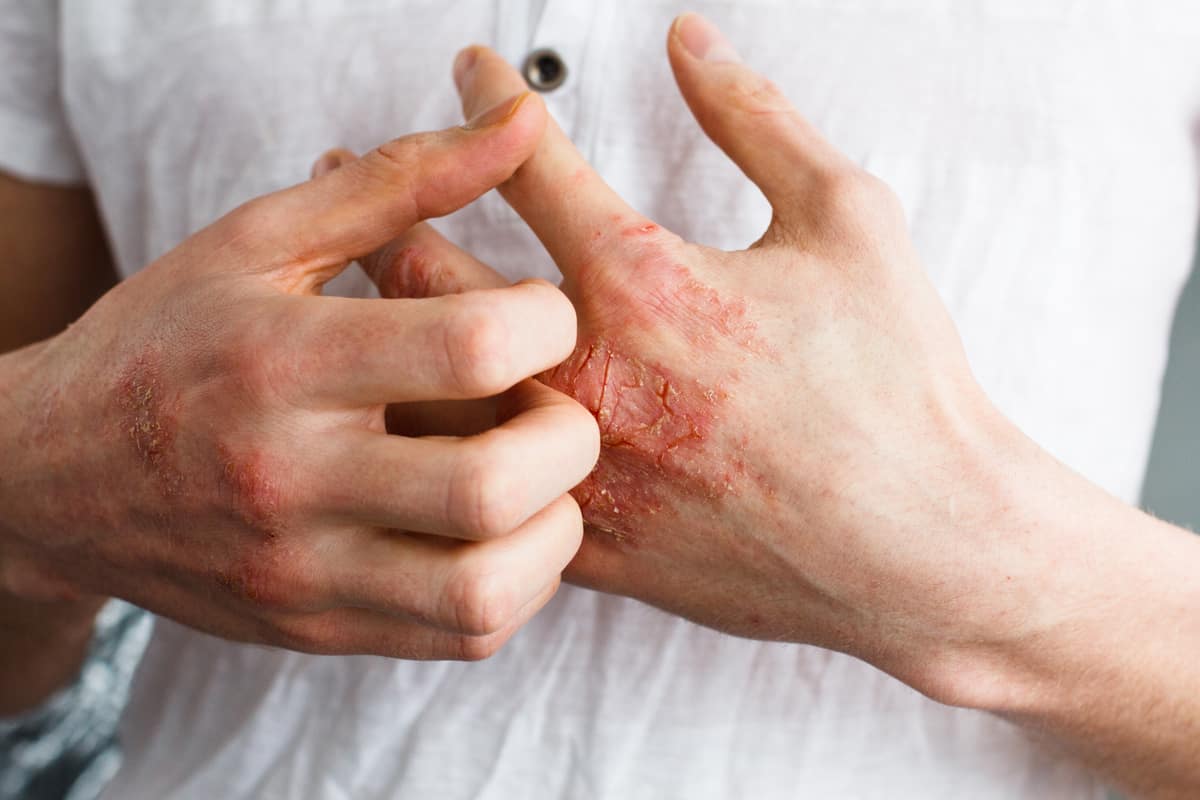
Before exploring how CBD oil may assist in managing eczema, it’s crucial to understand the condition itself. Eczema is primarily characterized by inflammation, itching, and the formation of red patches on the skin. It is often triggered by various environmental factors such as allergens, irritants, or stress. While the exact cause remains unknown, eczema is believed to involve an overactive immune response leading to chronic inflammation.
Common types of eczema include:
- Atopic dermatitis: The most typical type, which is common in adults as well as children.
- Contact dermatitis: Happens when allergens or irritants come into touch with the skin.
- Nummular eczema: Characterized by circular, coin-shaped spots of irritated skin.
- Dyshidrotic eczema: Results in blisters on the hands and feet.
Managing eczema typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, topical treatments, and sometimes oral medications, but these approaches may not be sufficient or desirable for everyone. Many patients turn to alternative treatments, including CBD oil, to address both the symptoms and underlying causes of the condition.
What is CBD Oil?

One of the compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant is called CBD (cannabidiol). Tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is the psychoactive ingredient in cannabis; in contrast, CBD doesn’t get users “high.” It is a good option for treating a number of illnesses, including eczema, because research has demonstrated that it has a wide range of therapeutic qualities, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antioxidant benefits.
The hemp form of the cannabis plant, which has very little THC, is usually used to produce CBD oil. Because it doesn’t have the same intoxication effects as THC, CBD oil is utilized for a variety of medical purposes and is legal in many nations. This makes it a desirable choice for people seeking all-natural remedies that don’t interfere with their day-to-day activities.
The Benefits of CBD Oil for Eczema
The potential benefits of CBD oil in managing eczema are largely linked to its anti-inflammatory and skin-soothing properties. Here are some of the key benefits supported by emerging research:
1. Anti-inflammatory Properties
One of the primary causes of eczema is inflammation. When the immune system becomes overactive, it triggers an inflammatory response in the skin, leading to the symptoms of eczema. CBD has been shown to have powerful anti-inflammatory effects, largely through its interaction with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS).
The ECS consists of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) found throughout the body, including in the skin. When CBD interacts with these receptors, it can modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation, potentially easing the redness, swelling, and irritation associated with eczema.
Studies have demonstrated that CBD may inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are molecules that play a central role in the body’s inflammatory response. By reducing the activity of these cytokines, CBD oil may help to alleviate the chronic inflammation seen in eczema.
2. Moisturizing and Hydrating Effects
Eczema is often accompanied by dry, cracked skin, which can exacerbate itching and irritation. CBD oil is rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential for maintaining healthy skin barrier function. These fatty acids help lock in moisture, keeping the skin hydrated and preventing the dryness that can trigger eczema flare-ups.
Additionally, topical application of CBD oil can soothe the skin by creating a protective barrier that helps retain moisture, reducing the discomfort and itching associated with eczema. While moisturizers alone may not be enough to address the underlying inflammation, combining them with CBD oil may offer more comprehensive relief.
3. Anti-Itch Properties
Itching is one of the most troublesome symptoms of eczema, and it can lead to a vicious cycle where scratching further irritates the skin, worsening the condition. CBD oil has been shown to have anti-pruritic (anti-itch) effects, potentially providing relief to patients with eczema.
CBD’s ability to interact with TRPV1 receptors (transient receptor potential vanilloid 1), which are involved in mediating pain and itch signals, may help to reduce the sensation of itching. By calming these receptors, CBD oil can decrease the urge to scratch, preventing further damage to the skin and promoting healing.
4. Antimicrobial Effects
Eczema patients are more susceptible to skin infections, particularly from bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus, which can worsen eczema symptoms and lead to complications. CBD oil has demonstrated antimicrobial properties in several studies, suggesting it may help reduce the risk of secondary infections in eczema patients.
By inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria on the skin, CBD oil can support the skin’s natural defense mechanisms and aid in preventing infections that could worsen eczema.
5. Reduction of Stress and Anxiety
While eczema is primarily a skin condition, stress and anxiety are well-known triggers for flare-ups. Many eczema patients report that their symptoms worsen during periods of heightened emotional stress. CBD oil may offer indirect benefits by reducing stress and anxiety levels.
CBD has been studied for its anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects and is thought to influence the brain’s serotonin receptors, which play a role in regulating mood and stress responses. By promoting relaxation and reducing stress, CBD oil may help to minimize the risk of eczema flare-ups triggered by emotional factors.
Effectiveness of CBD Oil for Eczema
While the research into CBD oil for eczema is still in its early stages, several studies and anecdotal reports suggest that it may be an effective treatment for managing eczema symptoms. The following sections explore some of the scientific evidence supporting the use of CBD oil in the medical treatment of eczema.
1. Studies on CBD and Inflammation
Several preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated the anti-inflammatory properties of CBD, which are highly relevant to its potential use for eczema. For example, a study published in the Journal of Dermatological Science found that CBD reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human skin cells, indicating its potential to reduce skin inflammation associated with eczema.
Additionally, a 2019 review in the journal Molecules highlighted the role of the endocannabinoid system in regulating skin homeostasis and inflammation. The review emphasized that cannabinoids like CBD could modulate inflammatory pathways in the skin, making them promising candidates for treating inflammatory skin conditions such as eczema.
2. Clinical Evidence from Topical CBD Use
While much of the research is still preclinical, there have been promising results from clinical studies investigating topical CBD formulations for inflammatory skin conditions, including eczema.
In a 2020 study published in Clinical Therapeutics, researchers tested a topical formulation of CBD on patients with inflammatory skin conditions, including eczema. After using the CBD cream for a few weeks, the majority of individuals in the research reported a significant decrease in symptoms like itching, discomfort, and dryness.
Furthermore, the National Eczema Association (NEA) has recognized the potential of CBD and other cannabinoids as an emerging therapy for eczema, although they call for more rigorous clinical trials to fully establish its efficacy.
3. Patient Testimonials and Anecdotal Evidence
While scientific studies provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of CBD oil, anecdotal evidence from eczema patients also offers encouraging feedback. Many individuals with eczema who have used CBD oil report improvements in their symptoms, particularly in reducing itching, inflammation, and dryness.
These testimonials, combined with the growing body of research, suggest that CBD oil could be a viable option for managing eczema, particularly in cases where traditional treatments have proven ineffective or have caused unwanted side effects.
Recommended Dosage of CBD Oil for Eczema
Determining the appropriate dosage of CBD oil for eczema can be challenging, as it may vary depending on factors such as the severity of the condition, the individual’s body weight, and the concentration of the CBD product being used. Since there are no standardized dosing guidelines for CBD, it is important to approach dosage recommendations with caution.
Here are some general considerations for dosing CBD oil for eczema:
1. Topical Application
For topical use, most CBD products designed for skin application come in the form of creams, lotions, or balms. The concentration of CBD in these products can vary widely, typically ranging from 100 mg to 1000 mg of CBD per container. When using CBD oil topically for eczema, it’s essential to apply the product directly to the affected area and massage it into the skin for optimal absorption.
A pea-sized amount of a CBD cream or balm can usually be applied to a localized area, such as a patch of eczema on the arm or leg. Users may need to apply the product 1-2 times daily for consistent results.
It’s important to note that CBD oil applied topically is not absorbed into the bloodstream in significant amounts, so it primarily provides localized relief.
2. Oral Use (Under Medical Supervision)
While this article excludes any discussion of CBD consumption methods, it’s worth mentioning that some patients may explore the use of oral CBD oil under medical supervision to manage eczema. This would involve taking CBD tinctures, capsules, or edibles. However, any form of oral CBD should be discussed with a healthcare provider, as it may interact with other medications or conditions.
Safety and Side Effects of CBD Oil for Eczema
CBD oil is generally well-tolerated by most individuals, especially when used topically. However, like any therapeutic agent, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects, especially for individuals with sensitive skin or those prone to allergies.
1. Topical Side Effects
When using topical CBD products, side effects are relatively rare but can include mild skin irritation or allergic reactions, particularly if the product contains additional ingredients such as fragrances or preservatives. To reduce the risk of skin reactions, patients should choose CBD products that are free of irritants and perform a patch test before applying the product to a larger area of the skin.
2. Oral CBD Side Effects
While this discussion excludes consumption methods, it’s worth noting that patients considering oral CBD oil should be aware of potential side effects, which may include dry mouth, drowsiness, and changes in appetite. Even though these adverse effects are usually transient and mild, it’s nevertheless advisable to speak with a doctor, particularly if the patient is also on other medications.
3. Interactions with Medications
Patients who are using other treatments for eczema, such as topical corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, should consult their healthcare provider before adding CBD oil to their treatment regimen. CBD has the potential to interact with certain medications, and professional guidance can help ensure that the combined use of CBD and other treatments is safe and effective.
Restrictions on Using CBD in the Medical Field as a Last Resort

While CBD is increasingly accepted as a therapeutic agent in many countries, its use is often subject to stringent regulatory restrictions, especially when considered as a last resort treatment. These restrictions arise from concerns about its safety, efficacy, and potential interactions with other medications.
1. Legislative and Regulatory Barriers
In many regions, the use of CBD is heavily regulated by national health authorities, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other global regulatory bodies. These authorities require extensive clinical trials and scientific evidence to prove the efficacy and safety of CBD for specific medical conditions before it can be approved for use in mainstream medicine.
When it comes to using CBD as a last resort, the regulatory hurdles can be even more significant. For example:
- Clinical Trial Requirements: Regulatory bodies often require that all other approved treatment options have been exhausted before CBD can be considered. In some cases, healthcare providers must provide documented evidence that standard treatments have failed to produce the desired outcome.
- Strict Guidelines on Dosage and Formulation: In many countries, medical professionals must adhere to specific dosing guidelines when prescribing CBD. This is particularly relevant for patients with severe conditions, where the risk of side effects may be higher, or when CBD is used as a final option after traditional treatments have failed.
- Prescription-Only Access: In some jurisdictions, CBD is only available through prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. Patients cannot legally access CBD products without a doctor’s recommendation, which limits its availability for last-resort treatments.
2. Use in Pediatric and Vulnerable Populations
Another major restriction on the use of CBD as a last resort involves its use in pediatric and vulnerable populations. For example, while CBD has shown promise in treating certain forms of epilepsy in children, such as Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, regulatory authorities often impose strict guidelines on its use in minors. This is due to concerns about long-term effects, the potential for drug interactions, and the risk of THC contamination, which can have more pronounced psychoactive effects in younger patients.
Additionally, healthcare providers may be required to obtain special authorization or follow specific protocols when prescribing CBD to populations with pre-existing conditions or compromised immune systems, where standard treatments are either ineffective or contraindicated.
3. Insurance and Reimbursement Limitations
In many countries, the cost of CBD-based medications is not covered by health insurance, making it difficult for patients to access CBD as a last resort treatment. This financial barrier can be particularly challenging for individuals who have exhausted other therapeutic options and are left with out-of-pocket costs for their treatment.
In jurisdictions where CBD is approved for medical use, it is often only available for certain conditions, and only after patients have tried all other approved medications. Even in these cases, insurance companies may require proof of the patient’s unsuccessful response to other treatments before covering the cost of CBD.
4. Ongoing Research and Lack of Standardization
One of the key limitations to using CBD as a last resort in the medical field is the lack of standardized dosing and long-term safety data. Since CBD is still a relatively new treatment option, especially in comparison to traditional pharmaceuticals, there is ongoing research to determine the optimal dosage, frequency, and delivery methods for various medical conditions.
Healthcare providers are often required to proceed with caution when prescribing CBD, particularly for conditions where there is insufficient clinical data. This may limit its use as a last resort, as doctors may hesitate to prescribe CBD without clear evidence of its efficacy and safety.
Monitoring THC Levels in Medications to Prevent Psychoactive Effects on Patients
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the psychoactive compound in cannabis, can cause mind-altering effects such as euphoria, paranoia, and altered perception of time. While CBD is non-psychoactive, there is always a risk that THC contamination in CBD products could lead to unintended psychoactive effects. For patients seeking medical treatment, particularly those who are sensitive to THC or vulnerable populations like children and the elderly, monitoring THC levels in CBD products is essential to ensure safety.
1. Legal Limits on THC in CBD Products
Most countries have set strict legal limits on the amount of THC that can be present in CBD products. For example:
- United States: Under the 2018 Farm Bill, CBD products derived from hemp must contain less than 0.3% THC by dry weight. Any product exceeding this threshold is classified as marijuana, which is still federally illegal in the U.S., though some states have different laws.
- European Union: In the EU, the legal limit for THC content in hemp-derived CBD products is 0.2% in most member states.
- Canada: Canada has more lenient regulations, allowing CBD products to contain up to 0.3% THC. However, these products are subject to stringent licensing requirements under the Cannabis Act.
By setting legal limits on THC, regulatory bodies aim to prevent any psychoactive effects from occurring in patients using CBD for medical purposes. Healthcare providers are responsible for ensuring that the CBD products they recommend comply with these regulations and do not exceed the allowed THC content.
2. Testing and Labeling Requirements
To ensure the safety of CBD-based medications, many countries impose testing and labeling requirements on manufacturers. These regulations require that all CBD products undergo rigorous third-party testing to verify their CBD and THC content before they are sold to consumers.
- Third-party testing: Independent laboratories test CBD products for their cannabinoid profile, ensuring that the THC levels are within the legal limits and that the product contains the stated amount of CBD.
- Certificate of Analysis (COA): After testing, the laboratory provides a COA, which confirms the levels of CBD and THC in the product. Manufacturers are required to make this information available to consumers, either through product labeling or by providing a QR code linking to the COA on their website.
Healthcare providers must be vigilant in recommending CBD products that have undergone proper testing and are accurately labeled. Patients should be encouraged to check the COA for their product to ensure that the THC levels are compliant with legal standards.
3. The Importance of Full-Spectrum vs. Isolate Products
When monitoring THC levels in CBD medications, it’s important to understand the difference between full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, and CBD isolate products:
- Full-spectrum CBD: Contains all cannabinoids and compounds found in the cannabis plant, including trace amounts of THC (within the legal limit). Full-spectrum products may offer the entourage effect, where the different cannabinoids work together synergistically, but they may also carry a higher risk of THC exposure.
- Broad-spectrum CBD: Similar to full-spectrum but with THC completely removed. Broad-spectrum products are a safer option for patients who want the benefits of other cannabinoids without the risk of THC’s psychoactive effects.
- CBD isolate: Contains only pure CBD and no other cannabinoids, including THC. CBD isolate is the safest option for patients concerned about psychoactive effects, as there is no risk of THC contamination.
Healthcare providers should consider recommending CBD isolate or broad-spectrum products for patients who need to avoid THC entirely, particularly in cases where there is a heightened sensitivity to THC or concerns about psychoactive effects.
4. Patient Education and THC Sensitivity
Not all patients respond to THC in the same way. Some individuals are more sensitive to its psychoactive effects, even at trace levels found in legal CBD products. For these patients, even minimal THC exposure could result in undesirable effects such as dizziness, anxiety, or altered cognitive function.
Healthcare providers should educate patients on the potential risks of THC in CBD medications and help them select products that best meet their medical needs. For patients with THC sensitivity, CBD isolate or broad-spectrum products are typically recommended to avoid any risk of psychoactive effects.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations in Monitoring THC Levels in Medical CBD Products
In addition to ensuring the safety and efficacy of CBD products, healthcare providers and manufacturers must adhere to ethical standards and regulatory guidelines when it comes to monitoring THC levels. Key considerations include:
1. Patient Safety and Well-Being
The primary responsibility of healthcare providers when recommending CBD products is to prioritize patient safety. By carefully selecting tested, regulated products with low or no THC, healthcare professionals can ensure that their patients receive the therapeutic benefits of CBD without the risk of psychoactive effects.
For patients using CBD as a last resort, providers must carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of THC exposure, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children, elderly patients, or individuals with a history of mental health conditions.
2. Regulatory Compliance
All CBD medications used in the medical field must comply with regional regulations regarding THC content. Healthcare providers must stay informed about local laws and ensure that the CBD products they recommend are compliant with legal THC limits.
Manufacturers are equally responsible for ensuring that their products are properly tested and labeled, and that they provide accurate information to both healthcare providers and patients regarding the THC content of their products.
Conclusion
In summary, CBD oil presents a promising option for addressing a variety of medical conditions, including eczema. Its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anti-itch, and moisturizing properties make it a potentially effective treatment for alleviating the symptoms of chronic skin disorders like eczema. Emerging scientific evidence and anecdotal reports support its use in reducing inflammation, itching, and dryness, which are hallmark symptoms of eczema. However, as a relatively new treatment modality, CBD oil requires further research to establish standardized dosing guidelines and long-term safety data, particularly for specific medical conditions.
When considering CBD in the medical field as a last resort treatment, it is essential to recognize the restrictions imposed by regulatory bodies. These limitations include the need for comprehensive clinical trials, adherence to strict guidelines on dosage, and ensuring that CBD is only considered when all other conventional treatments have failed. Moreover, vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly require special consideration, with healthcare providers carefully evaluating the risks and benefits of CBD for these groups.
A major concern in the use of CBD medications is the potential for THC contamination, which can result in unintended psychoactive effects on patients. Regulatory bodies in various countries have imposed strict THC limits in CBD products to safeguard patient safety, with 0.2% to 0.3% THC being the legal threshold in many regions. Healthcare providers and patients alike must ensure that CBD products are properly tested and labeled to avoid the risk of psychoactive exposure.
The importance of monitoring THC levels in CBD medications cannot be overstated. Healthcare providers must guide patients in choosing the appropriate full-spectrum, broad-spectrum, or CBD isolate products based on their medical needs and THC sensitivity. Patient education on the potential risks of THC and careful selection of high-quality CBD products with third-party testing are critical to ensuring safe and effective medical treatment.
In conclusion, while CBD oil offers significant therapeutic potential, especially for conditions like eczema and other chronic inflammatory diseases, its use in the medical field as a last resort requires careful consideration of legal restrictions, patient safety, and the need for rigorous THC monitoring. With further research and adherence to regulatory standards, CBD oil could become an integral part of medical treatment plans, offering patients a natural and effective alternative, particularly when conventional therapies have proven inadequate.