
Medical Cannabis vs. Alcohol: Societal Implications
Introduction
The debate over the societal implications of medical cannabis versus alcohol is multifaceted, involving various health, social, and economic dimensions. Both substances have been used for centuries, albeit for different purposes and with varying degrees of acceptance and regulation. While alcohol is widely accepted and legally consumed in many parts of the world, cannabis remains controversial, particularly its use for recreational versus medical purposes. This paper explores the negative effects of alcohol and recreational cannabis in contrast to the benefits of medical cannabis, highlighting their respective impacts on society.
Historical Context
Alcohol
There is historical proof that alcohol has been used for thousands of years, going all the way back to the early civilizations. It has been integral to cultural, religious, and social rituals. Despite its deep-rooted presence in society, alcohol consumption has been associated with numerous adverse effects, including addiction, health problems, and social issues.
Cannabis
Cannabis has a similarly long history of use, primarily for medicinal and spiritual purposes. Its psychoactive properties have been recognized for centuries, but its legal status has fluctuated dramatically, particularly in the 20th and 21st centuries. The distinction between medical and recreational cannabis is crucial, as the former is used under medical supervision for therapeutic purposes, while the latter is often consumed for its psychoactive effects.
The Negative Effects of Alcohol
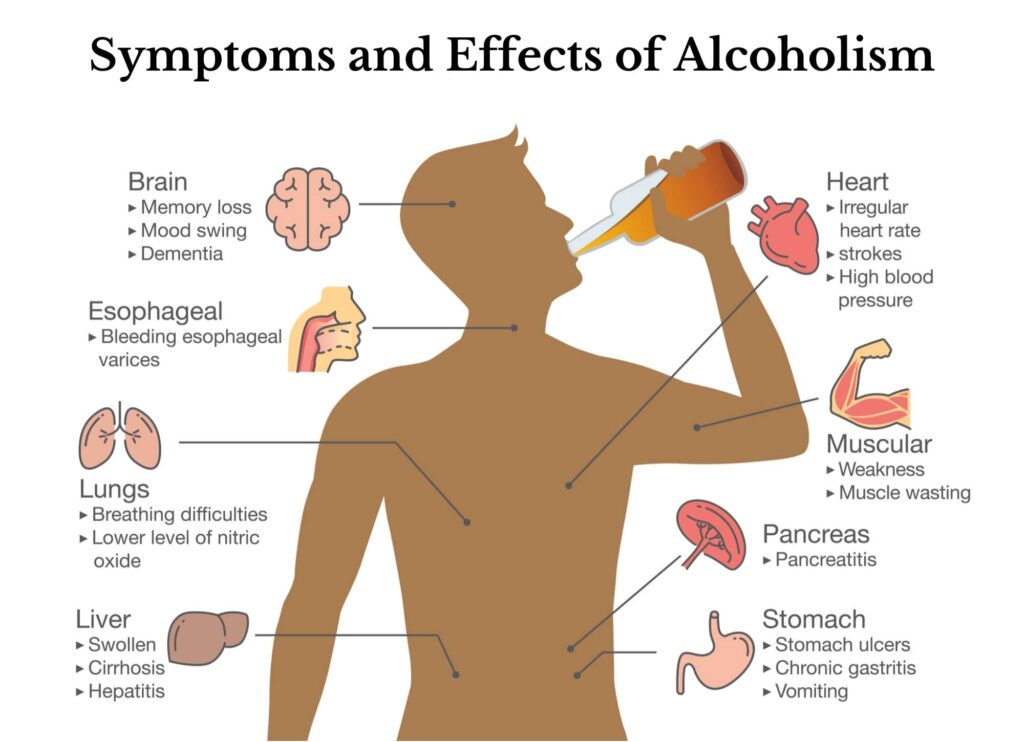
Health Implications
There are numerous health issues that are connected to alcohol usage. Chronic alcohol consumption can cause heart problems, pancreatitis, liver illnesses including cirrhosis, and a number of malignancies, including throat, oral, esophageal, liver, and breast cancer. A significant factor in mishaps and injuries, particularly those brought on by intoxicated driving, is alcohol.
Mental Health
Alcohol use and abuse can significantly impact mental health. It is often associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. Moreover, alcohol dependency, or alcoholism, is a severe condition that can lead to long-term psychological and physiological damage.
Social Consequences
The social implications of alcohol abuse are profound. It is a leading cause of domestic violence, child abuse, and other forms of interpersonal violence. Alcohol-related accidents and injuries place a significant burden on healthcare systems and contribute to lost productivity in the workplace.
The Negative Effects of Recreational Cannabis
Health Implications
Cannabis use for recreational purposes carries some dangers even though it’s frequently thought to be less hazardous than alcohol. Respiratory issues produced by cannabis smoke are comparable to those brought on by tobacco smoke. Additionally, heavy and prolonged use of cannabis has been linked to cognitive impairment, memory loss, and decreased IQ, particularly when use begins in adolescence.
Mental Health
Anxiety, depression, and psychosis are among the mental health conditions that are linked to recreational cannabis usage. Those who are predisposed to mental health illnesses are at a higher risk. Cannabis dependence, though less common than alcohol dependence, is a recognized condition that can lead to significant personal and social problems.
Social Consequences
The social effects of recreational cannabis use are less well-documented than those of alcohol but can include impaired academic and occupational performance, relationship issues, and legal problems. The illegal status of cannabis in many regions can also result in criminal records and associated social stigmas.
The Benefits and Potential Side Effects of Medical Cannabis

Therapeutic Uses
The potential of medicinal cannabis to relieve symptoms and enhance the quality of life for individuals with a range of medical diseases has attracted attention. Its therapeutic uses include:
- Chronic Pain Management:
- Cannabis is effective in managing chronic pain conditions such as neuropathic pain, multiple sclerosis, and arthritis. Studies have shown that cannabinoids, particularly THC and CBD, can reduce pain and inflammation, offering an alternative to opioids and other pain medications.
- Nausea and Vomiting:
- Medical cannabis is often used to alleviate nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy. Patients receiving cancer therapy have been reported to benefit most from THC’s antiemetic qualities.
- Appetite Stimulation:
- Patients with conditions like HIV/AIDS and cancer may experience significant weight loss and reduced appetite. Medical marijuana, especially THC-rich strains, has been shown to increase appetite and encourage weight gain.
- Seizure Disorders:
- Non-psychoactive cannabinoid CBD has demonstrated potential in lowering seizure frequency and intensity in epileptic patients, especially those with treatment-resistant types like Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome.
- Mental Health Conditions:
- Medical cannabis is used to manage symptoms of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). While evidence is mixed, some patients report significant relief from anxiety and improved mood with cannabis use.
- Sleep Disorders:
- Medical cannabis has the potential to mitigate sleep problems such as insomnia. Certain strains, particularly those high in CBD, can help improve sleep quality and duration.
- Inflammatory Conditions:
- Cannabis has anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Crohn’s disease, and other inflammatory conditions.
Side Effects
Despite its therapeutic benefits, medical cannabis is not without side effects. The severity and type of side effects can vary depending on the dosage, method of consumption, and individual patient factors. Common side effects include:
- Dizziness:
- Patients may experience dizziness or lightheadedness, particularly with high doses of THC. This effect can be more pronounced in older adults or those with low blood pressure.
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia):
- Dry mouth is a common side effect of cannabis use, caused by the cannabinoids’ effect on saliva production.
- Fatigue:
- Cannabis can cause drowsiness or fatigue, which may be beneficial for patients with sleep disorders but problematic for those needing to stay alert.
- Changes in Appetite and Weight:
- While appetite stimulation can be beneficial for some, it may lead to unwanted weight gain in others. Conversely, some patients may experience a decrease in appetite.
- Cognitive Impairment:
- THC can impair short-term memory, attention, and cognitive function, particularly at high doses. This effect is generally temporary but can be more significant in frequent users.
- Paranoia and Anxiety:
- High doses of THC can induce paranoia, anxiety, and panic attacks in some individuals. These effects are more likely in patients with a predisposition to mental health disorders.
- Hallucinations and Psychosis:
- In rare cases, particularly with high THC concentrations, patients may experience hallucinations or symptoms of psychosis. Those with a history of mental illnesses are more susceptible to this risk.
- Dependency and Withdrawal:
- While it is less common than with drugs like alcohol or opioids, cannabis addiction is nonetheless possible. Symptoms of withdrawal may include irritability, insomnia, and mood swings.
Comparative Analysis: Medical Cannabis vs. Alcohol
Health Outcomes
Alcohol
Alcohol consumption has a well-documented history of negative health outcomes. Chronic use can lead to:
- Liver Disease: Conditions like cirrhosis and hepatitis are directly linked to prolonged alcohol use.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Alcohol can cause hypertension, cardiomyopathy, and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Cancer: Alcohol is a known carcinogen associated with various cancers, including liver, breast, mouth, esophagus, and throat.
- Accidents and Injuries: Alcohol significantly impairs motor skills and judgment, leading to accidents, particularly those related to driving.
Medical Cannabis
Medical cannabis, when used appropriately, has demonstrated positive health outcomes, though it is not without risks:
- Chronic Pain Relief: It offers an alternative to opioids for managing chronic pain, reducing the risk of opioid addiction.
- Symptom Management: It helps manage symptoms of chemotherapy, such as nausea and vomiting, and stimulates appetite in patients with HIV/AIDS.
- Seizure Control: Particularly CBD, has shown efficacy in reducing seizures in epilepsy patients.
- Potential Side Effects: These include dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue, and cognitive impairment, but they are generally considered less severe compared to chronic alcohol use.
Mental Health
Alcohol
Alcohol can have severe negative impacts on mental health, including:
- Depression and Anxiety: Chronic alcohol use is linked to increased rates of depression and anxiety.
- Alcohol Dependency: Alcohol use disorder is a major mental health issue, leading to significant personal and social problems.
- Cognitive Impairment: Long-term alcohol use can lead to memory loss and cognitive decline.
Medical Cannabis
Medical cannabis has mixed impacts on mental health:
- Therapeutic Benefits: It can alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and PTSD in some patients.
- Risk of Psychosis: High THC levels can increase the risk of paranoia, anxiety, and psychosis, particularly in individuals predisposed to mental health disorders.
- Dependency: Cannabis dependency, while less common than alcohol dependency, can still occur, leading to withdrawal symptoms like irritability and insomnia.
Social Impact
Alcohol
The social impact of alcohol is profound and predominantly negative:
- Domestic Violence: Alcohol is a leading factor in domestic violence cases.
- Workplace Productivity: Alcohol use leads to absenteeism, decreased productivity, and increased workplace accidents.
- Public Safety: Alcohol-related incidents, such as drunk driving, pose significant public safety risks.
- Healthcare Burden: The treatment of alcohol-related illnesses and injuries places a heavy burden on healthcare systems.
Medical Cannabis
The social impact of medical cannabis is more nuanced:
- Reduced Criminalization: Legalizing medical cannabis reduces the criminal justice system’s burden associated with prosecuting cannabis-related offenses.
- Economic Benefits: Legalization can create jobs, generate tax revenue, and boost the economy.
- Social Acceptance: Increasing acceptance of medical cannabis can reduce the stigma associated with its use, but recreational use still faces significant stigma.
- Workplace Impacts: While less impairing than alcohol, high doses of cannabis can affect job performance and safety.
Economic Impact
Alcohol
The economic costs of alcohol are substantial:
- Healthcare Costs: Treating alcohol-related diseases and injuries is costly.
- Lost Productivity: Alcohol abuse leads to significant economic losses due to absenteeism and reduced productivity.
- Law Enforcement: Policing and prosecuting alcohol-related crimes also incur high costs.
Medical Cannabis
Medical cannabis offers several economic benefits:
- Healthcare Savings: Cannabis can reduce healthcare costs by providing an alternative treatment for chronic pain and other conditions, potentially reducing the use of more expensive medications like opioids.
- Tax Revenue: Legalizing medical cannabis generates substantial tax revenue.
- Job Creation: Jobs related to cannabis are generated in the retail, distribution, retail cultivation, and research sectors.
Responsible Use of Medical Cannabis

The responsible use of medical cannabis is crucial to ensuring that patients receive its therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential risks and side effects. This entails a number of crucial ideas and methods:
Medical Cannabis as a Last Resort
Medical cannabis ought to be saved for last-resort situations. This means it is typically prescribed only after other conventional treatments have failed or proven inadequate. This approach ensures that patients receive the most effective and well-established treatments first. Some specific considerations include:
- Thorough Diagnosis: Patients should undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation to confirm the diagnosis and assess whether traditional treatments have been exhausted.
- Documenting Treatment History: Healthcare providers should maintain detailed records of previous treatments and their outcomes to justify the use of medical cannabis.
Monitoring and Regulation
Careful monitoring and regulation of medical cannabis are essential to ensure its safe and effective use. Key measures include:
- THC Levels: Regulating THC levels in medical cannabis products is crucial to preventing psychoactive effects. By balancing THC with higher levels of CBD, which has therapeutic benefits without psychoactivity, the safety profile of medical cannabis can be improved.
- Dosage Control: Proper dosing is essential to avoid side effects and achieve the desired therapeutic outcomes. Healthcare providers should tailor the dosage to the individual patient’s needs and monitor their response.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that medical cannabis products meet high standards for purity and potency is vital. Testing for pollutants like pesticides, heavy metals, and microbiological impurities is part of this.
Patient Education
Educating patients about the potential benefits and risks of medical cannabis is vital. This includes:
- Understanding Side Effects: Patients should be informed about possible side effects, such as dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue, and cognitive impairment, and how to manage them.
- Safe Consumption Methods: Educating patients on safe methods of consumption, such as vaporizing or using tinctures, can reduce the risks associated with smoking cannabis.
- Interaction with Other Medications: It’s important for patients to understand how medicinal cannabis may interact with other prescription drugs they use.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Continuous monitoring and follow-up with patients using medical cannabis are essential to assess its efficacy and manage any adverse effects. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers can help to adjust dosages, switch strains, or explore alternative treatments if necessary. Key practices include:
- Regular Assessments: Conducting regular assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of medical cannabis and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Patient Feedback: Encouraging patients to provide feedback on their experiences, including any side effects or concerns, to tailor their treatment plan effectively.
Guidelines for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in the responsible use of medical cannabis. Guidelines for providers include:
- Comprehensive Training: Providers should receive comprehensive training on the therapeutic uses, potential risks, and legal considerations of medical cannabis.
- Patient Selection: Carefully selecting patients who are likely to benefit from medical cannabis based on their medical history and current condition.
- Informed Consent: Obtaining informed consent from patients, ensuring they understand the potential risks and benefits of medical cannabis.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Adhering to legal and ethical standards is paramount in the responsible use of medical cannabis. This includes:
- Compliance with Laws: Ensuring compliance with local, state, and federal laws regarding the prescription and use of medical cannabis.
- Patient Privacy: Protecting patient privacy and confidentiality in accordance with healthcare regulations and standards.
- Ethical Prescribing: Prescribing medical cannabis ethically, avoiding conflicts of interest, and prioritizing patient welfare.
Policy Implications
Regulation and Legalization
The regulation and legalization of substances are critical in mitigating their negative effects and maximizing benefits. Strict regulation of alcohol has been implemented in many regions, with measures such as age restrictions, licensing, and taxation. Similarly, the regulation of medical cannabis can ensure its safe and effective use while minimizing the risks associated with recreational use.
Public Health Strategies
Public health strategies should focus on education and harm reduction. Educating the public about the risks of alcohol and recreational cannabis and the benefits of medical cannabis can lead to informed decision-making. Harm reduction approaches, such as providing safe consumption spaces and support for addiction treatment, can mitigate the negative impacts of these substances.
Conclusion
The comparative analysis of medical cannabis and alcohol reveals significant differences in their health outcomes, social impacts, and economic implications. While both substances have the potential for misuse and adverse effects, alcohol is associated with more severe health risks, including liver disease, cardiovascular issues, cancer, and cognitive impairment. Alcohol abuse also has profound negative social consequences, such as domestic violence, impaired workplace productivity, and public safety hazards, which impose a substantial burden on healthcare and law enforcement systems.
In contrast, medical cannabis, when used responsibly and under medical supervision, offers notable therapeutic benefits. It is effective in managing chronic pain, alleviating symptoms of chemotherapy, stimulating appetite in patients with severe weight loss, and reducing seizures in epilepsy. Despite these benefits, medical cannabis is not without side effects, which can include dizziness, dry mouth, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and, in rare cases, psychosis and dependency. These side effects, however, are generally considered less severe than the chronic health impacts associated with alcohol.
The responsible use of medical cannabis involves considering it as a treatment of last resort, ensuring that it is prescribed only after other conventional treatments have proven inadequate. Monitoring and regulating THC levels in medical cannabis products is crucial to minimizing psychoactive effects and enhancing safety. Continuous patient education, careful dosing, and regular follow-up with healthcare providers are essential to maximize therapeutic benefits while mitigating risks.
The economic benefits of legalizing medical cannabis include job creation, tax revenue generation, and potential healthcare cost savings by providing alternatives to more expensive medications like opioids. Reduced criminalization associated with medical cannabis legalization also alleviates the burden on the criminal justice system.
Public health strategies should prioritize education, harm reduction, and informed policy decisions to enhance societal well-being. Educating the public about the risks of alcohol and recreational cannabis, along with the benefits and potential side effects of medical cannabis, can lead to more informed decision-making and safer use of these substances.
In conclusion, while both alcohol and cannabis have their respective risks and benefits, the therapeutic potential and relatively lower health risks of medical cannabis position it more favorably in terms of societal impacts. By understanding and addressing the distinct impacts of alcohol, recreational cannabis, and medical cannabis, society can make informed decisions about their use and regulation, ultimately promoting public health, safety, and well-being. The careful and responsible use of medical cannabis, along with effective monitoring and regulation, can help maximize its benefits while minimizing potential harms.