
Foliar Spraying and Medical Cannabis
Introduction
Foliar spraying is a method of applying nutrients directly to the leaves of plants, providing a more immediate nutrient uptake compared to soil applications. This technique is increasingly popular in the cultivation of medical cannabis due to its efficiency and effectiveness in addressing nutrient deficiencies and enhancing plant growth. This comprehensive guide will delve into the science behind foliar spraying, its benefits, best practices, and its specific application in the cultivation of medical cannabis.
The Science Behind Foliar Spraying

Foliar spraying involves the application of nutrient solutions directly onto the leaves of plants. The process relies on the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients through its stomata and cuticle. Stomata are tiny openings on the leaf surface that facilitate gas exchange, while the cuticle is a waxy layer that covers the leaf and helps retain water. When nutrients are sprayed onto the leaves, they are absorbed quickly and transported to various parts of the plant.
Key Components of Foliar Spraying:
- Stomatal Absorption: Stomata open and close to regulate gas exchange and water loss. When open, they allow nutrients in the foliar spray to enter the leaf.
- Cuticular Penetration: The cuticle can absorb small amounts of nutrients. Nutrient uptake through the cuticle is slower than through the stomata but still significant.
- Nutrient Mobility: Once inside the leaf, nutrients can be transported to other parts of the plant, ensuring that the entire plant benefits from the foliar application.
Benefits of Foliar Spraying
Foliar spraying offers several advantages, especially in the context of medical cannabis cultivation:
- Rapid Nutrient Uptake: Foliar spraying allows for faster nutrient absorption compared to soil application. This rapid uptake can quickly address nutrient deficiencies and improve plant health.
- Increased Efficiency: Applying nutrients directly to the leaves can be more efficient than soil applications, as it reduces the risk of nutrient leaching and runoff.
- Targeted Application: Foliar spraying allows for precise targeting of specific nutrients to address particular deficiencies or growth stages.
- Improved Plant Health: Frequent use of foliar spraying can improve the general health of plants, making them more robust and resilient.
- Enhanced Yield and Quality: Healthier plants with optimal nutrient levels tend to produce higher yields and better-quality flowers, which is particularly important in the cultivation of medical cannabis.
Best Practices for Foliar Spraying
Foliar spraying, the application of liquid nutrients directly onto the leaves of plants, is a valuable technique for delivering essential nutrients rapidly and effectively. When done correctly, it can significantly enhance the health, growth, and yield of medical cannabis plants. Here are the best practices to ensure the effectiveness and safety of foliar spraying in medical cannabis cultivation:
1. Choosing the Right Time for Foliar Spraying
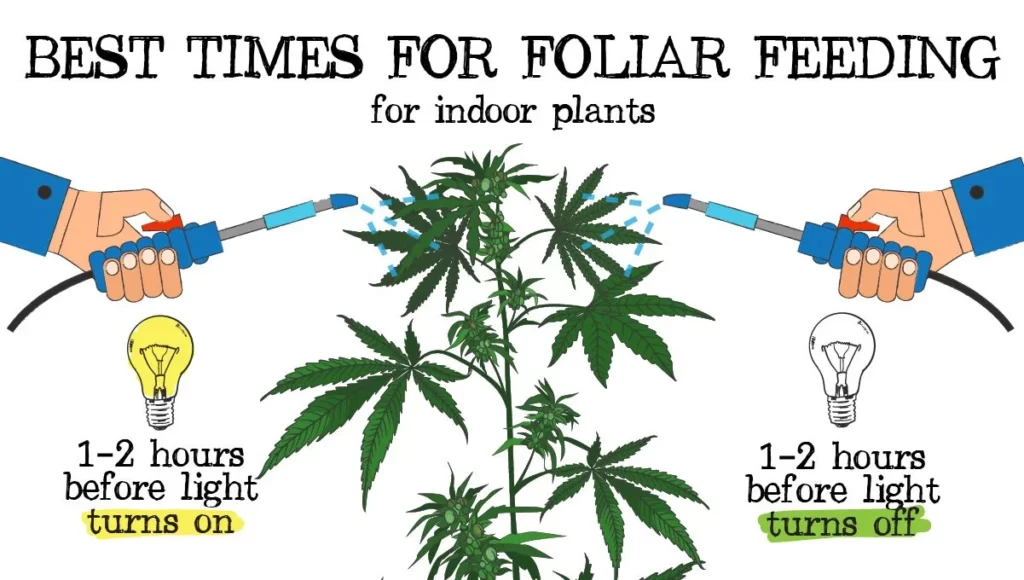
Timing is critical to maximize nutrient uptake and minimize potential damage to the plants:
- Early Morning or Late Afternoon: Spray early in the morning or late in the afternoon when temperatures are cooler, and the risk of evaporation is lower. This timing also coincides with the natural opening of stomata, facilitating better nutrient absorption.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Avoid spraying during the heat of the day when direct sunlight can cause the solution to evaporate quickly and potentially burn the leaves.
2. Using Proper Equipment
Selecting the right equipment ensures even distribution and effective application of the foliar spray:
- Fine Mist Sprayer: Use a fine mist sprayer to ensure even coverage of the leaf surfaces. Fine mist sprayers create small droplets that are easily absorbed by the leaves.
- Avoid High-Pressure Sprayers: High-pressure sprayers can damage the delicate leaf tissue and cause uneven distribution of the nutrient solution.
3. Preparing the Nutrient Solution
The correct preparation of the nutrient solution is essential for the safety and effectiveness of foliar spraying:
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Adhere to the recommended dilution rates provided by the nutrient manufacturer. Over-concentration can cause leaf burn, while under-concentration may be ineffective.
- Mix Thoroughly: Ensure the solution is well-mixed to provide consistent nutrient delivery.
- Adjust pH Levels: The pH of the foliar spray solution should be between 5.5 and 7.0 for optimal nutrient uptake. To test and modify the pH as necessary, use a pH meter or pH strips.
4. Applying the Foliar Spray
Proper application techniques maximize nutrient absorption and minimize waste:
- Spray Both Sides of the Leaves: Ensure thorough coverage by spraying both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves, as stomata are more concentrated on the underside.
- Apply Evenly: Aim for even application to avoid areas of excess or insufficient nutrient concentration.
- Avoid Over-Spraying: Apply enough solution to wet the leaves but avoid excessive runoff. Over-spraying can lead to nutrient wastage and potential leaf damage.
5. Frequency of Application
Regular but controlled application is crucial for maintaining plant health without overloading the plants:
- Weekly or Bi-Weekly: Depending on the plant’s needs and growth stage, foliar spraying can be done weekly or bi-weekly. Keep an eye out for any indications of nutrient surpluses or deficits in the plants and modify the frequency as necessary.
6. Monitoring and Adjusting
Continuous monitoring and adjustment are key to successful foliar spraying:
- Observe Plant Response: After foliar spraying, observe the plants for any signs of improvement or adverse effects such as leaf burn or discoloration.
- Adjust Nutrient Levels: Based on plant response and visual inspection, adjust the concentration and frequency of the foliar spray applications.
7. Maintaining Cleanliness
Cleanliness is vital to prevent contamination and ensure effective nutrient delivery:
- Clean Leaves: Ensure the leaves are free of dust and debris before spraying. Dirty leaves can obstruct nutrient absorption.
- Sanitize Equipment: Regularly clean and sanitize sprayers and mixing containers to prevent the buildup of residues and potential pathogen contamination.
Application of Foliar Spraying in Medical Cannabis Cultivation
Foliar spraying is a critical technique in medical cannabis cultivation, allowing growers to provide precise and immediate nutrient delivery to their plants. This method is particularly beneficial in addressing nutrient deficiencies, enhancing growth, and improving the quality of the final product. Here’s a detailed look at how foliar spraying can be applied in the cultivation of medical cannabis:
1. Nutrient Supplementation
Medical cannabis plants have specific nutrient requirements at various stages of growth. Foliar spraying can effectively address these needs:
- Vegetative Stage:
- Nitrogen: High levels of nitrogen are crucial during the vegetative stage to promote vigorous leaf and stem growth. A foliar spray containing nitrogen can help boost vegetative development.
- Micronutrients: Zinc, iron, and manganese are essential for chlorophyll production and enzyme function. Including these in the foliar spray ensures that the plants receive an adequate supply.
- Flowering Stage:
- Phosphorus and Potassium: These nutrients are vital during the flowering stage to support bud formation and enhance flower quality. A foliar spray rich in phosphorus and potassium can significantly improve flower development and potency.
- Calcium and Magnesium: These nutrients support cell structure and chlorophyll production, which are essential during the flowering stage.
2. Stress Mitigation
Environmental stresses such as temperature fluctuations, drought, or pest infestations can negatively impact medical cannabis plants. Foliar spraying can help mitigate these stresses:
- Biostimulants: Foliar sprays containing biostimulants like kelp extract, amino acids, and humic acids can help plants recover from stress and enhance their resilience.
- Anti-Stress Agents: Products like silicon can be included in foliar sprays to improve the plant’s resistance to environmental stresses.
3. Pest and Disease Control
Foliar spraying can be integrated with pest and disease management strategies to protect medical cannabis plants:
- Organic Pesticides: Neem oil, insecticidal soaps, and other organic pesticides can be applied as foliar sprays to control pests such as spider mites, aphids, and whiteflies.
- Fungicides: Organic fungicides like potassium bicarbonate and copper-based products can be used in foliar sprays to prevent and control fungal infections such as powdery mildew and botrytis.
4. Enhancing Flower Quality
The quality of medical cannabis flowers is paramount, as it directly affects the therapeutic efficacy of the final product. Foliar spraying can enhance flower quality in several ways:
- Terpene Production: Foliar sprays containing sulfur and potassium can boost terpene production, enhancing the aroma and therapeutic properties of the flowers.
- Bud Density and Size: By ensuring optimal nutrient levels during the flowering stage, foliar spraying can improve bud density and size, resulting in higher yields and better quality.
Detailed Steps for Foliar Spraying in Medical Cannabis
Foliar spraying, when done correctly, can significantly enhance the growth, health, and yield of medical cannabis plants. This method allows for rapid nutrient uptake, targeted application, and immediate correction of deficiencies. Here are the detailed steps for effective foliar spraying in medical cannabis cultivation:
1. Preparation
Identify Nutrient Needs
- Soil and Tissue Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of the soil and plant tissue to identify any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances. This information will guide the selection of appropriate nutrients for foliar spraying.
- Growth Stage Requirements: Understand the specific nutrient needs of cannabis plants at different growth stages (vegetative, flowering, etc.).
Choose the Right Nutrients
- Commercial Solutions: Select high-quality, commercially available foliar spray solutions designed for cannabis or general horticultural use.
- DIY Nutrient Solutions: Consider making your own nutrient solutions if you have a good understanding of the required nutrients. Common nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese.
2. Mixing the Solution
Dilution
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Dilute the nutrient solution according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid over-concentration, which can burn the leaves, or under-concentration, which may be ineffective. Typically, 1-2 teaspoons of concentrate per gallon of water is recommended.
- Mix Thoroughly: Ensure that the solution is mixed thoroughly to provide consistent nutrient delivery.
pH Adjustment
- Test pH Levels: Use a pH meter or pH strips to test the pH of the foliar spray solution. The optimal pH range for nutrient uptake through the leaves is between 5.5 and 7.0.
- Adjust pH: If necessary, adjust the pH using pH up or down solutions to ensure it falls within the optimal range.
3. Application
Timing
- Early Morning or Late Afternoon: When the weather is colder and there is less chance of evaporation, apply the foliar spray in the early afternoon or early morning. This timing also coincides with the natural opening of stomata, facilitating better nutrient absorption.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Do not spray during the heat of the day to prevent rapid evaporation and potential leaf burn.
Equipment
- Fine Mist Sprayer: Use a fine mist sprayer to ensure even coverage of the leaf surfaces. Fine mist sprayers create small droplets that are easily absorbed by the leaves.
- Avoid High-Pressure Sprayers: High-pressure sprayers can damage the delicate leaf tissue and cause uneven distribution of the nutrient solution.
Spray Coverage
- Upper and Lower Leaf Surfaces: Ensure thorough coverage by spraying both the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves, as stomata are more concentrated on the underside.
- Even Application: Aim for even application to avoid areas of excess or insufficient nutrient concentration.
Spray Volume
- Wet the Leaves: Apply enough solution to wet the leaves without causing runoff. Over-application can lead to nutrient wastage and potential leaf damage.
4. Post-Spraying Care
Monitor Plants
- Observe Plant Response: After foliar spraying, closely observe the plants for any signs of improvement or adverse effects such as leaf burn, discoloration, or wilting.
- Adjust Nutrient Levels: Based on plant response and visual inspection, adjust the concentration and frequency of the foliar spray applications.
Rinse Leaves Occasionally
- Prevent Residue Buildup: Rinse the leaves occasionally with plain water to prevent the buildup of nutrient residues, which can interfere with photosynthesis and nutrient absorption.
Common Nutrients Used in Foliar Spraying

- Nitrogen (N): Essential for vegetative growth, nitrogen is often applied during the early stages of cannabis growth. It promotes leaf development and overall plant vigor.
- Phosphorus (P): Crucial for root development and flowering, phosphorus is typically applied during the flowering stage to enhance bud formation and potency.
- Potassium (K): Important for overall plant health and disease resistance, potassium helps regulate water uptake and enzyme activation.
- Calcium (Ca): Vital for cell wall structure and stability, calcium prevents issues like blossom end rot and promotes strong, healthy growth.
- Magnesium (Mg): A key component of chlorophyll, magnesium is essential for photosynthesis and overall plant energy production.
- Trace Elements: Micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and boron (B) are required in small amounts but are crucial for various metabolic functions.
DIY Foliar Spray Recipes for Medical Cannabis
Creating your own foliar spray recipes allows for customization based on the specific needs of your cannabis plants at different stages of growth. Here are some effective DIY foliar spray recipes tailored for medical cannabis cultivation:
1. Basic Nutrient Solution
Ingredients:
- 1 teaspoon calcium nitrate
- 1 teaspoon magnesium sulfate (Epsom salt)
- 1 gallon of water
Instructions:
- Dissolve the calcium nitrate and magnesium sulfate in 1 gallon of water.
- Mix thoroughly until all the salts are completely dissolved.
- Adjust the pH to 6.0 using a pH up or down solution.
- Apply the solution to both the top and below leaf surfaces using a fine mist sprayer.
Benefits:
- Calcium nitrate provides essential calcium and nitrogen.
- Magnesium sulfate supplies magnesium and sulfur, vital for photosynthesis and enzyme function.
2. Organic Kelp Extract Spray
Ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons of kelp extract
- 1 gallon of water
Instructions:
- Mix 2 tablespoons of kelp extract with 1 gallon of water.
- Make sure the extract is well dispersed by giving it a good stir.
- Adjust the pH to 6.0 if necessary.
- Apply with a fine mist sprayer to the leaves, covering both sides.
Benefits:
- Kelp extract is rich in natural growth hormones, trace elements, and biostimulants that enhance plant growth and stress resistance.
3. Compost Tea Foliar Spray
Ingredients:
- 1 part compost
- 5 parts water
Instructions:
- Place the compost in a mesh bag or cheesecloth and steep in water for 24-48 hours to brew compost tea.
- After brewing, remove the compost and dilute the tea with water at a 1:5 ratio.
- Adjust the pH to 6.0.
- Douse the leaves with the compost tea using a fine mist sprayer.
Benefits:
- Compost tea provides a rich source of nutrients and beneficial microorganisms that promote plant health and vigor.
4. Fish Emulsion Foliar Spray
Ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons of fish emulsion
- 1 gallon of water
Instructions:
- Pour one gallon of water and two tablespoons of fish emulsion into it.
- Stir well to ensure even distribution.
- Adjust the pH to 6.0 if necessary.
- Apply with a fine mist sprayer, ensuring thorough coverage of the leaves.
Benefits:
- Fish emulsion is an excellent source of nitrogen and other essential nutrients that promote robust vegetative growth.
5. Epsom Salt Foliar Spray
Ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon of Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate)
- 1 gallon of water
Instructions:
- Dissolve 1 tablespoon of Epsom salt in 1 gallon of water.
- Stir until completely dissolved.
- Adjust the pH to 6.0.
- Apply with a fine mist sprayer to the upper and lower leaf surfaces.
Benefits:
- Epsom salt provides magnesium and sulfur, which are crucial for chlorophyll production and overall plant health.
6. Neem Oil Foliar Spray
Ingredients:
- 1 teaspoon of neem oil
- 1 teaspoon of liquid soap (as an emulsifier)
- 1 gallon of water
Instructions:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of neem oil with 1 teaspoon of liquid soap in 1 gallon of water.
- Stir thoroughly to emulsify the neem oil.
- Apply with a fine mist sprayer, ensuring thorough coverage of the leaves.
Benefits:
- Neem oil acts as a natural pesticide and fungicide, protecting cannabis plants from pests and diseases while providing some nutritional benefits.
7. Silica Foliar Spray
Ingredients:
- 1 teaspoon of silica solution
- 1 gallon of water
Instructions:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of silica solution with 1 gallon of water.
- Stir well to ensure even distribution.
- Adjust the pH to 6.0 if necessary.
- Apply with a fine mist sprayer to the leaves, covering both sides.
Benefits:
- Silica strengthens cell walls, enhancing the plant’s resistance to environmental stress and physical damage.
Potential Challenges and Solutions in Foliar Spraying for Medical Cannabis

While foliar spraying can significantly benefit medical cannabis cultivation, it also presents certain challenges that need to be carefully managed to ensure optimal plant health and productivity. Here are some potential challenges and their solutions:
1. Leaf Burn
Challenge:
- Over-application or using a highly concentrated nutrient solution can cause leaf burn, which manifests as yellow or brown spots and can damage the plant.
Solution:
- Proper Dilution: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended dilution rates for foliar sprays. For DIY solutions, ensure accurate measurement of ingredients.
- Test Spraying: Perform a test spray on a small section of the plant before full application. Observe for any adverse reactions within 24-48 hours.
- Application Timing: Spray early in the morning or late in the afternoon when temperatures are cooler to minimize evaporation and reduce the risk of leaf burn.
2. Pathogen Spread
Challenge:
- Foliar spraying can spread pathogens, especially if the water or equipment used is contaminated.
Solution:
- Sanitize Equipment: Regularly clean and sanitize sprayers and mixing containers to prevent contamination.
- Use Clean Water: Use distilled or purified water to mix foliar sprays to avoid introducing pathogens.
- Monitor Plant Health: Inspect plants regularly for signs of disease and treat any infections promptly.
3. Residue Buildup
Challenge:
- Repeated foliar spraying can lead to nutrient residue buildup on the leaves, which can obstruct photosynthesis and nutrient absorption.
Solution:
- Occasional Rinsing: Rinse the leaves occasionally with plain water to remove any residue buildup. Depending on how frequently foliar spraying is done, this can be done either weekly or bi-weekly.
- Moderate Application: Avoid over-application of foliar sprays to minimize residue accumulation.
4. Inconsistent Results
Challenge:
- Variability in plant response to foliar sprays can occur due to differences in environmental conditions, plant genetics, and nutrient formulations.
Solution:
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the plants for signs of improvement or adverse effects and adjust the foliar spray regimen as needed. Keep records of applications and plant responses to identify patterns and make informed adjustments.
- Tailor to Growth Stage: Customize foliar spray formulations based on the specific needs of the plants at different growth stages (vegetative, flowering, etc.).
5. Evaporation
Challenge:
- Rapid evaporation of the foliar spray solution can reduce its effectiveness, especially in hot and dry conditions.
Solution:
- Timing: Apply foliar sprays during early morning or late afternoon when temperatures are cooler and humidity is higher.
- Humidity Control: Maintain adequate humidity levels in the growing environment to reduce evaporation rates.
6. Sprayer Clogging
Challenge:
- Nutrient solutions, especially those containing organic materials, can clog sprayer nozzles, leading to uneven application.
Solution:
- Filter Solutions: Filter nutrient solutions through a fine mesh or cheesecloth before adding them to the sprayer to remove any particulate matter.
- Clean Nozzles: Regularly clean sprayer nozzles to prevent clogs and ensure even distribution of the foliar spray.
7. Environmental Conditions
Challenge:
- Folar spray efficiency is influenced by temperature, humidity, and light intensity, among other environmental conditions.
Solution:
- Control Environment: Maintain a controlled environment with stable temperature and humidity levels to optimize foliar spray effectiveness.
- Monitor Weather Conditions: If growing outdoors, monitor weather conditions and avoid foliar spraying during extreme heat or when rain is expected.
8. Pest and Disease Integration
Challenge:
- Integrating pest and disease management with foliar spraying can be complex, especially when using organic treatments.
Solution:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Incorporate foliar sprays with an overall IPM strategy. Use organic pesticides and fungicides in combination with nutrient sprays to protect plants from pests and diseases without leaving harmful residues.
- Compatibility Testing: Test the compatibility of different products before mixing them in foliar sprays to avoid adverse reactions.
9. Nutrient Lockout
Challenge:
- Overuse of certain nutrients can lead to nutrient lockout, where excessive levels of one nutrient inhibit the uptake of others.
Solution:
- Balanced Formulations: Use balanced nutrient formulations and avoid excessive application of any single nutrient.
- Soil Testing: Regularly test the soil and plant tissue to monitor nutrient levels and adjust foliar spray formulations accordingly.
10. Plant Sensitivity
Challenge:
- Some cannabis strains may be more sensitive to foliar sprays than others, leading to varied responses.
Solution:
- Strain-Specific Adjustments: Be aware of the specific needs and sensitivities of different cannabis strains and adjust foliar spray formulations and application techniques accordingly.
- Start Small: When trying a new foliar spray formulation or on a new strain, start with a small test application and monitor the plant’s response before full-scale use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, foliar spraying is an effective and versatile technique for enhancing the cultivation of medical cannabis. By directly applying nutrients to the leaves, growers can achieve rapid nutrient uptake, correct deficiencies swiftly, and support overall plant health. This method, when executed with precision and care, offers numerous benefits that translate into higher yields and superior quality of medical cannabis.
Understanding the science behind foliar spraying helps in leveraging the natural absorption mechanisms of cannabis leaves, ensuring that nutrients are delivered efficiently and effectively. Following best practices—such as choosing the right time for application, using proper equipment, and preparing the nutrient solutions correctly—ensures optimal results and minimizes potential issues like leaf burn and pathogen spread.
Applying foliar sprays strategically during different growth stages, from vegetative to flowering, allows for tailored nutrient support that meets the specific needs of the plants. This targeted approach not only enhances plant growth but also improves the potency and therapeutic quality of the cannabis flowers.
DIY foliar spray recipes provide an opportunity for customization, enabling growers to create nutrient solutions that are perfectly suited to their plants’ requirements. However, it is crucial to address potential challenges such as residue buildup, evaporation, and environmental control to maximize the benefits of foliar spraying.
By integrating foliar spraying into a comprehensive cultivation strategy and continuously monitoring and adjusting based on plant responses, growers can ensure the production of high-quality medical cannabis. This method, combined with proper soil nutrition and pest management, creates a holistic approach that supports robust plant growth and exceptional yields.
Ultimately, foliar spraying is a valuable tool in the arsenal of medical cannabis cultivators, offering a practical and efficient way to enhance plant health and productivity, thereby meeting the high standards required for therapeutic cannabis products.