
5 Different Ways to Take CBD for Medical Use
CBD (cannabidiol) is a non-psychoactive compound derived from the cannabis plant that has gained widespread attention for its potential therapeutic benefits. For medical purposes, CBD can be administered in various forms, each offering unique advantages. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore five different methods of taking CBD that are specifically designed for medical use, excluding recreational consumption and avoiding smoking, vaporizing, or edible methods. These methods focus on maximizing the therapeutic effects of CBD for managing conditions such as pain, anxiety, epilepsy, and more.
1. Topical Application
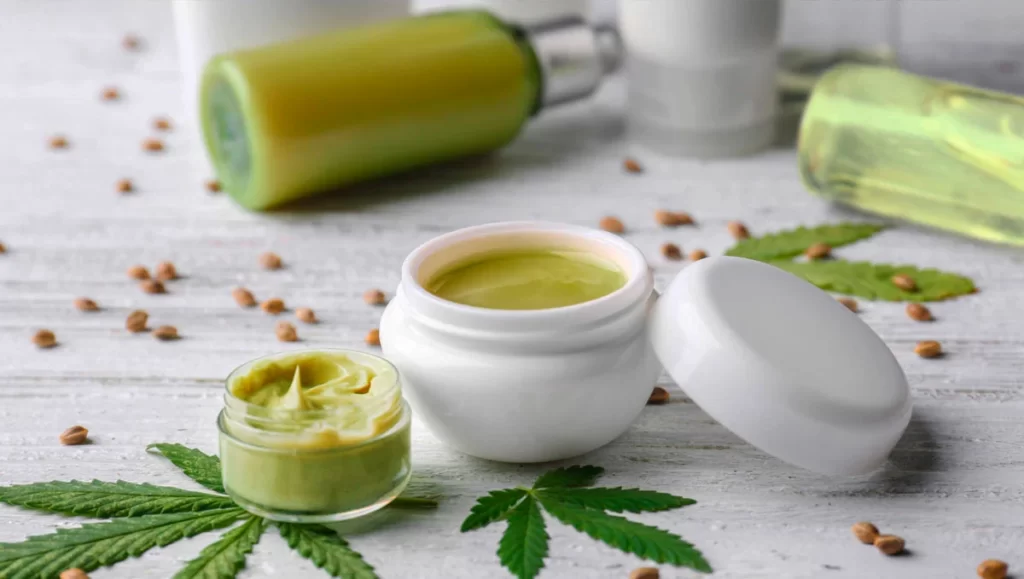

Topical CBD products, such as creams, balms, lotions, and patches, are applied directly to the skin. This method is particularly beneficial for localized pain, inflammation, and skin conditions. Applying CBD topically produces focused alleviation without systemic effects since it interacts with the skin’s endocannabinoid receptors without entering the bloodstream.
Advantages of Topical Application:
- Localized Treatment: Ideal for conditions like arthritis, muscle soreness, neuropathic pain, and inflammatory skin conditions (e.g., psoriasis or eczema).
- Minimal Systemic Absorption: lowers the possibility of systemic CBD use negative effects, making it safer for individuals who are on many drugs or who have other medical issues.
- Ease of Use: Simple to apply and can be integrated into daily routines without special equipment or preparations.
How to Use Topical CBD for Medical Purposes:
- Identify the Affected Area: Apply the CBD product directly to the area of concern.
- Massage Gently: Massage the product into the skin to enhance absorption.
- Reapply as Needed: Depending on the severity of the condition, reapply every few hours or as recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Consider CBD Patches: For continuous and controlled release, CBD patches can be applied to the skin. These patches release CBD slowly over time, providing sustained relief for chronic conditions.
Medical Conditions Benefiting from Topical CBD:
- Arthritis and Joint Pain: Topical CBD can reduce inflammation and pain in joints, helping improve mobility and quality of life for arthritis patients.
- Neuropathic Pain: Conditions like diabetic neuropathy can be managed with the targeted pain relief provided by CBD topicals.
- Skin Conditions: CBD’s anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties make it suitable for treating acne, psoriasis, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
2. Sublingual Administration
Sublingual administration involves placing CBD oil, tinctures, or sprays under the tongue. The sublingual gland absorbs the CBD directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system and liver, which results in faster onset and more efficient absorption.
Advantages of Sublingual Administration:
- Rapid Onset of Action: Effects can be felt within 15-30 minutes, which is beneficial for acute symptoms like anxiety or sudden pain.
- High Bioavailability: Because it bypasses the digestive tract, sublingual CBD has a higher bioavailability compared to oral methods, leading to better therapeutic outcomes with lower doses.
- Precision Dosing: Precise dosage can be readily modified using tinctures and oils to suit the needs of each patient.
How to Use Sublingual CBD for Medical Purposes:
- Measure the Dose Carefully: Use a dropper to measure the recommended amount of CBD oil or tincture.
- Place Under the Tongue: Hold the oil or tincture under the tongue for at least 60 seconds to allow maximum absorption.
- Avoid Swallowing Immediately: Wait before swallowing to maximize the absorption through the mucous membranes.
- Follow a Regular Schedule: For chronic conditions, consistent sublingual dosing at regular intervals can maintain steady CBD levels in the body.
Medical Conditions Benefiting from Sublingual CBD:
- Anxiety and Panic Disorders: Rapid onset makes sublingual CBD ideal for managing acute anxiety or panic attacks.
- Epilepsy: CBD’s anticonvulsant properties can be harnessed quickly in cases of seizure onset.
- Pain Management: Good for a variety of pain conditions, including fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis, both acute and chronic.
3. Transdermal Delivery Systems
Transdermal patches offer a controlled release of CBD directly into the bloodstream through the skin. Unlike topical applications that act locally, transdermal delivery systems are designed for systemic absorption, allowing CBD to enter the bloodstream and provide long-lasting therapeutic effects.
Advantages of Transdermal Delivery Systems:
- Controlled Release: Provides a gradual release of CBD, guaranteeing sustained blood levels and extended therapeutic benefits.
- Convenience: Requires minimal intervention; once the patch is applied, it can provide benefits for several hours to days.
- Reduced First-Pass Metabolism: Bypasses the liver, minimizing the degradation of CBD and enhancing bioavailability.
How to Use Transdermal CBD Patches for Medical Purposes:
- Select an Appropriate Site: Apply the patch to a clean, dry, and hairless area of the skin (e.g., the upper arm or lower back) to ensure optimal adhesion and absorption.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Adhere to the guidelines provided for patch duration and frequency of replacement.
- Monitor for Skin Reactions: Observe the application site for any irritation or allergic reactions. If any negative effects appear, stop using the product and see a doctor.
Medical Conditions Benefiting from Transdermal CBD:
- Chronic Pain: Provides continuous pain relief for conditions like cancer pain, post-surgical pain, and neuropathic pain.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Helps manage pain and spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Offers potential benefits for symptom management, including tremors and rigidity.
4. Nasal Sprays
Nasal sprays containing CBD are a relatively new method designed for rapid absorption. The nasal mucosa offers a direct route to the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system and liver. This method provides a fast onset of action, which can be advantageous for acute symptoms.
Advantages of Nasal CBD Sprays:
- Fast Absorption: Effects can be felt within minutes due to the high permeability of the nasal mucosa.
- High Bioavailability: Direct absorption into the bloodstream avoids the first-pass metabolism by the liver, increasing bioavailability.
- Localized and Systemic Effects: Suitable for both localized conditions (like migraines) and systemic needs (like epilepsy).
How to Use Nasal CBD Sprays for Medical Purposes:
- Shake the Bottle Well: Ensure the CBD is evenly distributed in the solution.
- Tilt Head Back Slightly: Spray the recommended dose into one or both nostrils as prescribed.
- Avoid Sneezing or Blowing Nose: Hold the solution in the nasal cavity for better absorption.
- Use Only as Directed: Follow the dosing schedule and frequency as advised by a healthcare provider.
Medical Conditions Benefiting from Nasal CBD Sprays:
- Migraines and Cluster Headaches: Rapid onset helps alleviate intense headaches and associated symptoms like nausea and light sensitivity.
- Epileptic Seizures: Nasal sprays can be used for immediate intervention during seizure episodes.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Offers quick relief from acute anxiety, flashbacks, and other PTSD symptoms.
5. Rectal Suppositories
CBD rectal suppositories are an effective method for individuals who require high doses of CBD and cannot take it orally due to nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal conditions. This method bypasses the digestive system and liver, allowing for high bioavailability and efficient absorption.
Advantages of Rectal CBD Suppositories:
- High Absorption Rate: Rectal administration provides high bioavailability, with a significant portion of CBD entering the bloodstream without first-pass metabolism.
- Ideal for Patients with Gastrointestinal Issues: Suitable for patients who cannot tolerate oral CBD due to digestive problems or nausea.
- Long-Lasting Effects: Provides sustained relief over several hours, making it ideal for chronic conditions requiring continuous symptom management.
How to Use CBD Suppositories for Medical Purposes:
- Ensure Proper Storage: Store suppositories in a cool place to maintain their solid form.
- Prepare for Insertion: Wash hands thoroughly and lie on one side with knees pulled up to the chest.
- Insert Suppository Carefully: Gently insert the suppository into the rectum, ideally after a bowel movement to ensure maximum absorption.
- Remain in Position: For a few minutes, remain in a prone position to stop the suppository from escaping.
- Follow Dosage Instructions: Use as directed by a healthcare professional, considering the frequency and duration of use.
Medical Conditions Benefiting from Rectal CBD Suppositories:
- Chronic Pain and Inflammation: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) benefit from the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of CBD.
- Cancer-Related Symptoms: Helps manage pain, nausea, and appetite loss associated with cancer and chemotherapy.
- Epilepsy: Provides an alternative for patients unable to take oral CBD, particularly for managing seizure activity.
Restrictions on Using Cannabis in the Medical Field as a Last Resort and Monitoring THC Levels to Prevent Psychoactive Effects

Numerous medical illnesses, such as multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and chronic pain, have been demonstrated to respond well to cannabis treatment. However, its use in the medical field remains highly regulated due to concerns about its psychoactive effects, primarily caused by tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The primary psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, THC, gives users the “high” they experience while using it recreationally. To utilize cannabis safely in medical settings, strict guidelines and restrictions are in place to ensure that its use is considered a last resort and that THC levels in medications are carefully monitored to prevent any psychoactive effects on patients.
Restrictions on Using Cannabis as a Last Resort
- Limited Indications and Approved Conditions
- In many countries, cannabis-based medications are approved only for specific medical conditions that have not responded to conventional therapies. For example, conditions like chronic pain, chemotherapy-induced nausea, spasticity due to multiple sclerosis, and certain types of epilepsy (such as Dravet syndrome) are among those where medical cannabis might be considered.
- Before cannabis is prescribed, healthcare providers must demonstrate that standard treatments have been exhausted or proven ineffective. This process typically involves documenting the patient’s medical history and previous therapies, ensuring that all other options have been thoroughly explored.
- Strict Prescription and Authorization Requirements
- In jurisdictions where medical cannabis is legal, its prescription is often highly regulated. Only licensed healthcare professionals, such as doctors with specific training or certifications, can prescribe cannabis-based treatments.
- In some countries, additional authorization may be required from a regulatory body or medical board before a prescription can be issued. This oversight ensures that cannabis use is justified and that it aligns with established medical guidelines.
- Patient Eligibility Criteria
- Patients must meet certain eligibility criteria to be considered for medical cannabis. These criteria may include age restrictions, specific diagnoses, and a documented failure of conventional treatments.
- Children, the elderly, people with a history of substance misuse, people with mental health issues, and other vulnerable groups may be subject to extra scrutiny or limitations. This ensures that cannabis use is carefully considered and that risks are minimized.
- Informed Consent and Education
- Before starting a cannabis-based treatment, patients must provide informed consent, acknowledging their understanding of the potential risks, benefits, and alternative treatment options. This process often involves a detailed discussion with a healthcare provider about the psychoactive effects of THC and the importance of using cannabis as a last resort.
- Education programs for both patients and healthcare providers are critical in ensuring that cannabis is used appropriately. These programs focus on dosing, potential side effects, interactions with other medications, and strategies to minimize risks, including psychoactive effects.
- Monitoring and Re-evaluation Protocols
- Once a patient begins using cannabis-based medication, regular monitoring and re-evaluation are required to assess its effectiveness and any adverse effects. This includes regular follow-up appointments, assessments of symptom relief, and monitoring for any signs of THC-related psychoactivity.
- If the treatment is not effective or causes significant side effects, including psychoactive effects, healthcare providers are required to discontinue the medication and explore alternative therapies.
Monitoring THC Levels in Medications
- Standardized THC Concentrations in Medications
- Medical cannabis products must adhere to strict standards regarding THC concentrations to minimize psychoactive effects. For instance, many formulations contain a higher ratio of cannabidiol (CBD) to THC, as CBD can mitigate some of THC’s psychoactive properties.
- Regulatory bodies often specify maximum allowable THC concentrations in medical cannabis products. For example, some countries limit THC content to less than 1% or require that THC be present only in trace amounts.
- Third-Party Testing and Quality Assurance
- All medical cannabis products must undergo rigorous testing by third-party laboratories to verify their THC content and ensure that it falls within the specified limits. In addition, these tests look for pollutants like mold, heavy metals, and pesticides.
- Quality assurance protocols include batch testing, where samples from each batch of medication are analyzed to confirm consistent THC levels. This helps prevent variability in THC concentration, which could inadvertently lead to psychoactive effects.
- Patient-Specific Dosing Regimens
- Healthcare providers create individualized dosing regimens based on the patient’s condition, weight, tolerance, and previous experience with cannabis. Low doses are typically initiated and gradually increased until the desired therapeutic effect is achieved without causing psychoactive side effects.
- Microdosing strategies, where very small amounts of THC are administered, are often employed to minimize the risk of psychoactive effects while still providing therapeutic benefits.
- Use of CBD-Dominant Formulations
- CBD-dominant formulations, which contain minimal THC, are preferred for medical use. It has been demonstrated that CBD counteracts some of the euphoric effects of THC despite being non-psychoactive. These formulations maximize the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without the risk of intoxication.
- In some cases, pure CBD isolates, which contain no THC, are used for patients who are particularly sensitive to THC or for conditions where any level of psychoactivity would be unacceptable.
- Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Based on Patient Response
- Continuous monitoring of patient response is essential to ensure that THC levels remain at a therapeutic, non-psychoactive level. Patients are regularly assessed for signs of psychoactive effects, such as dizziness, confusion, or euphoria.
- If any psychoactive effects are observed, the healthcare provider may adjust the dose, switch to a different formulation, or discontinue the medication. To recognize and address any possible side effects as soon as they arise, regular contact between the patient and the healthcare provider is essential.
Conclusion
For medical purposes, CBD offers a range of administration methods tailored to different needs and conditions, providing flexibility in how it can be used therapeutically. The five methods discussed—topical application, sublingual administration, transdermal patches, nasal sprays, and rectal suppositories—each offer unique benefits suited to various medical scenarios.
Topical applications are ideal for localized pain and inflammatory skin conditions, providing targeted relief without affecting the entire body. Sublingual administration offers rapid onset and high bioavailability, making it effective for acute symptoms like anxiety or sudden pain. Transdermal patches provide controlled, sustained delivery for chronic conditions such as neuropathic pain or multiple sclerosis. Nasal sprays enable fast absorption for acute conditions like migraines or seizures, and rectal suppositories are particularly beneficial for patients who require high doses or cannot tolerate oral administration due to gastrointestinal issues.
The use of cannabis in the medical field represents a complex but promising area of healthcare. While cannabis offers significant therapeutic potential for conditions such as chronic pain, epilepsy, and multiple sclerosis, its use must be carefully controlled and regulated due to concerns about its psychoactive effects, particularly those caused by THC. To ensure safety and effectiveness, cannabis is considered a last-resort treatment, employed only when conventional therapies have proven ineffective.
Strict regulations govern every aspect of medical cannabis use, from prescribing practices and patient eligibility to the formulation and monitoring of medications. These regulations aim to minimize the risk of psychoactive effects by limiting THC content, ensuring product quality through third-party testing, and tailoring treatment to the individual needs of each patient. Methods like topical applications, sublingual administration, transdermal patches, nasal sprays, and rectal suppositories provide versatile and medically-focused ways to deliver cannabis’s benefits without involving smoking, vaporizing, or recreational use.
By adhering to these guidelines and using cannabis only when truly necessary, healthcare providers can harness its potential to improve patient outcomes while safeguarding against unwanted effects. As research and understanding of cannabis continue to advance, it will be critical to maintain a balanced approach that prioritizes patient safety, therapeutic efficacy, and ethical medical practice. In doing so, cannabis can remain a valuable tool in the medical field, offering relief and improved quality of life for those who need it most.